Health
All Stories
The sober reality behind the effectiveness of two new drugs touted as Alzheimer’s breakthroughs: lecanemab and donanemab.
Twin Health lets patients with diabetes see what’s happening inside their own body and can model each patient’s unique metabolism.
Long overlooked, menstrual stem cells could have important medical applications, including diagnosing endometriosis
They call it “Judo T-cell therapy,” and it’s 100 times more potent than regular CAR-T cells.
Britain is profiling the genes, health and lifestyles of its citizens and handing the results to scientists across the world.
If you eat a diet full of refined grains, high-sugar drinks, and sweets, there’s a good chance you have too much insulin.
One dose of ibogaine was shown to dramatically reduce depression and PTSD.
Placebo treatments don’t always need to be given deceptively to have positive effects.
Growing evidence suggests a link between the debilitating neurological illness and the microbes that live in our intestines. The vagus nerve may be a pathway.
Western societies seem to be getting inflammation achingly wrong.
Could subfertility be an under-explored factor in autism risk?
The bots started as windpipe cells, yet they helped nerve cells repair and grow.
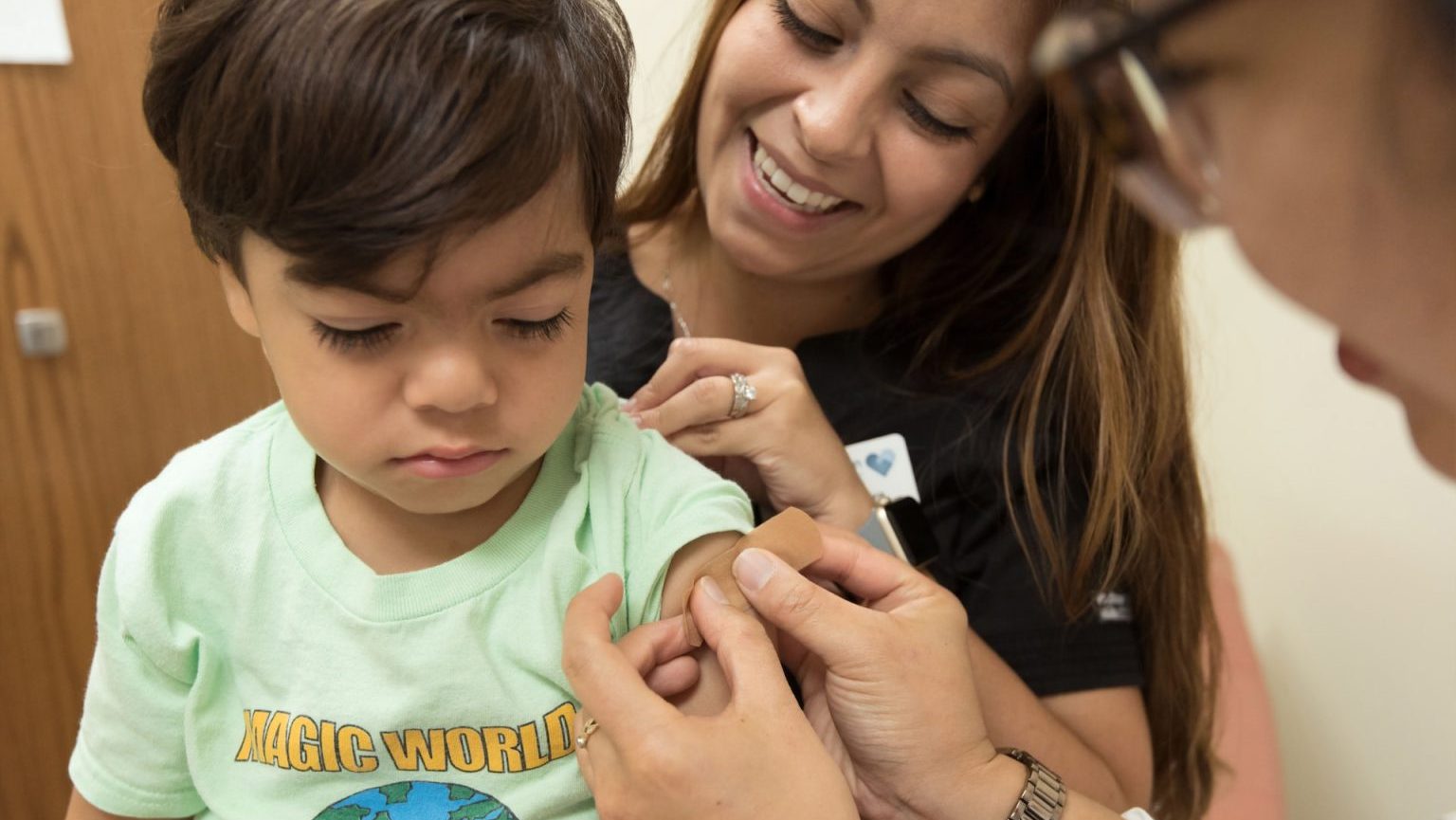
The FDA approved a single-dose, long-acting injection to protect babies and toddlers from RSV over the fall and winter.
