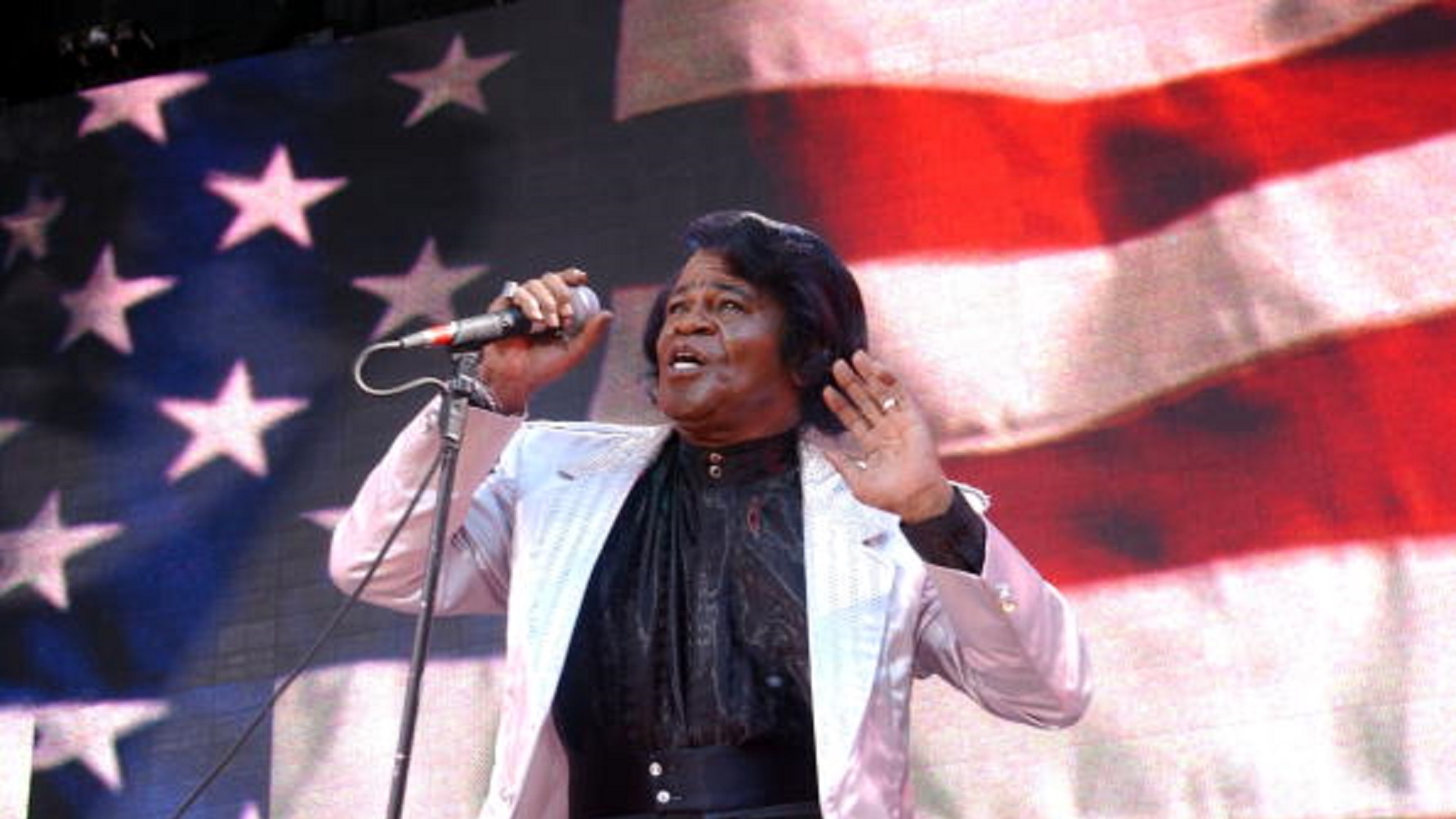
Author-musician James McBride claims that James Brown, the Godfather of Soul, holds the secret to America’s race-torn soul.
Search Results
You searched for: John James
Many of our best U.S presidents qualify as psychopaths, while Hitler doesn’t.
The most impactful technology inventions in history are ranked.
