Surprising Science
All Stories
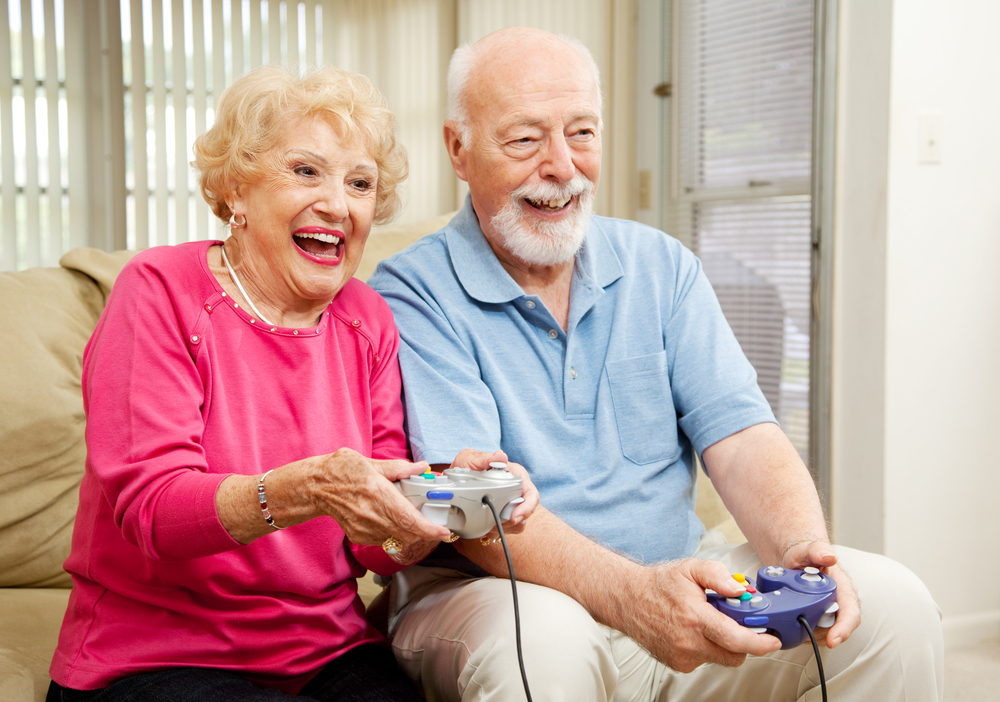
The kinds of multitasking abilities required by video games may help stem the tide of cognitive decline which naturally accompanies the aging process.
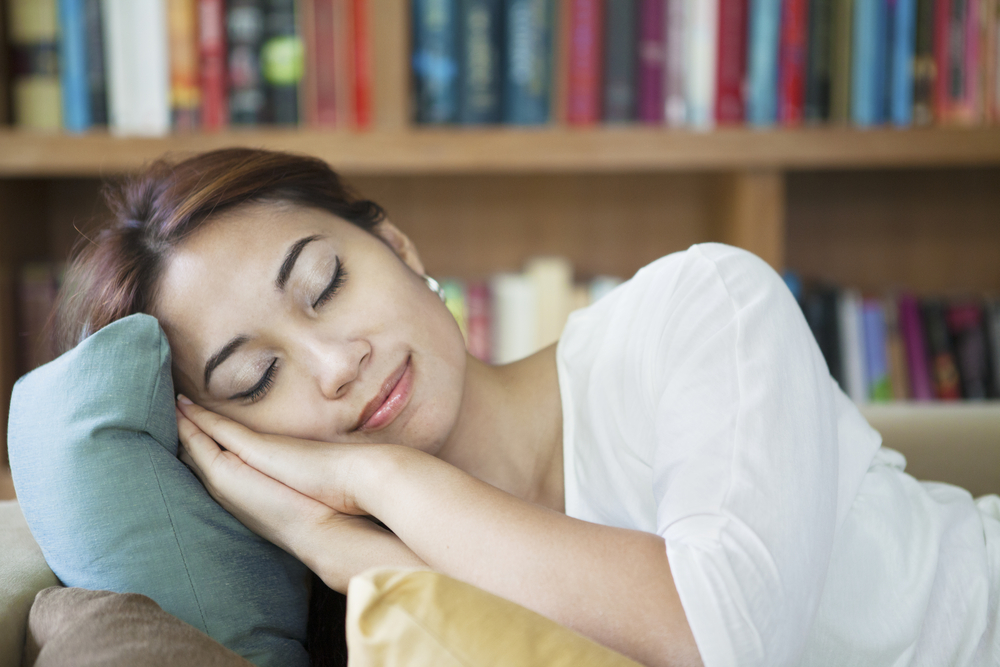
Sleep researchers better understand the components of a nap, what can make nappers groggy, and how you can take the best possible nap.
