NASA’s Cassini reveals the full glory of Saturn’s rings

They’re even more spectacular in the close-up detail it delivers.
“This then, I thought, as I looked round about me, is the representation of history. It requires a falsification of perspective. We, the survivors, see everything from above, see everything at once, and still we do not know how it was.” –W.G. Sebald
Saturn is remarkable in a number of ways; among all the planets we know of, it’s the least dense, and also the only one with a spectacularly visible set of rings.
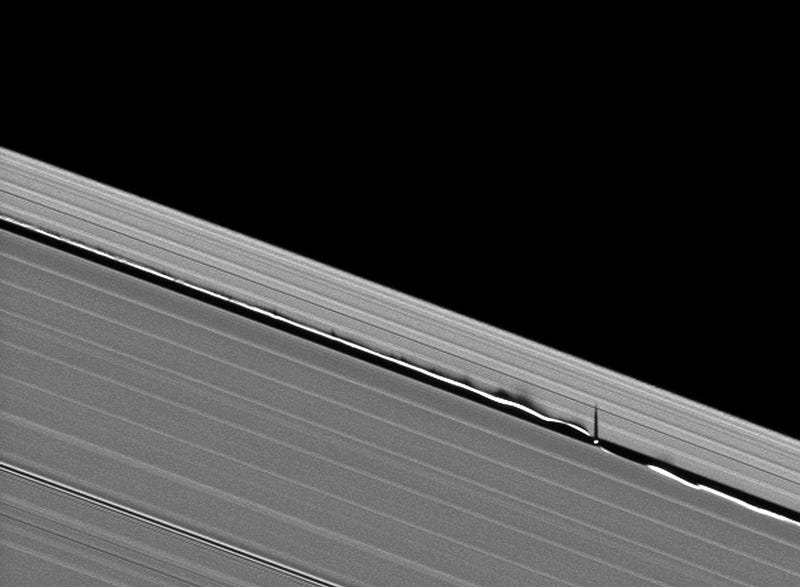

Composed of icy, dust-like material, these rings aren’t solid, but made up of particles that pass each other, sticking together briefly and torn apart by tidal forces.
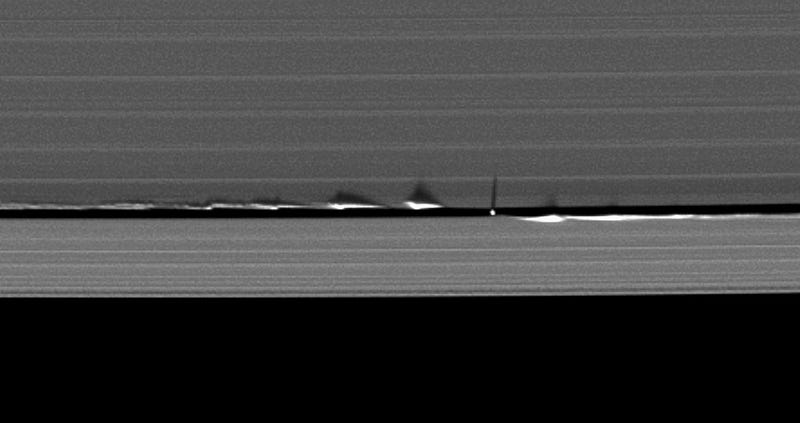
Snowballs and planetesimals coalesce, only to be torn apart by tidal forces exerted by Saturn and its passing moons.