And can we even agree on the definition of ‘nothingness’? “Alone, I often fall down into nothingness. I must push my foot stealthily lest I should fall off the edge […]
Bored by “Citizen Kane”? Looking back from our era of psychologically messed up lead characters (think Bryan Cranston’s Walter Whitein Breaking Bad), Vertigo seems decades ahead of its time.
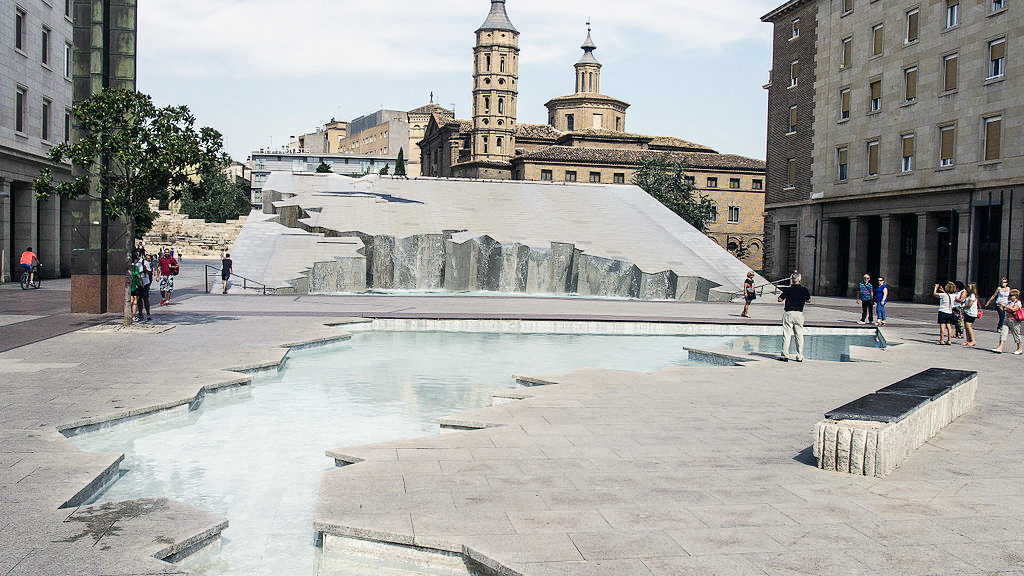
Celebrating Hispanic culture, the map-shaped fountain is one of Zaragoza’s more curious attractions
The sender didn’t have a name nor an address for his letter. So he drew a map instead.
Their thoughts were more complex than either side of the gun control / gun rights issue acknowledges.
The Lowline is the world’s first underground park. Well, almost: it’s testing the science of growing plants underground on Manhattan’s Lower East Side – and it’s a literal urban jungle.
Psychedelics came en vogue in the 1960s and since then have been maligned as inducing psychosis. Today, some evidence suggests that tiny doses of these drugs may be useful for curing psychological disorders such as depression, PTSD, and social anxiety, among others. But more research is needed and there are hurdles to overcome.
Apple and the FBI sat before the House Judiciary Committee. The group heard testimonies from both sides about the issue, including the Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation James Comey and Apple’s Senior Vice President and General Counsel Bruce Sewell.
How the biggest NASA mission of the decade will solve some of the Universe’s greatest mysteries. “Now the world has gone to bed,Darkness won’t engulf my head,I can see by […]
Roll over, Picasso, and tell Kandinsky the news.
This weekend, StoryCorps is asking us to interview our older relatives about their lives and upload it to the Library of Congress. What a wonderful way to spend your holiday.
Steven Spielberg, Tom Hanks, and Joel and Ethan Coen are bringing it all together.
Want to know how you can help stop ISIL? Stop buying their brand.
The “extraordinary authority” of maps helped perpetuate an erroneous image of West Africa for almost an entire century.
The standard line against painter John Singer Sargent goes like this: a very good painter of incredible technique, but little substance who flattered the rich and famous with decadently beautiful portraiture — a Victorian Andrea del Sarto of sorts whose reach rarely exceeded his considerable artistic grasp. A new exhibition of Sargent’s work and the accompanying catalogues argue that he was much more than a painter of pretty faces. Instead, the exhibition Sargent: Portraits of Artists and Friends and catalogues challenge us to see Sargent’s omnivorous mind, which swallowed up nascent modernist movements not just in painting, but also in literature, music, and theater. Sargent the omnivore’s dilemma thus lies in being too many things at once and tasking us to multitask with him.
