Surprising Science
All Stories
The theory that natural landscapes recharge minds that have been stretched thin by harsh urban environments is not new, but only recently has the theory become testable.
A team of British researchers will soon begin testing an electrical device which, by attaching to a nerve that controls the body’s appetite for food, could provide an alternative to weight-loss surgery.
By building circuits out of DNA, researchers at Stanford have found a way to program the body’s cells with logic functions, similar to how computer chips work on larger scales.
To help feed the world’s malnourished, a team of students at McGill University, Montreal, are putting forth a plan meant to facilitate the production of edible insects on an industrial scale.
Once infamous for how they objectified the female body, marketing departments at beer and spirit producers have begun selling their products to women as weight-loss drinks.
Think of it as a variation on the scratch-and-sniff: Designers at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology have created a “smelling screen” that’s able to emit scents at pixel level.
Researchers found that simply looking at and holding a bottle of pain medication “nonconsciously decrease[d] pain sensitivity” in test subjects.
In a survey conducted by AT&T, more adults than teens admitted to texting while driving. Interestingly, 60 percent of those said they only started doing so in the last three years, and 98 percent of them knew it was unsafe.
If so, the Gates Foundation wants to hear from you: They have launched a competition to find prophylactic designs that will encourage more people to use them, particularly in the developing world.
Originally designed for the elderly and disabled, the Hitachi Robot for Personal Intelligent Transport System negotiates itself around pedestrians and over uneven terrain using a variety of sensors and guidance systems.
A Florida-based startup has created a bracelet-type device that works with RFID tags at hand washing stations to ensure that its wearer is being thorough. It’s currently targeted at the healthcare industry, where infections can be very expensive.
Created by researchers at the University of Texas-Austin, the cloak only works in the microwave spectrum but could theoretically be used to hide objects in visible light.
Experts say that climate change is affecting the wine industry both in terms of budding grape growing locations — like Denmark — and the quality of wines produced in established locations.
A report out from the EPA this week says that only one in five rivers and streams are in good condition, and just over half are in poor condition.
3-D printers are currently capable of producing usable car parts, cat-scanned reproductions of ancient Sumerian clay envelopes with letters inside, and cool-looking geometric desktop toys. That’s very exciting indeed. But […]
By genetically modifying a unique microorganism, researchers have discovered a way to turn atmospheric carbon dioxide directly into useful industrial products. Their find could lead to the creation of biofuels that “remove plants as the middleman.”
A study published in the recent issue of Geology ties seismic events in central Oklahoma to wastewater produced from oil extraction and injected deep underground.
Experimental researchers at the Pentagon have just undertaken a four-year project to build artificially intelligent computers that can teach themselves new and better artificial intelligence.
Beyond the microchip lies quantum computing. Beyond that lies quark-scale computing, made from materials a billion billion billion times smaller than the current computational scale.
“It’s absolutely not true that we need natural gas, coal or oil—we think it’s a myth,” said Mark Z. Jacobson, author of a new energy report by the National Research Council.
Mindfulness, or mindfulness meditation, in which practitioners intentionally pay attention to the present in a nonjudgemental way, has become a useful tool in the stress management toolkit.
Dmitry Itskov, a Russian Internet mogul, is soliciting investment for what he expects will be the world’s first immortality research center. Immortality is not a bad return on investment.
Combining tactics from the fields of physics, computational biology, virology and immunology, scientists at MIT and Harvard have found a new path forward for the potential development of an HIV vaccine.
As a result of various social pressures, the stakes of producing positive results in medical experiments is very high and thanks to statistical tricks, researchers know how to create them.
Last week, England’s chief medical officer compared the problem of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to the threat of global terrorism. Surprisingly, the comparison was understated.
