Surprising Science
All Stories
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University have used tracking data from personal mobile phones to map transmission patterns of malaria, enabling more effective prevention schemes.
With three years of testing behind it, the bra could be on the market in the US by 2014 with FDA approval.
Alternatives to needle injections have been sought after for many years, and the results have had varying degrees of success. A team of scientists think they’ve come up with a solution.
Customers in underserved parts of America may soon be able to get reliable 4G wireless broadband via a frequency normally occupied by short-range communication devices.
Keyboards and mice are about to get some competition from wearable sensors that allow users to control electronics with gestures.
A company has completed a prototype of a robot designed specifically to look for lunar ice, a potentially rich source of water and other materials for use during other lunar expeditions.
In a national first, Karachi-based Dow University of Health Sciences students will be trained on reproductive health education starting next academic year.
Researchers have discovered the brain mechanism that prevents people from developing overwhelming fear.
Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis are using crowdsourcing to gather data on people’s ability to learn names and faces.
UK researchers want to see if polyphenols, the compounds that allegedly give foods such as broccoli and blueberries body-healing properties, actually make it past the gut lining.
At this week’s Body Computing Conference, one team of researchers is unveiling a car with special sensors that monitor its driver’s health and habits.
ICU doctors at a Kansas City hospital received results of a baby’s complete genome within just over two days, a new record.
A recently-published review of studies done on exercise interventions for young people shows that by themselves they don’t significantly increase children’s overall daily physical activity.
A restaurant check wallet currently being road-tested comes with its own mini-computer, letting patrons pay with a credit card right at the table.
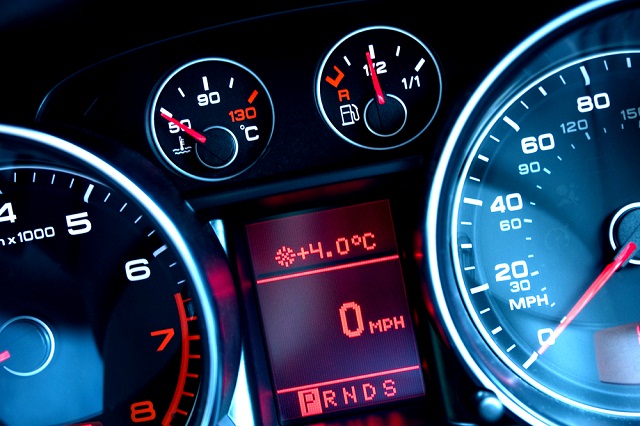
A new study out from MIT says that the scannability of typefaces used on auto dashboards can impact a driver’s ability to react to an unexpected road condition.
Improved ability to cope with cognitive dissonance is tied to a regular dose of Wolfgang Amadeus M., according to preliminary research.
Those windshields with embedded displays may be here sooner than you think: A team of Rice University researchers has come up with flexible high-capacity memory chips made of silicon oxide and graphene.
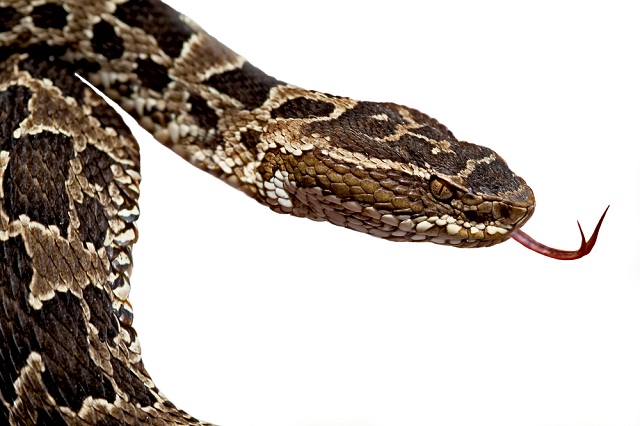
Two proteins found in the deadly snake’s venom kept mice pain-free longer, raising hopes for a medication that manages pain with fewer side effects.
Engineers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have created a handheld scanner that will give primary care physicians the same kind of 3D imaging that surgeons have had for years.
New Zealand researchers announce the existence of a cow, Daisy, that has been genetically engineered to produce milk that has very little whey, a common allergen.
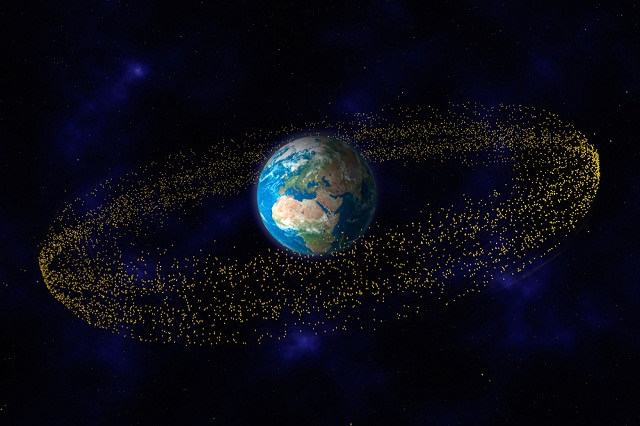
Today, a UK team presented a system designed to address the need to remove the many objects currently in orbit around the Earth.
It’s been 800,000 years since the last one, and the field’s been thinning for the last 150 years, so one space agency is launching measurement satellites.
Considering that it’s still late winter in the rover’s neck of the woods, discovering (relatively) warm temperatures boosts scientists’ hopes of finding evidence of microbial life.
Han Solo’s Millennium Falcon can take off at a moment’s notice and escape from pursuers into space. And can land on almost any patch of ground. Why can’t we do that in 2012? The problem is the puny power of the chemical rocket.
A number of different factors are involved in the decrease of marriage among Iranians, and some are calling for potentially radical solutions.
How is it possible that even in a time when encyclopedic knowledge is available at our fingertips, we still get the facts wrong and often get them wrong in egregious fashion?
Despite the seductive fusion of evolutionary principles with modern neuroscience, our search for an ultimate explanation of human behavior is not likely to find solutions any time soon.
By manipulating the communication abilities of a parasitic virus, geneticists have taken the first steps toward creating a biological Internet where natural processes can be augmented.
A team of medical researchers have created the first fully biodegradable electronic implants. The technology has already been used to help heal wounds before being absorbed by the body.
Despite the conventional wisdom that higher-ups suffer more pressure because they have more responsibility, new research concludes that its more stressful being on the bottom.