“We judge ourselves by what we feel capable of doing, while others judge us by what we have already done.”
Mama, Don’t Let Your Babies Grow Up To Deny Evolution If adults want to deny evolution, sure. That’s fine. Whatever. But those adults better not make their kids follow in […]
There were two periods of exponential expansion in the Universe: one today and one long ago. Are they related? “What is wild cannot be bought or sold, borrowed or copied. […]
If Flannery O’Connor somehow birthed the love child of Sid Vicious, she might end up sounding like novelist Nell Zink. Equal parts Southern Gothic’s grotesquely twisted charm and punk and alternative music’s insiderish anti-establishmentism, Zink’s second novel Mislaid will disorient you until you let it delight you. Zink’s mix — which I’ll call Southern Gothic Punk — might be an acquired taste, but a taste well worth experiencing if only to break out of the contemporary rut of MFA-programed, sound-alike fiction that’s become the bubblegum pop of today’s literature.
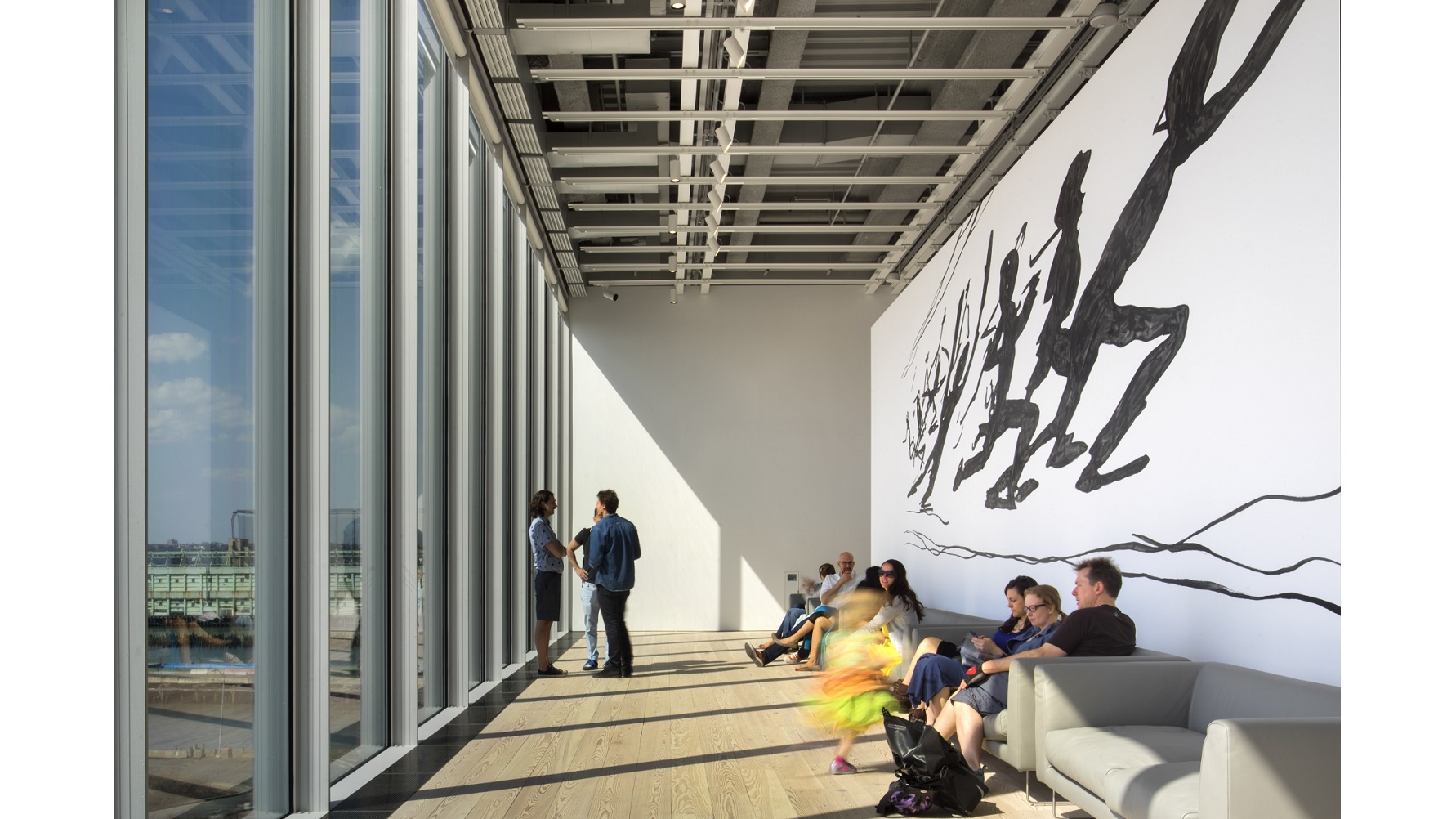
With the May 1st grand opening to the public of its new building in Manhattan’s Meatpacking District, the Whitney Museum launches a new era not only in the New York City art scene, but also, possibly, in the very world of museums. Thanks to a Renzo Piano-designed new building built, as Whitney Director Adam D. Weinberg put it, “from the inside out” to serve the interests of the art and the patrons first, the new Whitney and its classic collection of American art stretching back to 1900 has drawn excited raves and exasperated rants from critics. Their inaugural exhibition, America Is Hard to See, gathers together long-loved classic works with rarely seen newcomers to create a paradox of old and new to mirror the many paradoxes of the American history the art embodies and critiques by turns. This shock of the new (and old) is the must-see art event of the year.