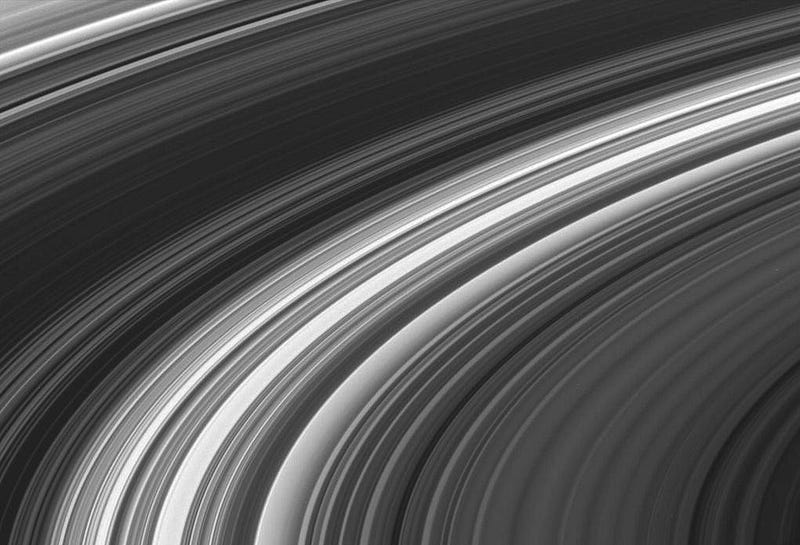

Gaps in the inner rings are caused by the gravitational presence of moons themselves, while many outer rings — like Saturn’s E-ring — are actuallycaused by emission from moons themselves.
