Surprising Science
All Stories
By producing medically useful amounts of endoderm cells from human stem cells, Canadian scientists have overcome a major hurdle in developing treatments for diabetes and liver diseases.
Some studies are finding that male circumcision decreases the odds that a heterosexual man will contract HIV by 57 percent or more. The operation is being performed more frequently.
Scientists in California have shown that a single injection of an HIV-neutralizing antibody into the muscle cells of live mice completely protected the animals against HIV transmission.
While inbreeding increases the risk of birth defects among close relatives, research demonstrates it is not the horror story we image. In some cases, it may produce healthier offspring.
By extracting stem cells from patients with diseases like diabetes, Down syndrome, Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia, scientists can examine how the disorders affect the body.
When the bodies of newborns lack iron, physical and mental development can be stifled. New research suggests that leaving the umbilical cord attached longer prevents iron deficiencies.
A new book argues “we and our children may be the most significant generations of humans that have yet lived,” which means we carry a far greater burden of responsibility than any previous generation.
When Facebook becomes a publicly traded company, it stands to earn $24 billion. So why doesn’t Mark Zuckerberg compensate us? After all, we supply all the personal data he sells to advertisers.
A 3D printer is being used to create ‘bone-like’ material which researchers claim can be used to repair injuries. The material would act like scaffolding on which new cells would grow.
Department of Energy scientists have engineered the E. coli bacteria to digest switchgrass biomass, which could be used create a domestic replacement for gasoline, diesel and jet fuels.
Google-funded research shows America’s potential for extracting geothermal energy is huge, but that harvesting it could cost a lot and even cause small earthquakes in the process.
New climate data taken from the peak of the last ice age suggests the Earth may be more resistant to carbon dioxide than previously thought. But there remains some ambiguity.
In the midst of the economic downturn, designer Sandra Garratt wanted to do something hopeful. So she integrated solar panels into her clothing designs to make green tech fashionable.
Running a mild electric current through the brain improves learning speed, according to Air Force researchers. The technique was used to teach personnel how to identify drone targets.
Economics is at the start of a revolution that is traceable to an unexpected source: medical schools and their research facilities. Welcome to the beginning of neuroeconomics.
Two independent studies conclude that stem cells can be used to repair damaged brain tissue, in mice at least. The advance could benefit humans with neurological diseases.
What if material from our food actually made its way into the innermost control centers of our cells, taking charge of fundamental gene expression? Actually, that is what happens.
Fears of a global bird flu pandemic have been abated by the fact that the virus is not communicable by air—until now. Dutch researchers want to publish their new virus recipe.
The remarkable magnetic properties of certain types of bacteria improve MRI scans by enhancing the appearance of unwanted structures in the body, like tumors and cancers.
CEOs who “crave acclaim and applause” are more likely to get ahead when it comes to innovation, says a new research study from a top business school in Switzerland.
“We don’t think a modern messaging system is going to be email,” said Mark Zuckerberg recently. He isn’t the first to suggest that email is dead and he definitely won’t be the last.
Politicians and commentators use the word “green” to discuss just about anything. Renewable energy, on the other hand, is clearly defined and does not exist as such.
Photonic chips, which use lightbeams to do computering instead of electrons, have advanced greatly in recent years. Now rearchers at MIT want to put them in your personal devices.
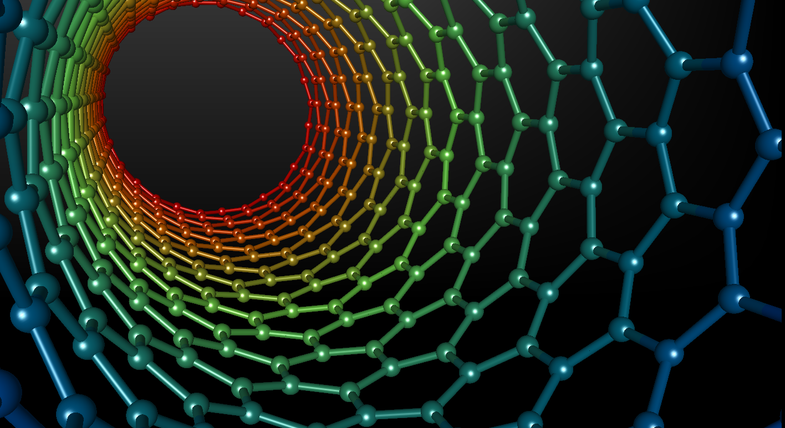
By taking advantage of the low refractive index of low-density aligned nanotubes, University of Michigan researchers have made 3-D objects appear as nothing more than a flat, black sheet.
The abundance of oil in the tar sands of Alberta, Canada, might fill state and private coffers but will the profit come at the expense of sustainable environmental policies?
Having a space vehicle capable of launching humans into orbit, and beyond, remains the gold standard among the international space community. For the moment, only Russia has that.
Our power to manipulate our brains and genes is increasing dramatically – and it raises serious ethical questions.
Researchers from the University of Milan and Facebook have found that the average number of acquaintances separating any two people in the world is now not six but 4.74.
“We are children when we talk about the cosmic scale of energies throughout the entire universe,” says theoretical physicist Michio Kaku. But with a little (okay, a lot) of human ingenuity, we may one day have the ability to harness the energy of the stars.
‘Tis the season to be savvy. Here’s a round-up of Big Thinkers’ favorite tech ideas for simplifying – and beautifying – your holiday.