What do “Yesterday,” “Satisfaction,” “My Generation,” “The Sound of Silence,” “California Girls,” and “Like a Rolling Stone” all have in common? They were all hits in 1965, the year author Andrew Grant Jackson calls “the most revolutionary year in music.” In 1965: The Most Revolutionary Year in Music, Jackson weaves a fascinating narrative of how popular music and social change influenced one another to create a year memorable not only for great music, but also for great progress in American culture. In this whirlwind tour of multiple genres of music as well as multiple pressing political issues, Jackson states a compelling case for 1965 as a key turning point in American music and society as well as provides a mirror for how music and society interact today, 50 years later.
We’ve only ever seen 2nd-generation stars and later. Until, just maybe, now. “For my part I know nothing with any certainty, but the sight of the stars makes me dream.” […]
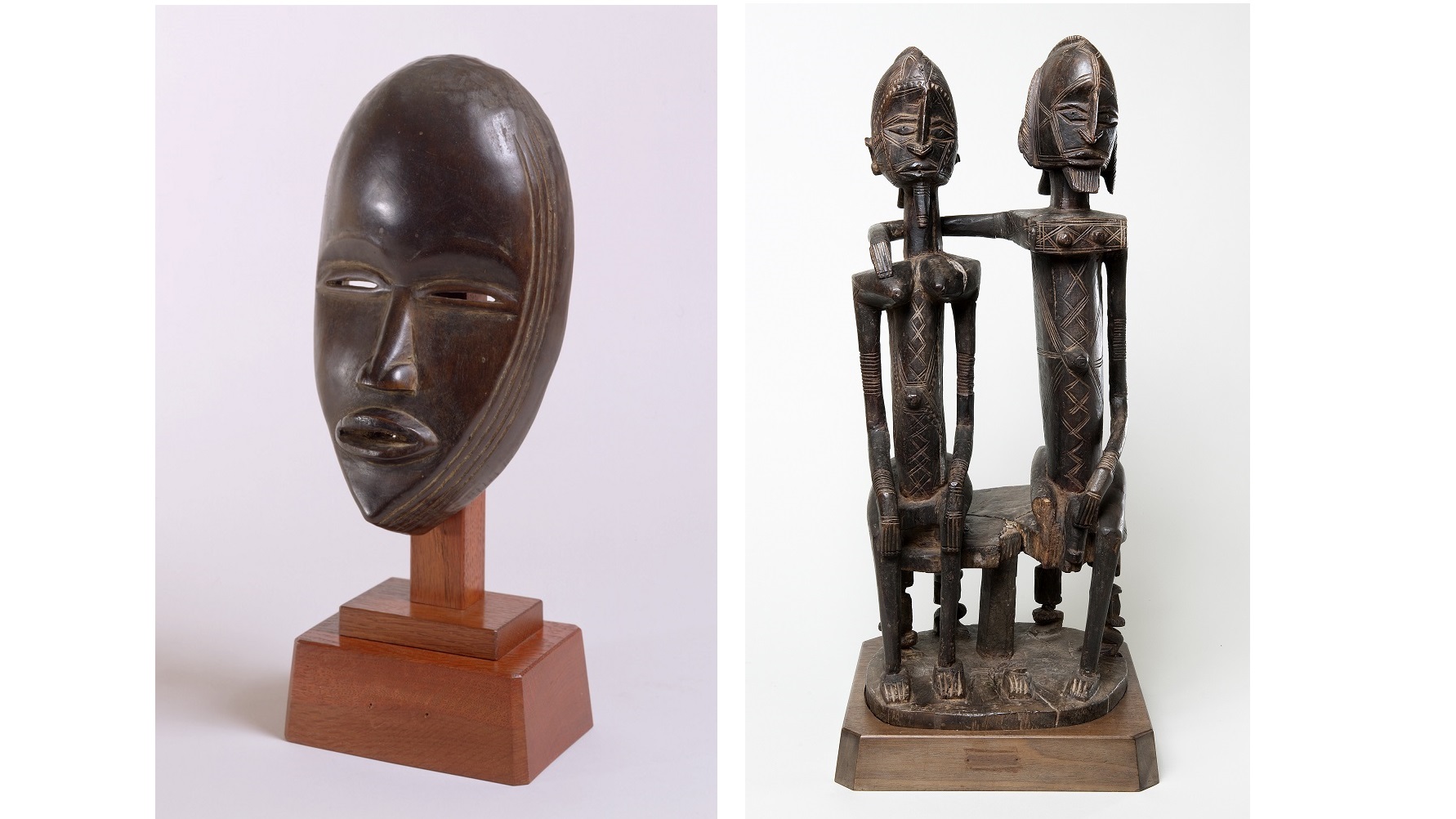
The Barnes Foundation’s current exhibition, Mark Dion, Judy Pfaff, Fred Wilson: The Order of Things, epitomizes the business buzz phrase “disruptive innovation” like few other museum shows (which I wrote about here). Disrupt or die, the thinking goes. Old orders must make way for new. Coincidentally, as the Barnes Foundation, home of Dr. Albert Barnes’ meticulously and idiosyncratically ordered collection of Impressionist and Post-Impressionist masterpieces left just so since his death in 1951, invites outsider artists to question and challenge Dr. Barnes’ old order, it also publishes their own insider’s critical “warts and all” assessment of Dr. Barnes’ relationship to African art and African-Americans. In African Art in the Barnes Foundation: The Triumph of L’Art nègre and the Harlem Renaissance, scholar Christa Clarke reassesses Dr. Barnes intentions and results in his building of the first great African art collection in America. “More than just formal accents to modernist paintings and other Western art in the collection,” Clarke argues, “African art deserves to be seen as central to the aesthetic mission and progressive vision that was at the very heart of the Barnes Foundation.”
NASA represents a full 50% of the world’s expenditures on space science & exploration. What should we expect from it? “This Administration has never really faced up to where we […]
“They f**k you up, your mum and dad,” poet Philip Larkin wrote in the late work “This Be the Verse.” “They may not mean to, but they do./ They fill you with the faults they had/ And add some extra, just for you.” Larkin kidded that those lines would be his best remembered, a guess not too far off 30 years after his death. Where others see in those lines a perfect portrait of the sour, sad curmudgeon poet, in the new biography Philip Larkin: Life, Art and Love, James Booth sees something different. “The poem’s sentiment is sad, but the poem is full of jouissance,” Booth argues. “This must bid fair to be the funniest serious English poem of the 20th century.” Likewise, Larkin — target of posthumous charges of racism, misogyny, and assorted cruelties — could lay claim to being the “funniest serious” English poet of the 20th century. Booth, who knew and worked with Larkin, shows the sweet, happy side of the sour, sad poet and makes a strong case for learning to love Larkin again, if not for the first time.