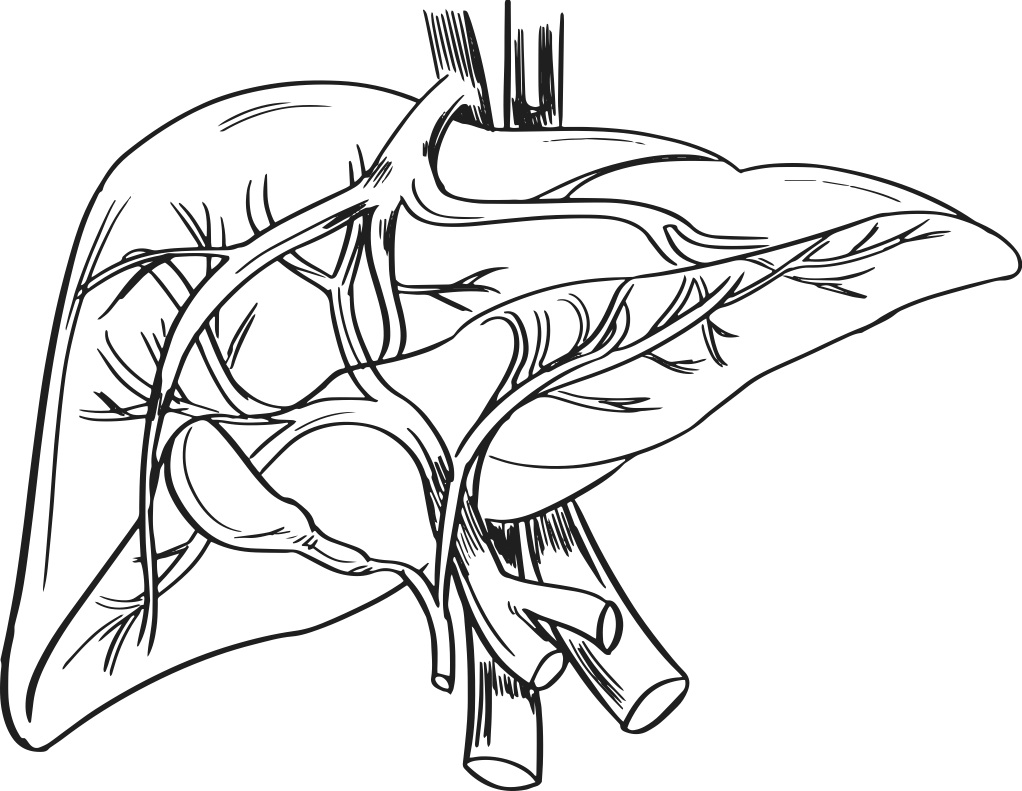
Researchers at a Chinese university have printed live human liver cells with high rate of success, ensuring that 90 percent of the cells leave the printer alive.
A presently untapped resource of medical innovation is coming into clearer view thanks to new DNA analyses that look closely at microbial presence in the human gut.
With the cost of sequencing a person’s entire genome falling, some experts in the field of genetics argue that all children should have their genomes sequenced at birth.
An Australian rocket scientist has engineered a new nano-device that injects vaccines into the human body at a level just beneath the skin, using a flat patch instead of a needle.
Cooperation and generosity are better modes of behavior than obstinance and self-interest when it comes to thriving within a society.
Researchers have confirmed that Tamu Massif, located in the northern Pacific, is a single volcano rather than a composite of different eruption points. At 120,000 square miles in size, it’s about as big as the entire state of New Mexico.
Carnegie Mellon researchers sent postcards to utility customers telling them their electricity usage was being observed for one month. Within that time period, consumption fell by an average of 2.7 percent.