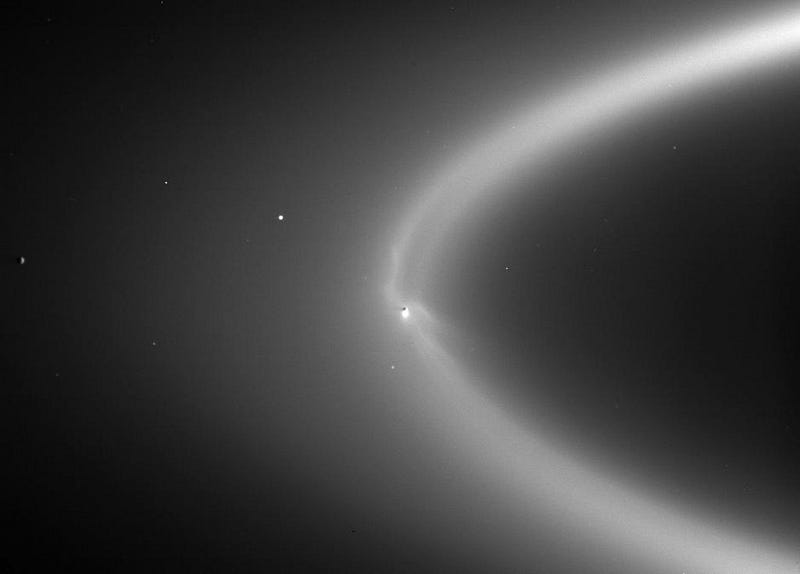

The main rings extend from 7,000 km to 80,000 km above Saturn’s equator: larger than Saturn’s radius.
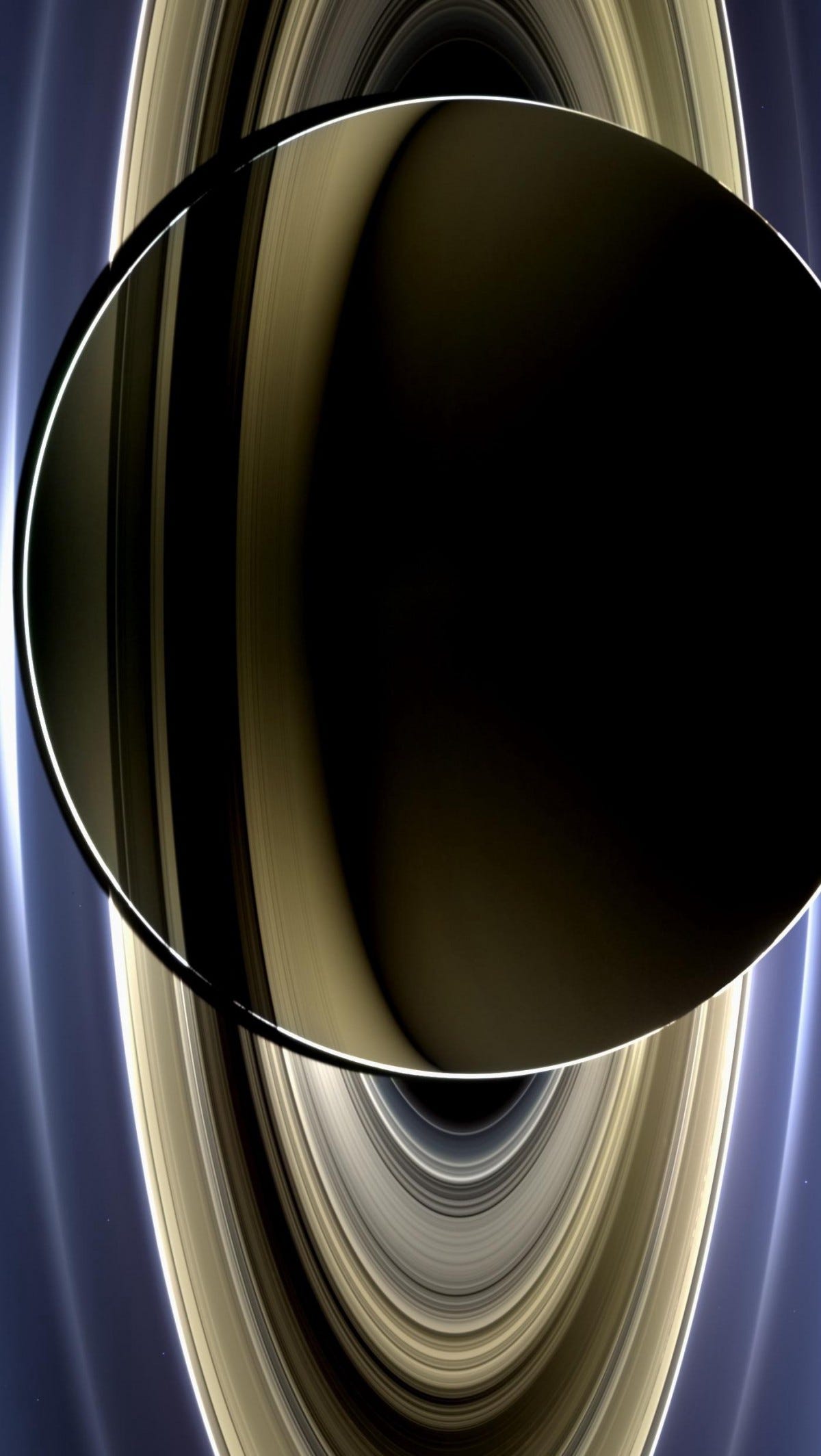