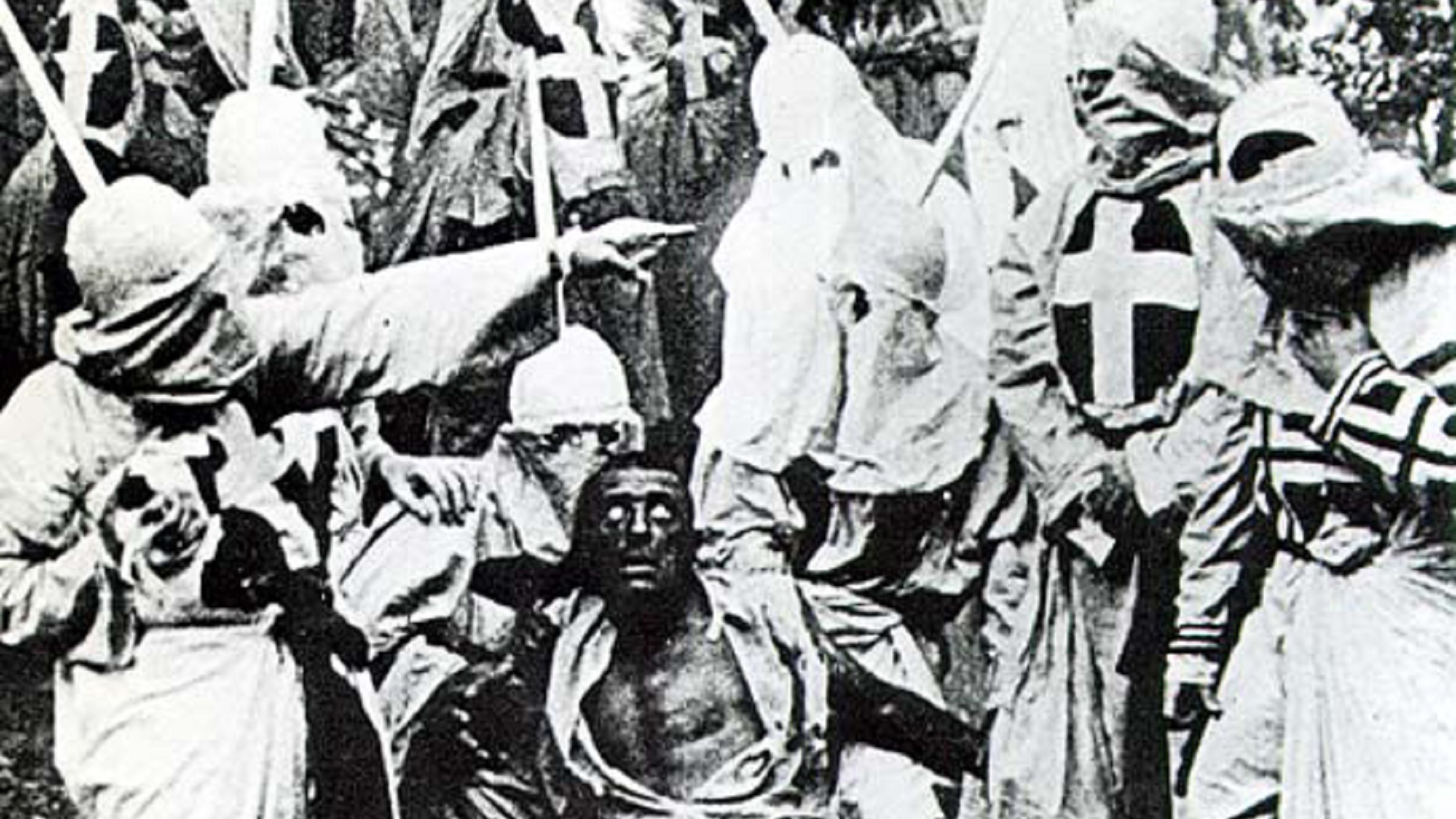
On February 8, 1915, at Clune’s Auditorium in Los Angeles, California, D. W. Griffith’s Birth of a Nation premiered. The fledgling art form of film would never be the same, especially in America, which even half a century after the end of the Civil War struggled to come to terms with race. Now, a century after Birth of a Nation’s premier, America still struggles not only with race, but also with how race plays out on the silver screen. For good and ill, Birth of a Nation marks the beginning of the first 100 years of the American Cinema—epically beautiful, yet often racially ugly.
Some health advocates believe the public would eat healthier if they were informed just how much they’d have to exercise to work off a bowl of sugary cereal or a liter of cola.