Scientists at two universities have come up with a method of targeted drug delivery involving self-powered nanoparticles that are drawn by ionic energy released by the bone’s minerals.
Nominated for an INDEX Award, David Swann’s ABC Syringe changes color when it’s exposed to air, thus providing a visual alert that it may be unsafe to use. The device could save more than a million lives each year.
After over a decade of research, biotech startup Bionym is ready to go public with Nymi, a bracelet that uses the unique electrical activity produced by the wearer’s heart as identification.
Oxford University researchers have discovered a protein that prevents genes from adapting to differing levels of light. Suppressing this protein in mice caused their body clocks to adjust much faster.
The massive storm that wrapped itself around the planet in 2010-2011 seems to have dredged up water ice from an invisible lower atmospheric layer, according to NASA researchers.
The building has been blamed for melting the plastic on a parked car, setting store carpets on fire, and shattering tiles. Believe it or not, it’s the second structure architect Rafael Viñoly has built that has this “feature.”
As part of last year’s UN Rio+20 Summit, a group of financial institutions are looking into ways to put monetary value on natural resources and add incentives and penalties for their preservation or destruction.
More importantly, would your dog want one? Two Auburn University engineers have created a system that in test environments produced an obedience accuracy rate of almost 98 percent.
Developed by a team of Brigham Young students, the Owlet sends vitals — including heart rate, temperature, and most notably, an alert in case the baby rolls over on their stomach — to a smartphone app.
Poor people’s bad decision-making may be at least partly a result of their circumstances, not due to any intrinsic lack of intelligence.
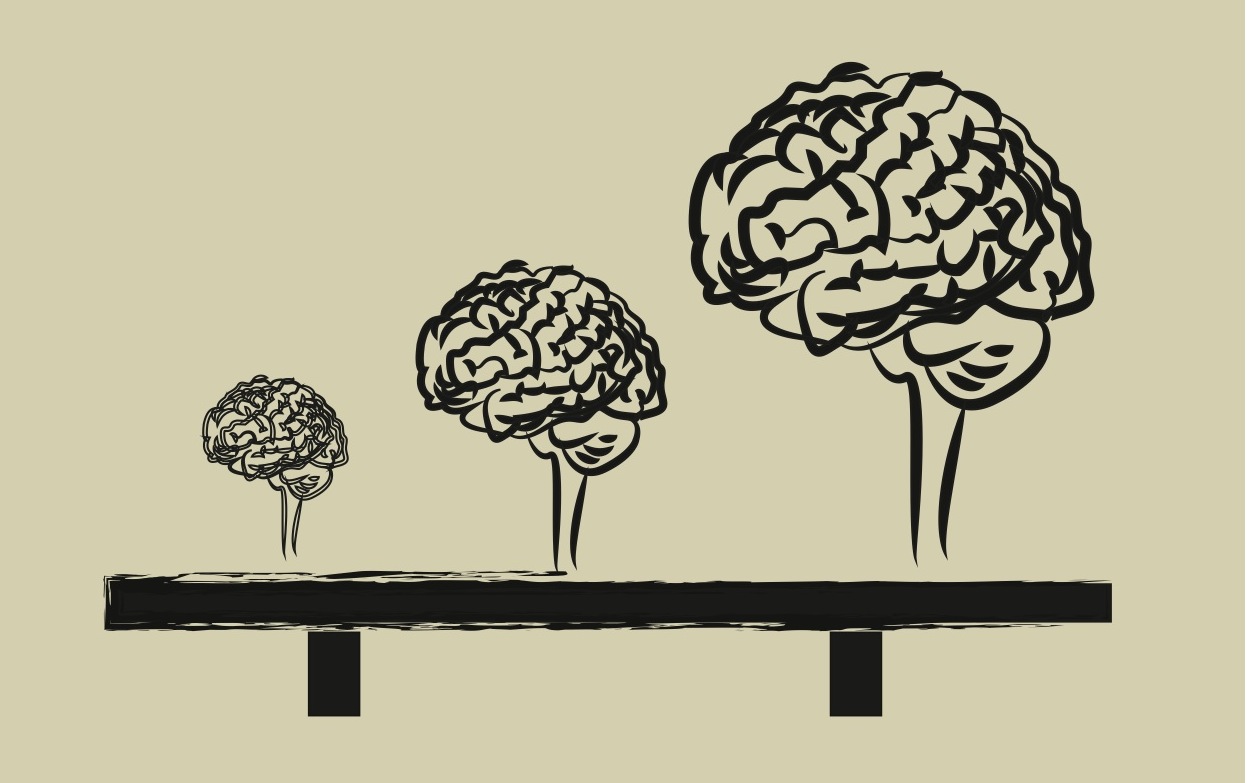
Scientists in an Austrian lab have created complex human brain tissue from stem cells, creating what the scientific community are now calling “mini-brains.”
