Ancient women with “tower-shaped” skulls were high-ranking political brides, says new study
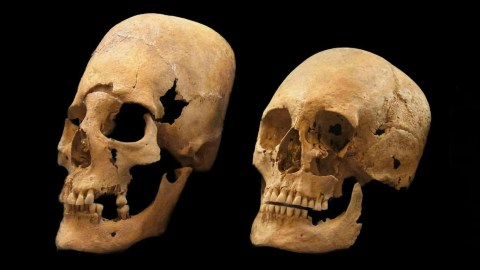
Scientists have a strange theory for how the 1,500-year-old remains of women who possessed features completely unlike the local population—including elongated skulls—ended up in present-day Bavaria.
Joachim Burger, an anthropologist and population geneticist at Johannes Gutenberg University, and colleagues posit the women were high-status “treaty brides” from Romania and Bulgaria, sent to marry men of distant tribes to strengthen political ties.
In a study recently published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Burger and his team analyzed remains unearthed in graves located in the present-day German state of Bavaria. They compared the DNA of bone fragments from the graves with each other, and with DNA of modern populations throughout Europe and Asia. The DNA of people with normal skulls was homogenous, closely matching genealogical profiles of modern people in central and northern Europe: blue eyes, light hair. But the DNA from nine women with elongated skulls suggested a distant origin, with dark hair and dark eyes—likely Bulgaria and Romania.

Why the long, “tower-shaped” skulls? They were almost surely the result of artificial cranial deformation, a long and tedious process in which the skull of an infant is repeatedly bound until the head grows into a distorted shape. It’s been practiced for millennia all around the world as a way for families, typically wealthy ones, to distinguish their children (boys and girls) with a mark of high status.
The women would have been distinguished in other ways, too. Among the local blue-eyed, blonde-haired populations, these Bulgarian and Romanian (and one possibly Asian) women would have stood out with their dark hair and dark eyes.
But not everyone’s convinced the paper gets the story right.
“This is one of the strangest things I’ve ever read,” Israel Hershkovitz, an anthropologist at Tel Aviv University in Israel, who specializes in ancient human anatomy, told Science. “I don’t buy it.”
His objections? Hershkovitz said it’s not clear the elongated skulls were formed intentionally, and that there are other ways deformation can occur: strapping an infant to a carrying bag too tightly, laying one down on a hard wooden surface. Also, he suggested that while inter-tribe marriage was common among ancient peoples, it’d be unusual to send more than one or two women to tribe, especially women of the same generation.
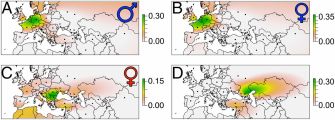
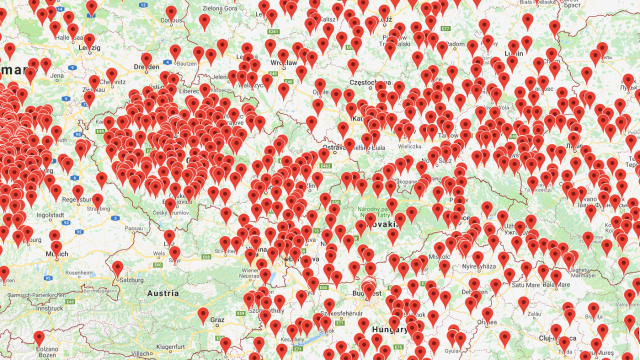
Map showing geographic distribution of genetic profiles of (A) all Bavarian males, (B) all Bavarian females with normal skulls, (C) all Bavarian females with elongated skulls
But Burger pointed out that the women with elongated skulls were spread across multiple villages, and that each village could have been a distinct political entity. He also said it’s extremely likely that so many women in the area would have had their skulls accidentally elongated.
As for the effects artificial cranial deformation has on cognitive development, osteologist Michaela Harbeck told Haaretz:
“There is a discussion going on whether the artificial cranial deformation causes cognitive deficiencies. Some studies suggest there were several pathological conditions associated with it, including bulging eyes—but this highly depends on the degree of the deformation. I would guess that our individuals, which had only medium deformed skulls, did not suffer from it.”