Surprising Science
All Stories
Aromatherapists rejoice: There’s now hard evidence showing that being exposed to the scent of nature — specifically trees and plants — is almost as good for the body as being outside.
Designed by mobile tech company Chaotic Moon to capture events taking place during an accident, it has one of the coolest names ever: The Helmet of Justice.
When applied to a wound, Veti-Gel, a plant-based version of the body’s natural clotting material, also “jump-starts” the healing process. Its inventor turns 21 next year.
Hyundai’s ix35 Fuel Cell, unveiled this week, is expected to hit the consumer market in 2015 as the world’s first mass-produced hydrogen-powered vehicle.
Two Texas A&M University engineers say their satellite would save fuel costs by using the momentum created by removing one piece of junk to propel itself to the next piece.
The icy surface of this Jupiter moon hides a vast body of liquid that most scientists believe is water. Thanks to improved spectrometry, they now believe that that water may be salty.
Far from the aloof practitioner of new-age feel-good solutions, viewing dilemmas as opportunities rather than life-crushing problems—in a word, being optimistic—has real benefits.
Researchers were surprised to find that fruit flies were given to impulsive eating patterns, similar to humans who will eat more of a food if it contains large amounts of sugar and fat.
Engineers have improved on the original and groundbreaking brain-computer interface by creating a wireless device that has successfully been implanted into the brains of monkeys and pigs.
The state of Colorado, one of the first in the country to legalize the general use of marijuana, is now facing a dilemma over how, and whether, to criminalize driving under its influence.
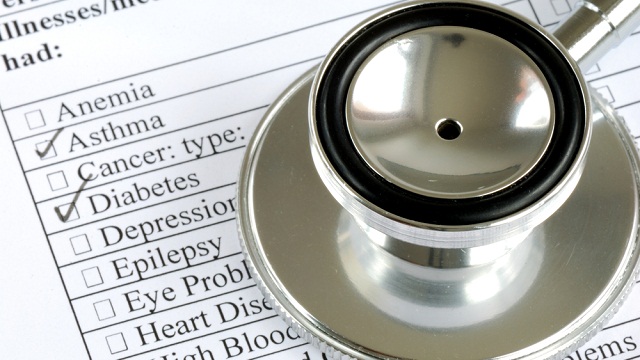
Some in America find their only path to healthcare is to manipulate the system, whether than means always going to emergency room or committing crimes to receive medical attention.
A new study out of Finland has found that having a boy may shorten mothers’ lifespans for biological and environmental reasons. Researchers will now look for more current data.
By studying how viruses work in plants, biologists are coming to see that far more species are symbiotic than purely independent. In other words, viruses can confer benefits on plants.
The second-largest desert city also has exceptionally high levels of humidity, which the billboard converts into water that citizens can access via a simple spigot.
The camera inside the BallCam compensates for the speed at which the ball rotates to provide a clear, wide-angle, “ball’s-eye” view.
Available for sale later this year, the Myo interprets muscle movements in the forearm and transmits them wirelessly to software-enabled devices that can understand them as commands.
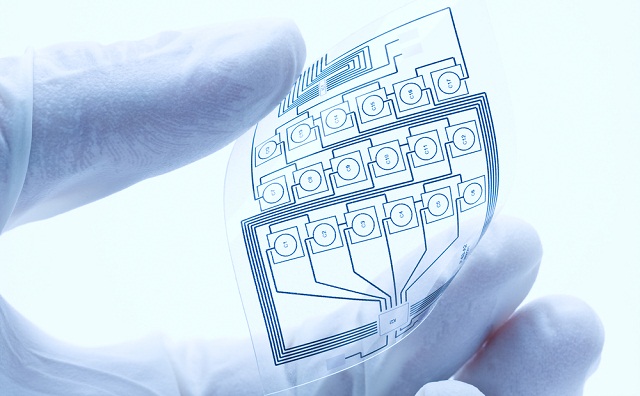
A team of researchers has developed a prototype battery that can stretch up to three times its size and can be recharged wirelessly.
A new paper suggests that it’s much easier to detect oxygen in the atmospheres of planets orbiting white dwarf stars, which are dimmer than the Sun.
At a conference titled “The Present-Day Habitability of Mars” scientists discussed the possible seasonal existence of liquid water as well as the survival tactics of Antarctic microbes, among other topics.
Even low levels of certain drugs found in waterways affect fish behavior. A team of Swedish researchers have created a wastewater treatment that reduces drug residue.
Science fiction writer William Gibson famously stated on NPR’s Fresh Air back in 1993, “The future is already here, it’s just not very evenly distributed.” It’s a quote that in […]
This week, PatientsLikeMe announced the building of an open science platform to allow its users to measure their diseases’ progress and share it with medical researchers.
A survey by office furniture company Steelcase reveals that the influx of smartphones and tablets is changing how workers sit and how designers think about seating options.