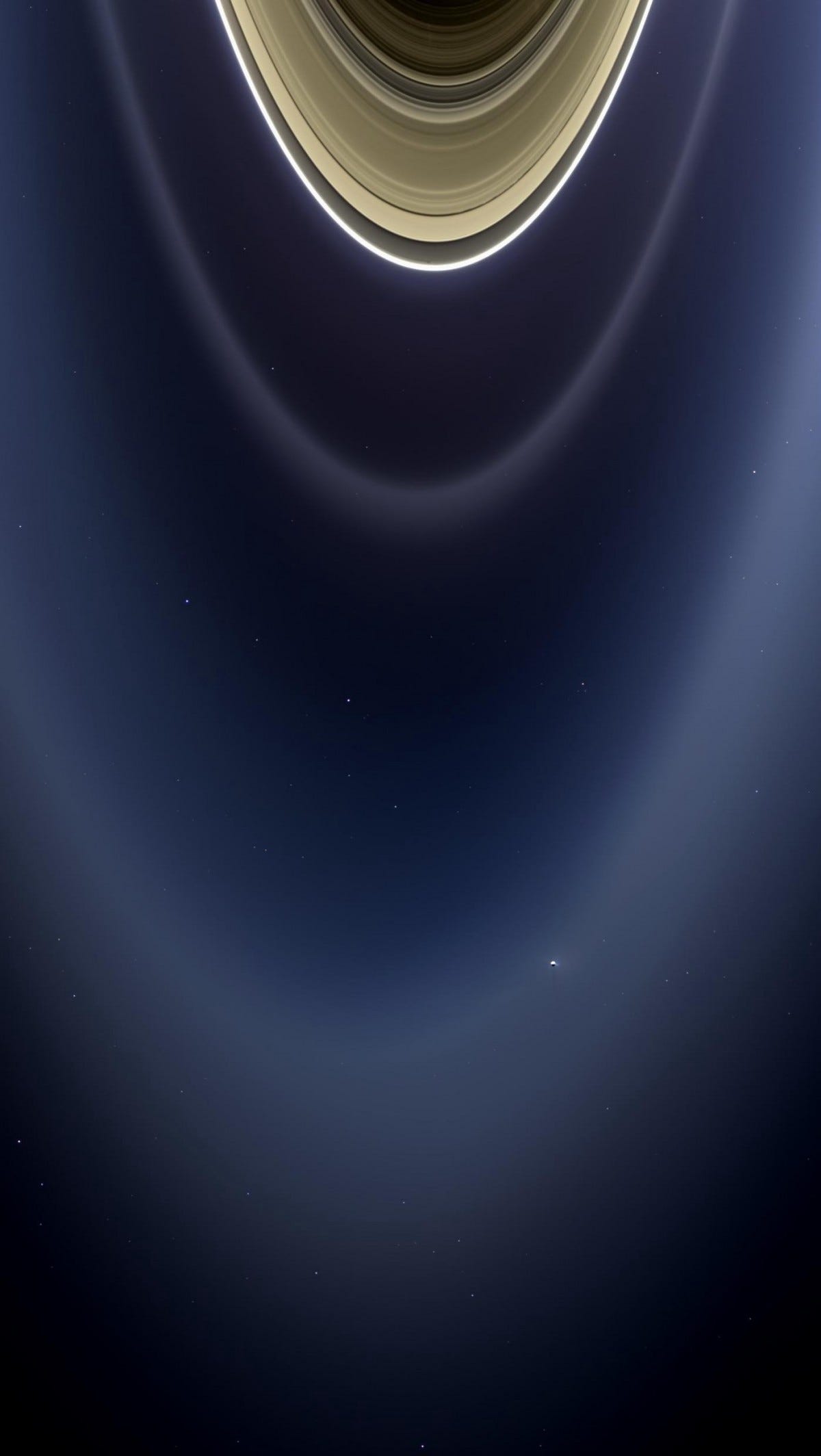



The ring system itself is just 10 meters to 1 kilometer thick all the way through, and is likely as old as Saturn itself.
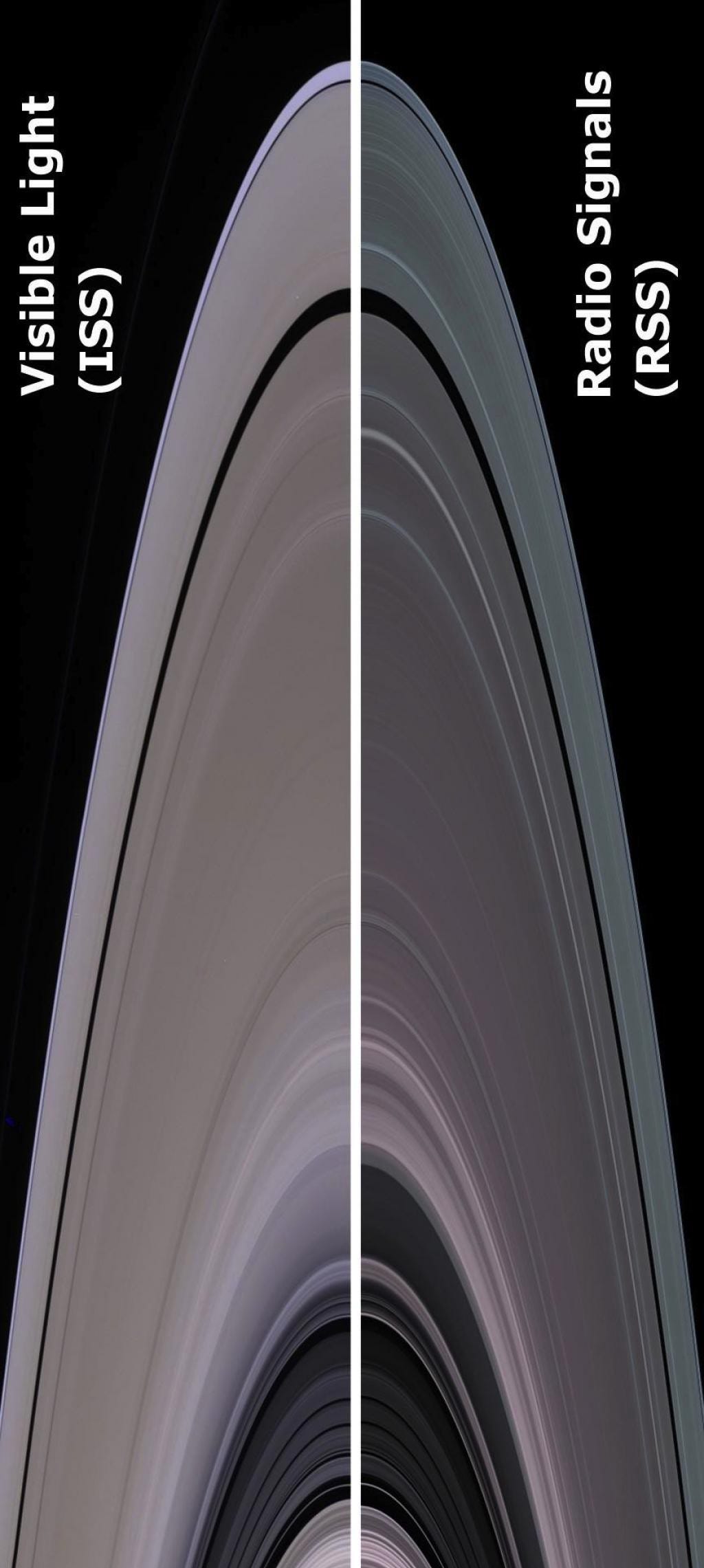
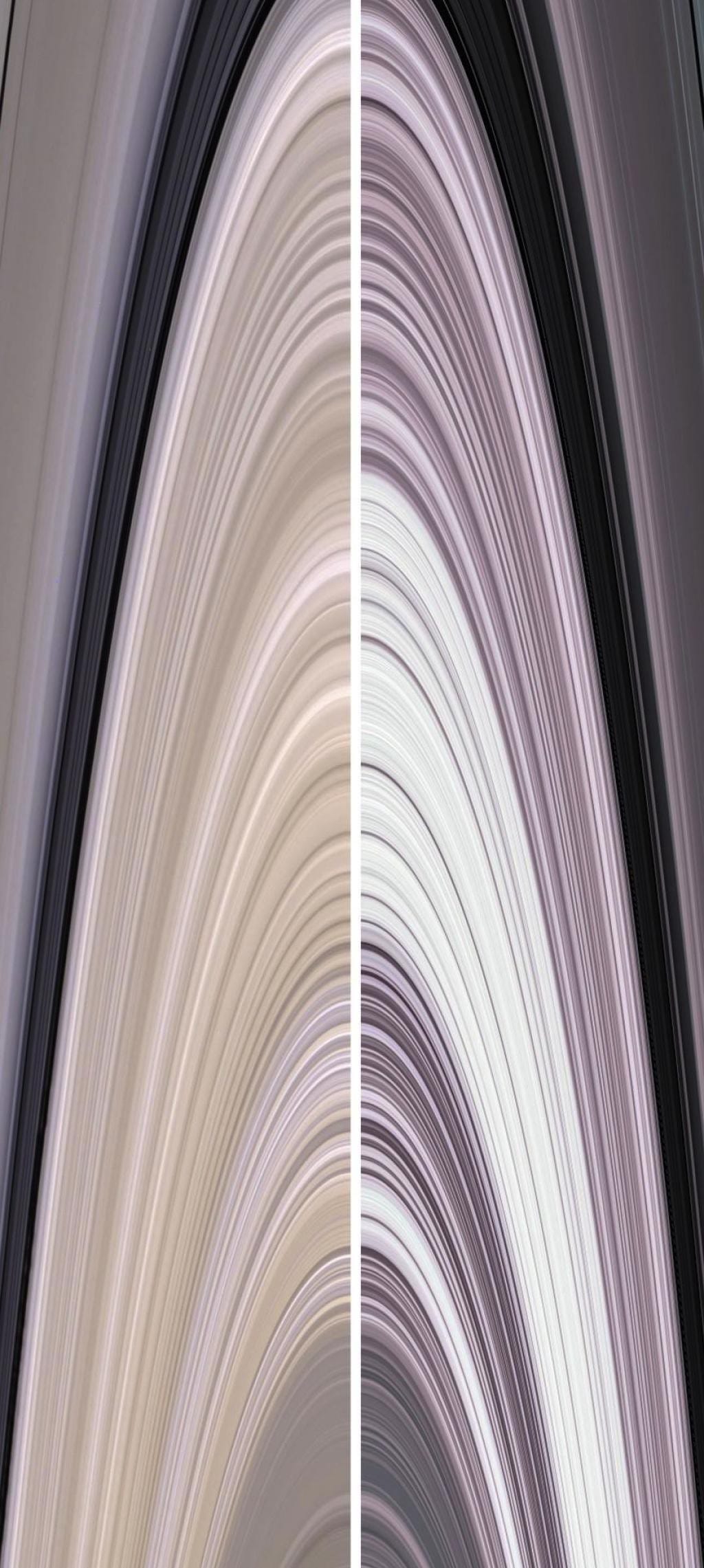


