Your Glorified Ignorance Wasn’t Cool Then, And Your Scientific Illiteracy Isn’t Cool Now
There are real problems that our society faces, and only through expert-level knowledge can we solve them.
All across the country, you can see how the seeds of it develop from a very young age. When children raise their hands in class because they know the answer, their classmates hurl the familiar insults of “nerd,” “geek,” “dork,” or “know-it-all” at them. The highest-achieving students — the gifted kids, the ones who get straight As, or the ones placed into advanced classes — are often ostracized, bullied, beat up, or worse.
The social lessons we learn early on are very simple: if you want to be part of the cool crowd, you can’t appear too exceptional. You can’t be too knowledgeable, too academically successful, or too smart. Someone who knows more, is more successful, or smarter than you is often seen as a threat, and so we glorify ignorance as the de facto normal position.
But ignorance isn’t normal at all. Choosing to remain ignorant harms your development as a child, but harms the world as an adult.
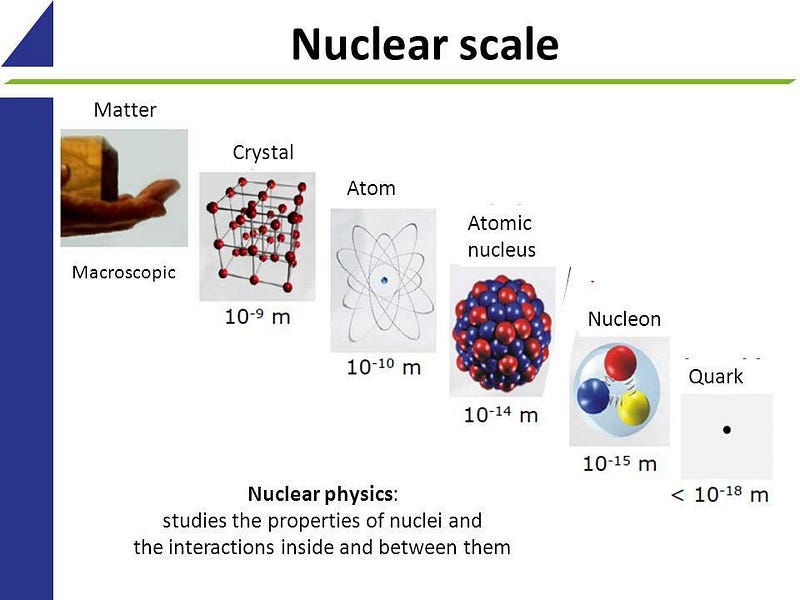
There are so many remarkable things that we — as a species — have figured out about existence. We know what life is: how to identify it, how it evolves, what the mechanisms and molecules are that underpin it, and how it came to survive and flourish on Earth. We know what reality is made of on a fundamental level, from the smallest subatomic particles to the nature of space and time that encompasses the entire Universe. We know how matter behaves under extreme conditions, from the vacuum of space to the centers of stars to the ultra-cold conditions we can only achieve in laboratories here on Earth.
Our most valuable explorations of the world and Universe around us have been scientific ones: where we learn about reality by asking it the right questions about itself, and listen to the answers that it reveals.

Of course, not everyone knows all (or even most) of these answers. It’s impossible, in this day and age, to be an expert in all possible things. Most of us learn this at an early age: that most of what is known to humanity is not known to us as individuals, and that we can either study to gain that expertise and learn it, or go find the appropriate expert to learn what the answer is from them.
At least, that’s how you behave if you’re genuinely interested in learning the actual answer. You’ll either undertake the research yourself to reach expert-level competence, where you’ll learn how to perform critical tests and experiments that determine the answer, or you can learn to discern whose expertise is worth listening to and why, and then to take that expert advice. That’s how you gain meaningful knowledge.
But many of us don’t choose that route for a number of reasons. First off, it requires making a series of admissions to ourselves that are very difficult to accept. These include:
- admitting that we don’t know everything,
- admitting that we might be wrong about something that we’ve thought or even publicly espoused,
- admitting that we might have been swindled or conned by a charlatan,
- requiring us to do additional research, work, and mental labor,
- and to admit to ourselves that our heroes — the people we admire most — are often flawed or incorrect.
This is not an easy situation to be in, regardless of your education or background. It’s human nature to want to save face and appear like we knew the right answer all along. But, if we’re being honest with ourselves, that isn’t a real solution.