A new study argues that the association between science and morality is so ingrained that merely thinking about it can trigger more moral behavior.
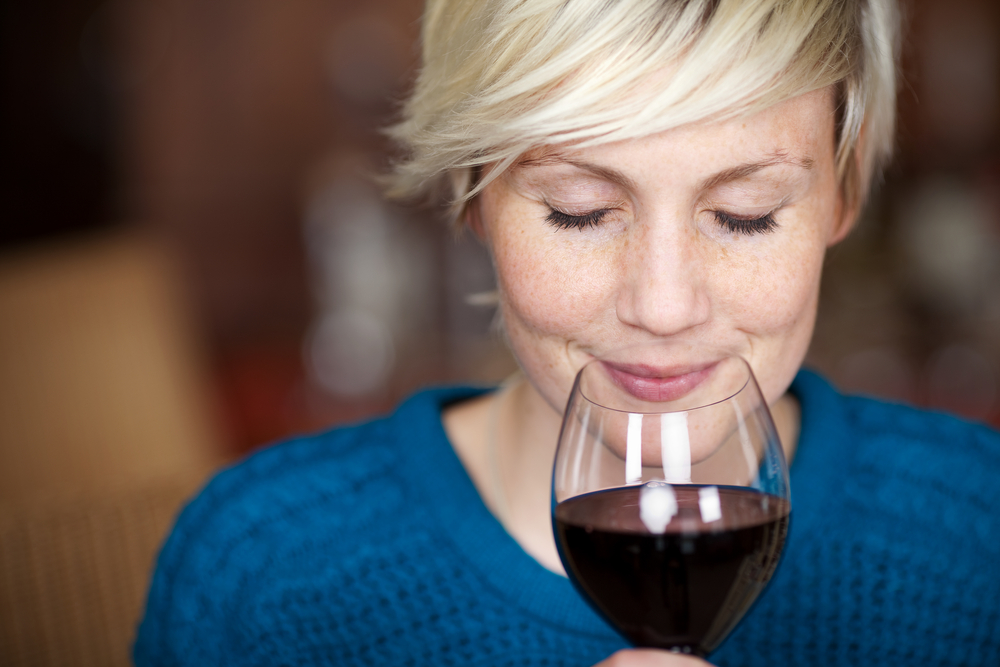
Research completed at the University of Navarra, Spain, suggests that a moderate level of wine drinking results in a lower risk of depression.
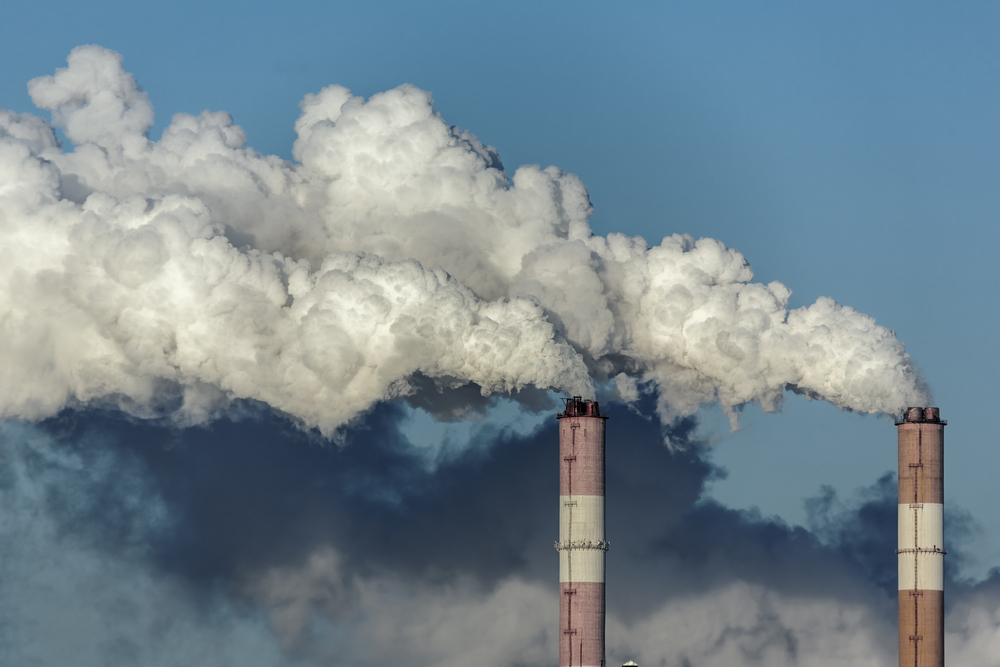
Researchers were surprised to learn that pollution created by road transportation proved deadlier than power generation stations.