Embedded in a cell phone or in accessories such as rings, bracelets or watches, the novel tools aim to make it easier to manage hypertension. But they must still pass several tests before hitting the clinic.
The study is a solid step toward developing gene therapies against neurodevelopmental disorders.
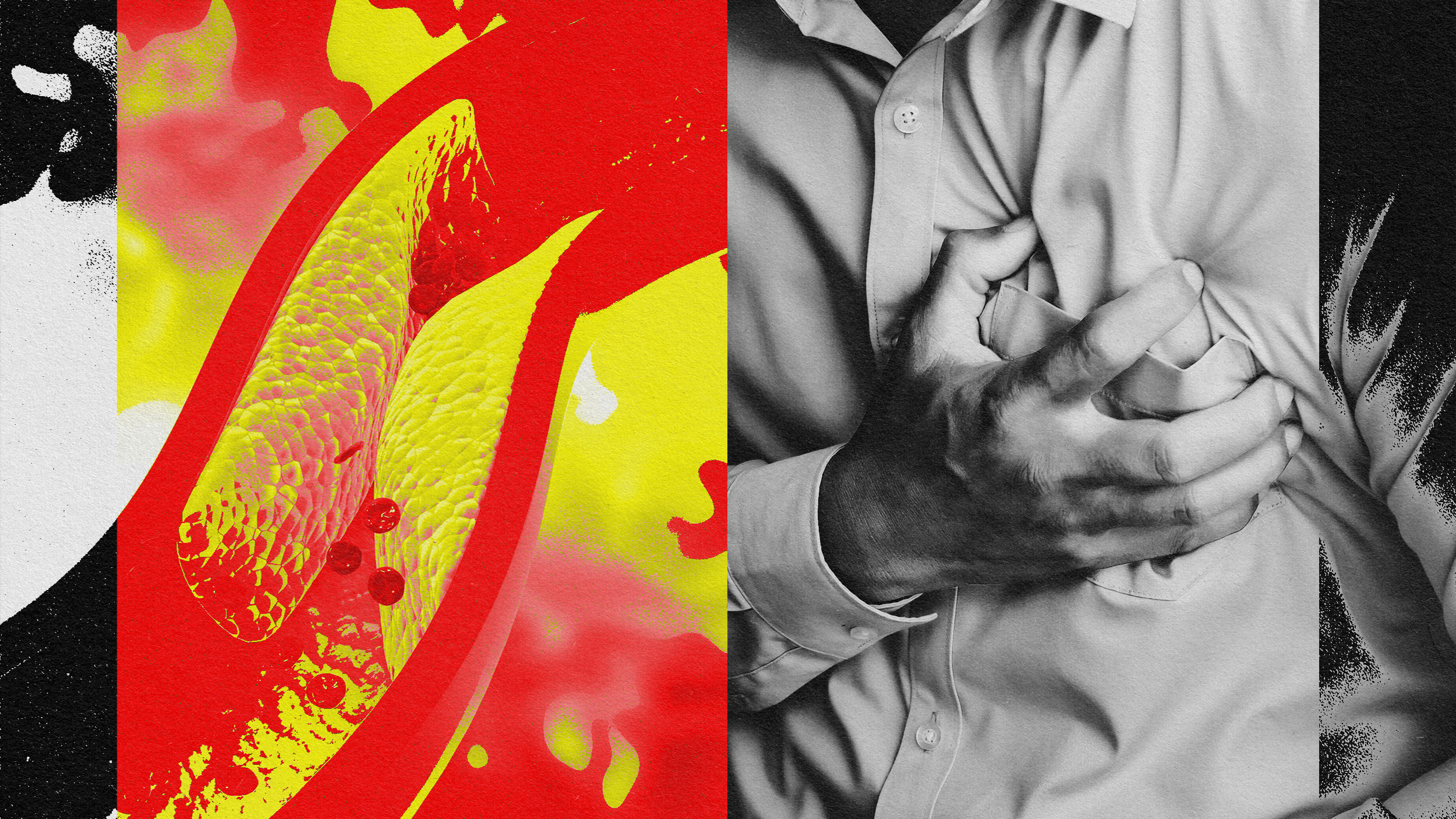
There is currently no easy way to treat high Lp(a). A single shot could change that.
Stem cells from a fetus can live within the mother for decades — and help her heal.
The evidence that pollution causes cancer is weak. Lifestyle factors, like smoking, obesity, and alcohol, matter far more.
The first human trial of base editing delivered strong results along with some safety concerns.