If you’ve ever pointed out a teacher’s mistake to them in school, you’ve likely gotten one of three types of responses. Perhaps the teacher considered what you said, admitted their mistake, and praised you for catching it. Perhaps the teacher recognized you were right and they were wrong, but wanted to save face, and so responded by ignoring your point or pretending that they didn’t make a mistake, such as by saying “I was just testing you.” Or, worst of all, perhaps the teacher dug in deeper to their demonstrably incorrect position, insisting that they were right despite the overwhelming evidence to the contrary.
We all hated the latter responses as kids, and knew that the adults were lying to us, themselves, and everyone else in the room. What we knew was wrong back then is still wrong today. Only, as adults, the consequences are dire.
When we deceive ourselves about the severity of an injury, the injury typically gets worse. When we deceive ourselves about an illness that we have and fail to get it treated appropriately, we significantly increase our risk of debilitating long-term consequences or even of death. If we are dishonest with ourselves about the reality of the situation we find ourselves in, our comfort is often short-lived, as it’s followed by potentially dire consequences.
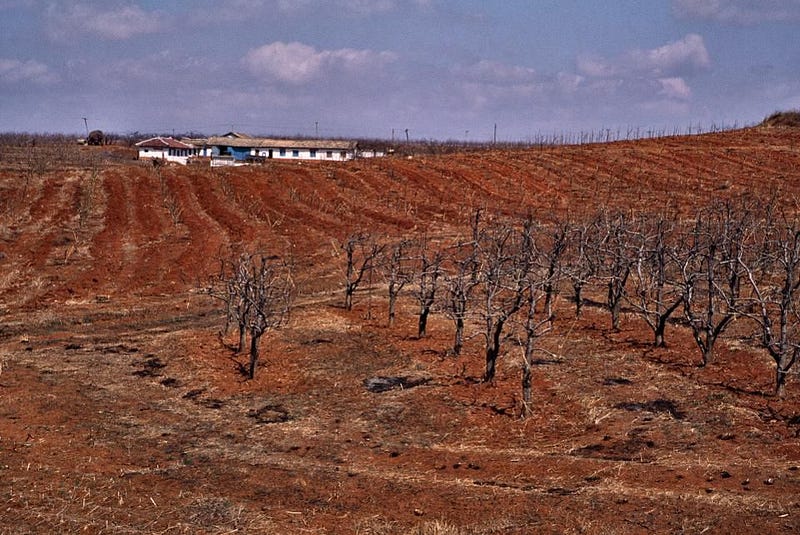
Sometimes, however, the consequences are either minor, invisible to us, longer-term than we’re willing to consider, or they affect someone other than ourselves. When your country doesn’t produce enough food, you might think about cutting down more trees to increase your farmland. But trees are essential for water management; without enough, your farmland might become a muddy wasteland, leading to a catastrophic famine. This recently occurred in North Korea, causing their great famine in the 1990s.

Every time we insist we already know everything, we lose an opportunity to learn and improve. When we insist that we’re perfect and infallible, we entrench ourselves in a position that runs the risk of being overturned when more and better information comes in. When the expert we once trusted turns out to be a huckster, fraud, or worse, we can either admit that we were tricked or try to defend the indefensible.
All of the solutions that require learning, incorporating new information, changing our minds, or re-evaluating our prior positions in the face of new evidence have something in common: they take effort. They require us to admit our own limitations; they require humility. And they require a willingness to abandon our preconceptions when the evidence demands that we do. The alternative is to live a contrarian life where you’re actively harming society.