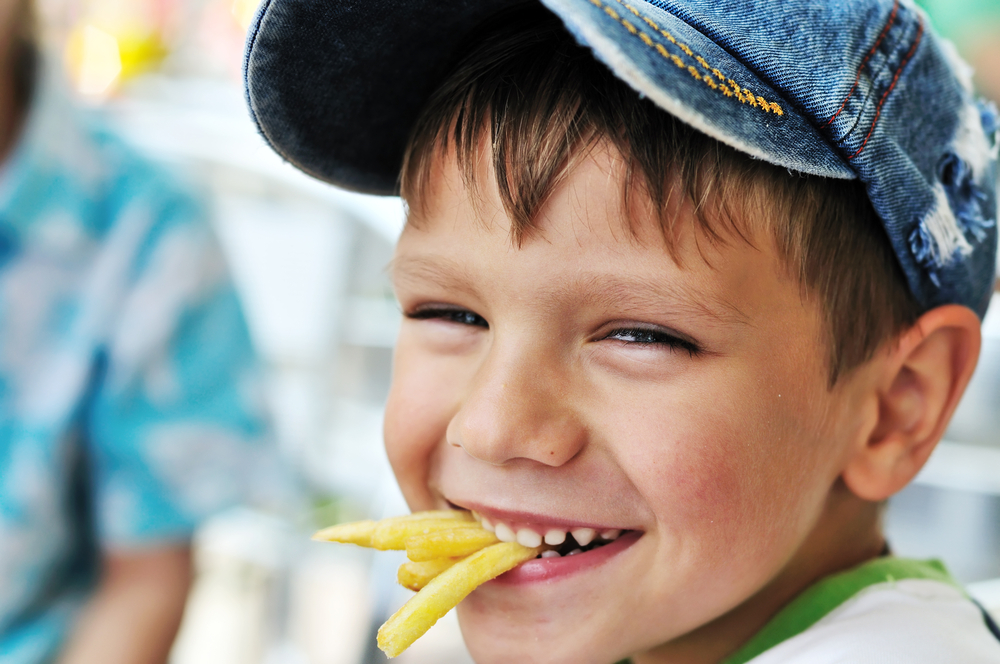
Savvy marketing strategies currently employed by quick service restaurants suggest the fast food industry is taking a page from Big Tobacco’s playbook.
Caffeine has enjoyed a surprisingly unregulated rise to its status as the drug of choice among many Americans, young and old.
Leaders from 17 countries recently met in Sumatra to discuss how handheld GPS devices and mapping apps have helped their communities retain lands held for generations.
Besides the obvious, both affect the brain in ways that make a person more susceptible to bad decisions, according to a new study involving subjects in New Jersey and rural India.
Studies show that weight gain is happening in the wider animal kingdom as well — in our pets, yes, but also among some captive and wild animals. No one really knows why.
This week a New Jersey state appeals court determined that if a person knowingly sends a text to someone who’s driving, and the driver is involved in an accident as a result, the texter could be held liable.
In an attempt to dial down sex trade street traffic, the city erected an outdoor compound on an industrial site. It consists of drive-in “sex boxes” with special precautions built in to protect prostitutes from predatory clients.