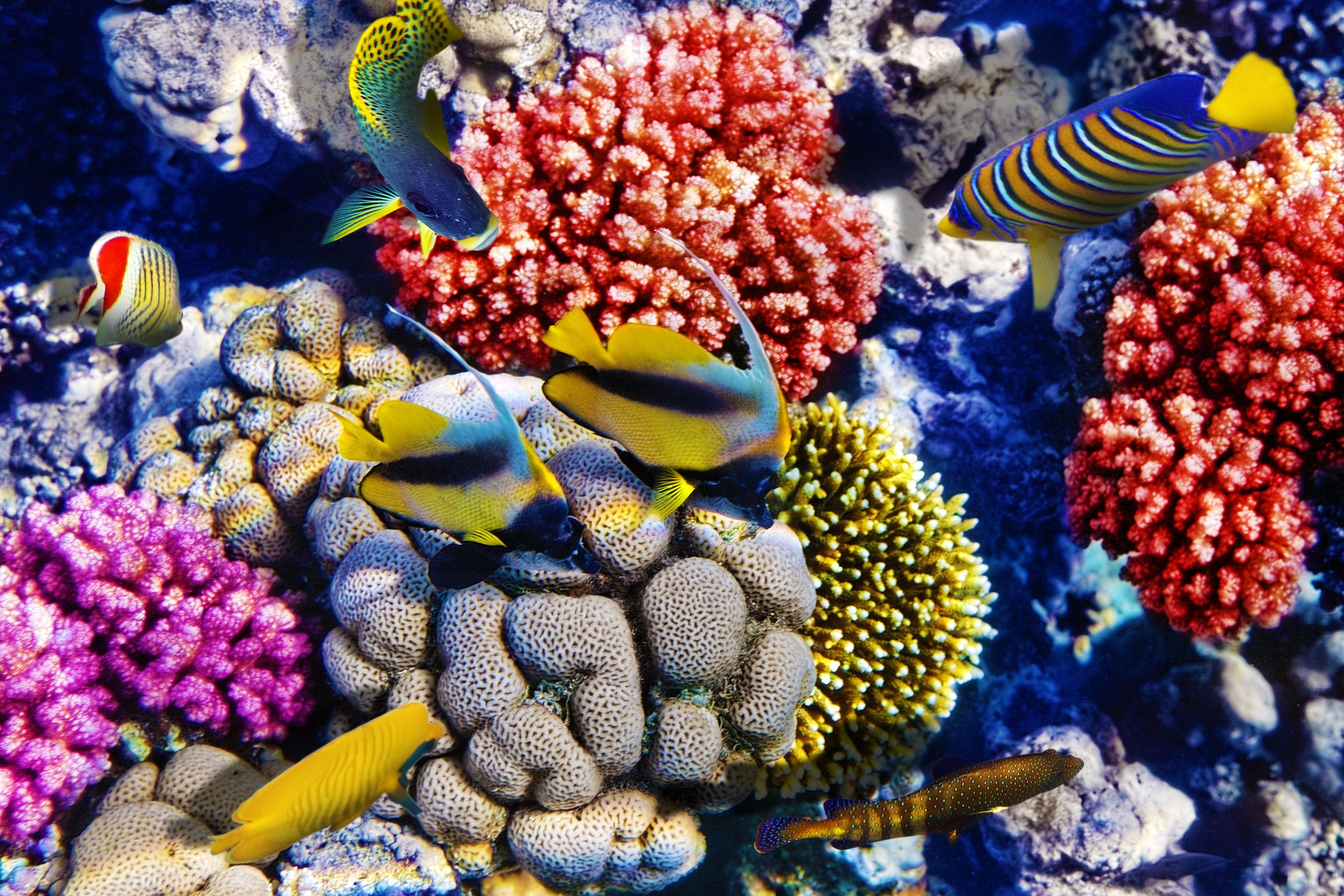
Biologists have begun to discover just what a treasure trove the oceans’ coral reefs are in terms of finding potential cures to some of humanity’s worst diseases, despite threats to the reefs’ existence.
A study published in this week’s Science provides the clearest proof yet that a series of volcanic eruptions wiped out half of Earth’s animal and plant species prior to the dinosaur era.
Researchers in France have created a tiny new medical device, designed to be implanted beneath the skin, that uses enzymes to analyse the quality of a patient’s blood.
NASA has announced that its most recent Mars rover, Curiosity, recently found evidence of substantial water stores present on the planet’s surface billions of years ago.
A new study that examined 30 years’ worth of data on cliff swallows shows that “vehicular selection” contributed to a drastic drop in the number of birds killed by cars during the period.