The popularity of scientific studies of the human subconscious have ballooned in the past decade, but verifying the studies’ results has proven difficult because of biases in academic journals.
The federal government is preparing to put $3 billion dollars into researching the human brain, which over the last decade has become the final frontier of terrestrial science.
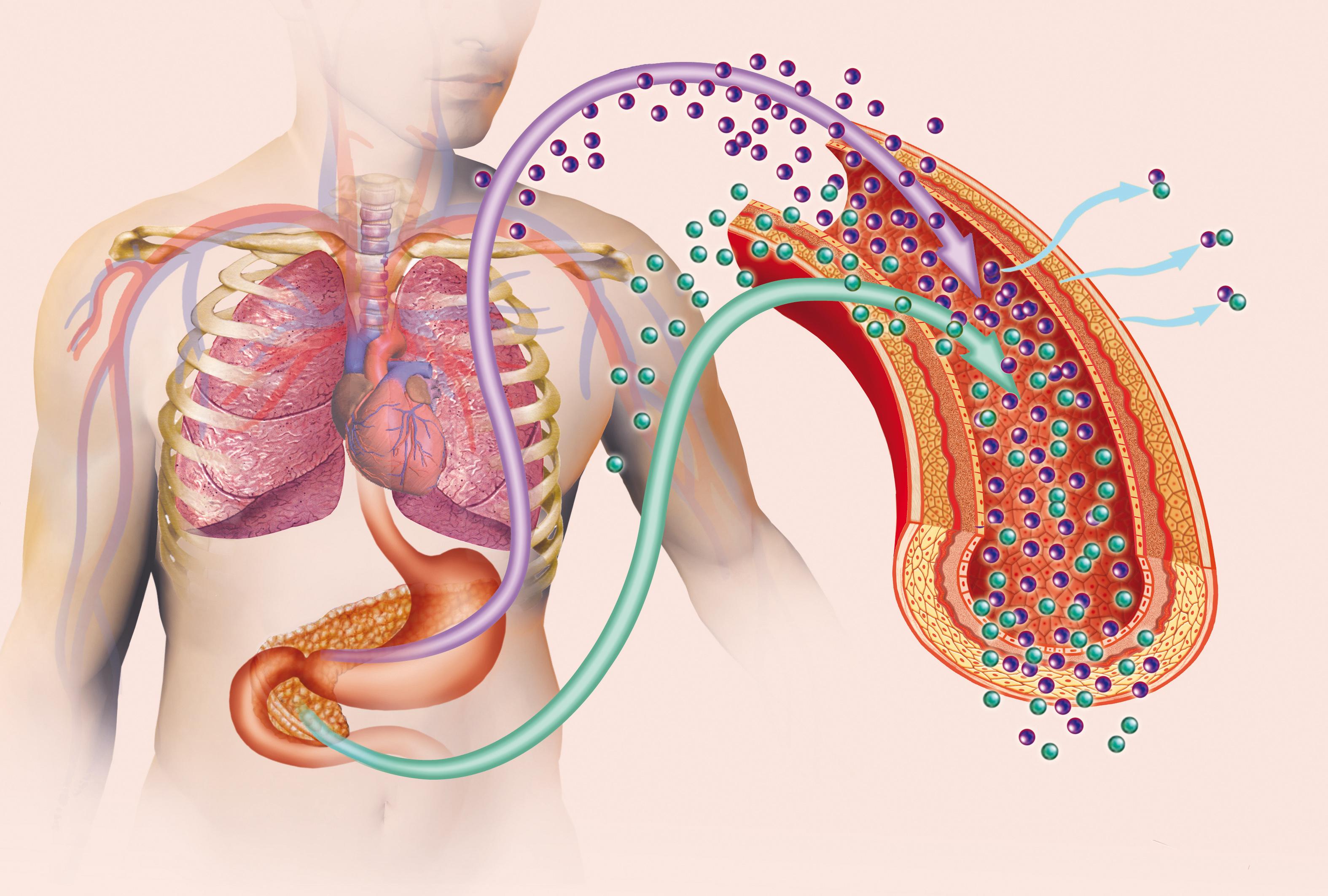
Researchers have successfully “reprogrammed” certain cells to produce more insulin in the body, representing a potential genetic treatment for patients diagnosed with diabetes.
Parents looking to keep their kids from experimenting with tobacco, drugs and alcohol should avoid mention of their own past drug use, according to a new study on human communication.
Just after the FDA approved a special pair of glasses that help restore vision to the blind, a German company has built a system which requires no external hardware to function properly.
Corporations like Frito-Lay and Coca-Cola have poured enormous amounts of money into creating snack foods and drinks filled with sugar and fat. The result has been a public health epidemic.
Researchers at the University of Washington have determined the molecular structure of certain compounds found in beer that give the brew its bitter flavor and confer health benefits.