Imagine a world where we followed the advice of the 1960s-era auto industry, who proclaimed that seat belts wouldn’t save lives, and so we never even bothered to install them in cars. Imagine a world where we never accepted the germ theory of disease, and therefore never incorporated appropriate sanitation or antisepsis practices into society.
Although these examples might be non-controversial in our society today, it’s only because public opinion on these matters — what we frequently call “common knowledge” — aligns very well with the scientific consensus on these issues. Frequently, public opinion and our proverbial common sense are terrible guides, and we are taken in by schemes, scams, and conspiracies that play on our fears. These pitfalls are not unique to laypersons; scientists and others with expert-level knowledge are frequently mistaken, too.

Some of the ways this manifests in society might seem like low-stakes affairs that aren’t worth much effort. Maybe you laugh when you hear about a rapper claiming the Earth is flat. Or a basketball player saying we never landed on the Moon. Or at the 25% of the population who thinks the Sun orbits the Earth. But it’s not laughable; it’s something we should all be ashamed of.
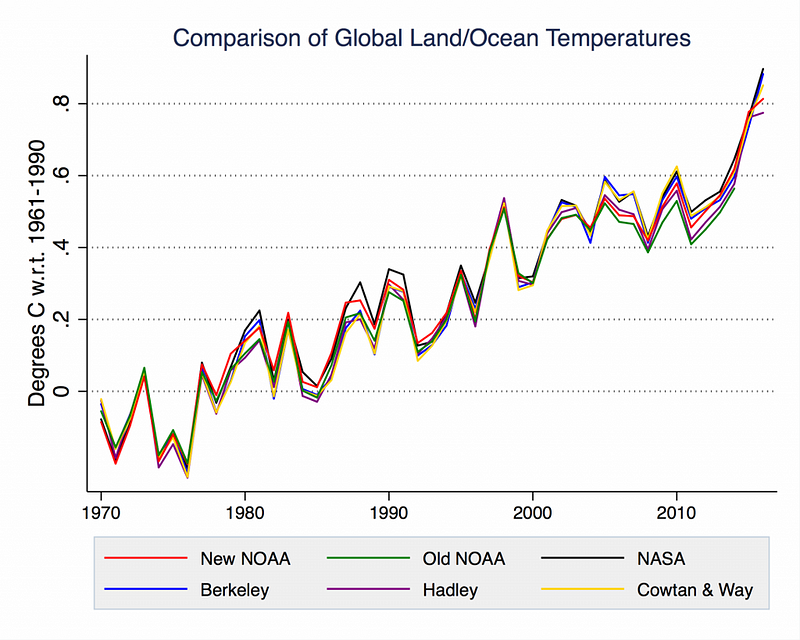
When we trust our own non-expertise over the genuine expertise of bona fide experts, terrible things happen. We wind up with cities without fluoridated drinking water, increasing cavities by 40% in the most low-income populations. We get vaccine-preventable diseases causing outbreaks and epidemics. We continue to pollute the Earth with greenhouse gases even as we’re experiencing the early consequences of global climate change.
In short, we act irresponsibly whenever we trust our own skewed assessments over the superior, expert-quality information that humanity worked so hard to obtain.
You are not right about everything. Many of the opinions that you hold — and some of the facts that you believe to be true — will turn out to be falsely-held beliefs. Some of them, most likely, have already had their falsehood demonstrated beyond a reasonable scientific doubt. Unless you yourself are a huckster, trying to profit off of the willful deception of others, you must be open to changing your mind and deferring to the genuine experts who know more than you.
Glorified underachieving, proclaiming falsehoods as truths, and the derision of actual knowledge are banes on our society. The world is made objectively worse by every anti-science element present within it. Nobody likes to hear that sometimes, they’re the problem. But sometimes, it really is on each of us to do better. The next time you find yourself on the opposite side of an issue from the consensus of experts in a particular field, remember to be humble. Remember to listen and be open to learning. The future of our civilization may hang in the balance.
Ethan Siegel is the author of Beyond the Galaxy and Treknology. You can pre-order his third book, currently in development: the Encyclopaedia Cosmologica.