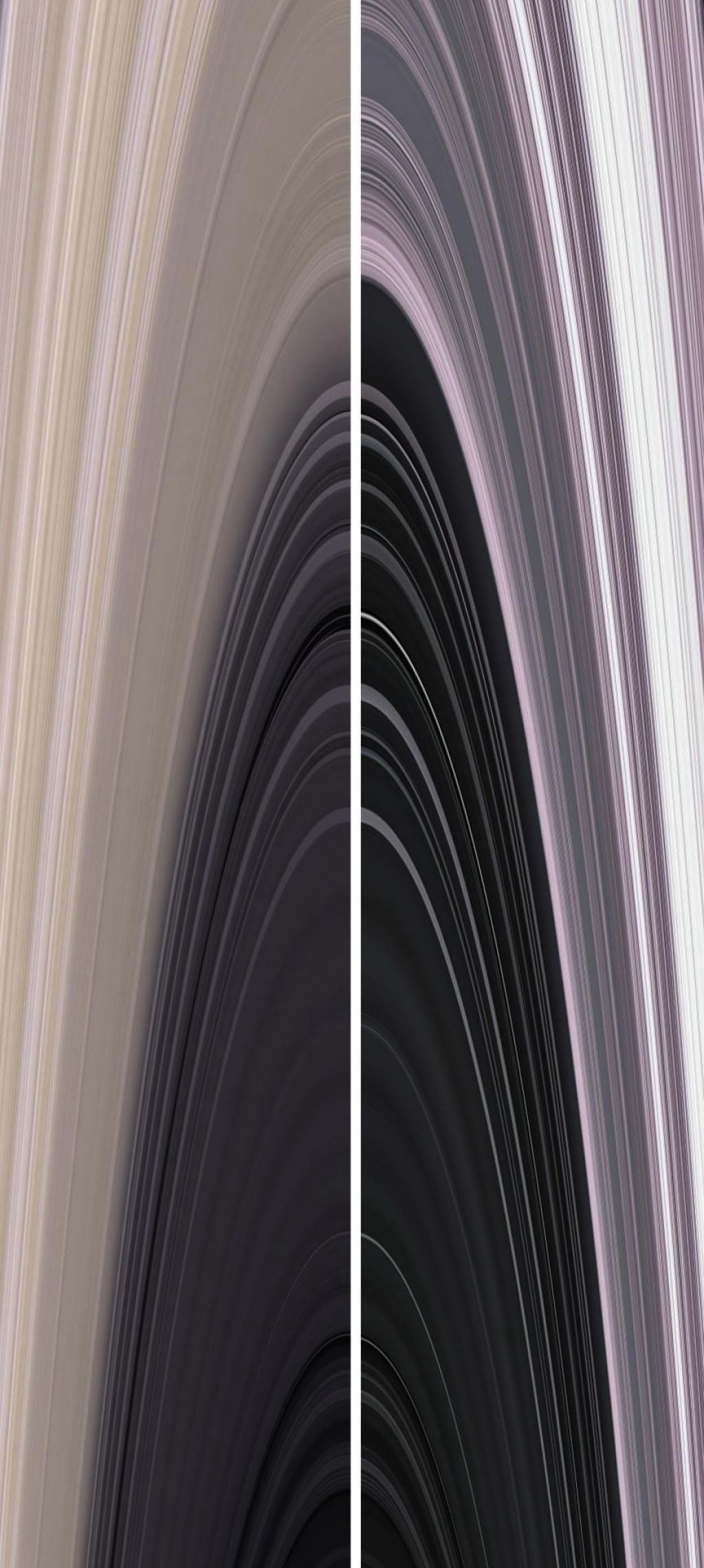
Composed of 99.9% water-ice, the ring system has thousands of thin gaps, and was thicker and more varied in the past.
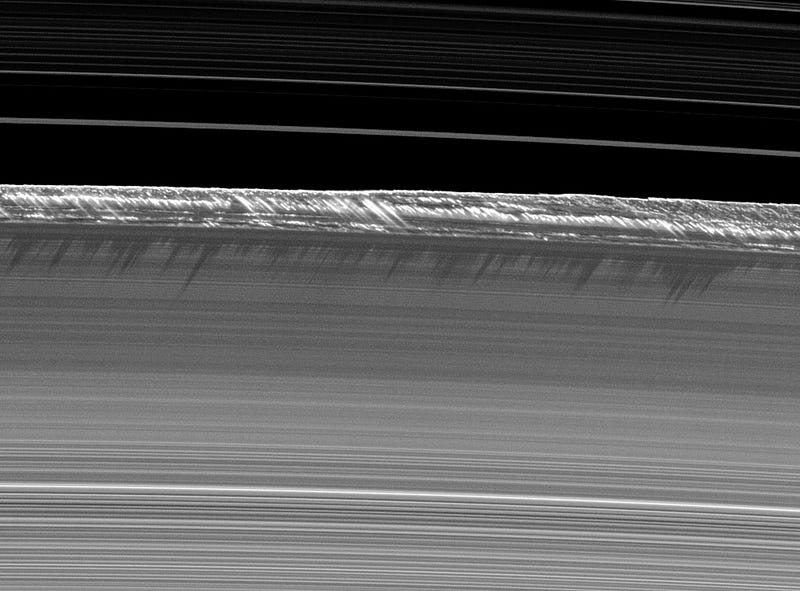
The once-rocky material has coalesced into moons, but the watery rings will remain for as long as our Solar System exists.
Mostly Mute Monday tells the story of a single astronomical phenomenon or object in pictures and other visuals, with no more than 200 words of text.
This post first appeared at Forbes. Leave your comments on our forum, check out our first book: Beyond The Galaxy, and support our Patreon campaign!