“Less is better” is not a catchy marketing slogan, but one doctor who didn’t shower for five years thinks there’s a lot of truth to it.
After turning up hundreds of genes with hard-to-predict effects, some scientists are now probing the grander developmental processes that shape face geometry.
People with higher immune resilience live longer, resist diseases, and are more likely to survive diseases when they do develop.
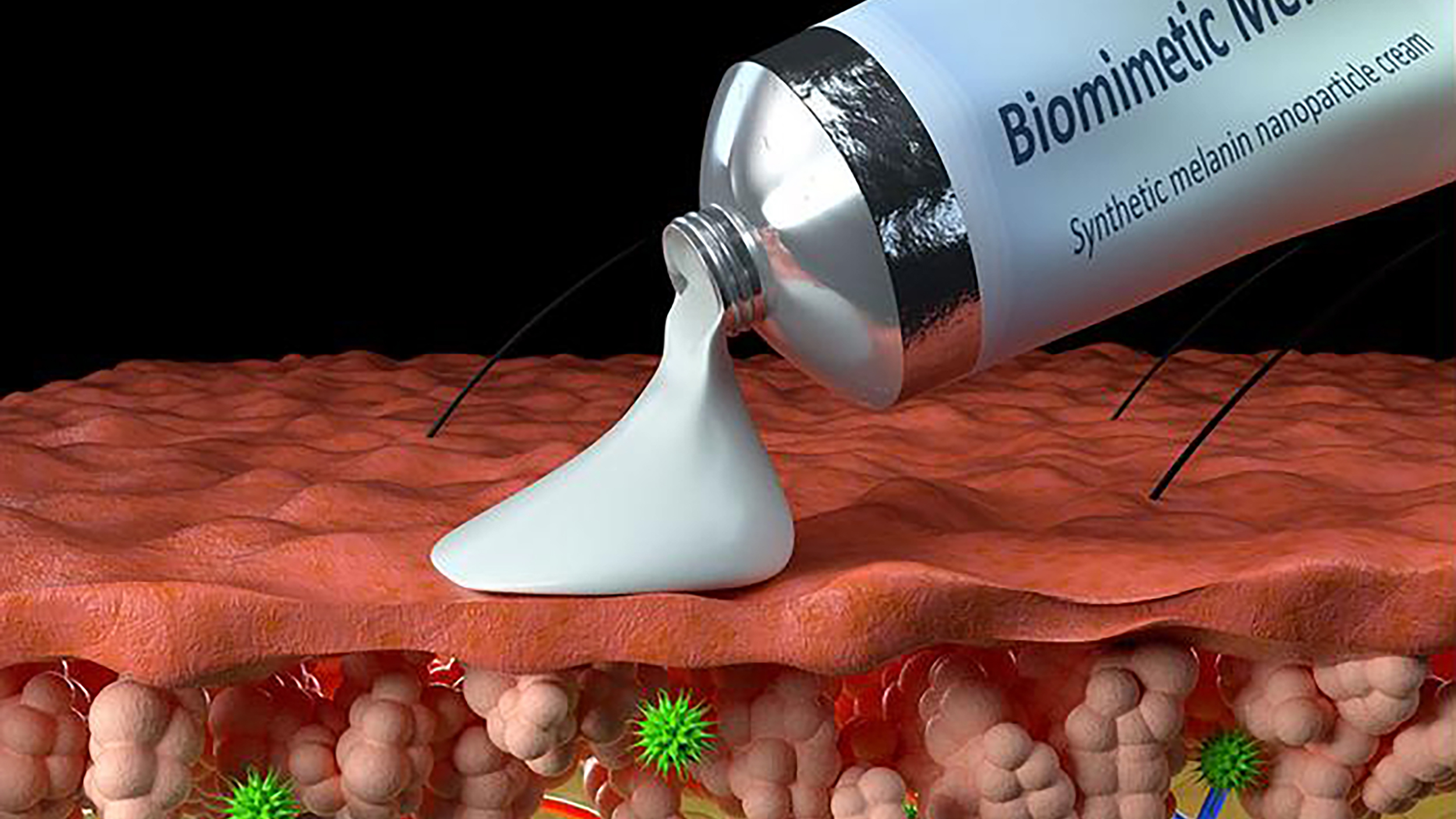
It could prevent sun damage and help chemical burns heal faster.
In December 2022, a company called BioAge Labs published findings on a drug that worked to prevent muscular atrophy, or the loss of muscle strength and mass, in older people.
Artificial intelligence can forecast the behavior of viruses and quickly make vaccines to thwart them.
Antioxidant vitamins don’t stress us like plants do—and don’t have their beneficial effect.
“Precarious manhood” is the belief that manhood must be earned and constantly defended. It has a poor outcome.
A cure may be on the horizon.