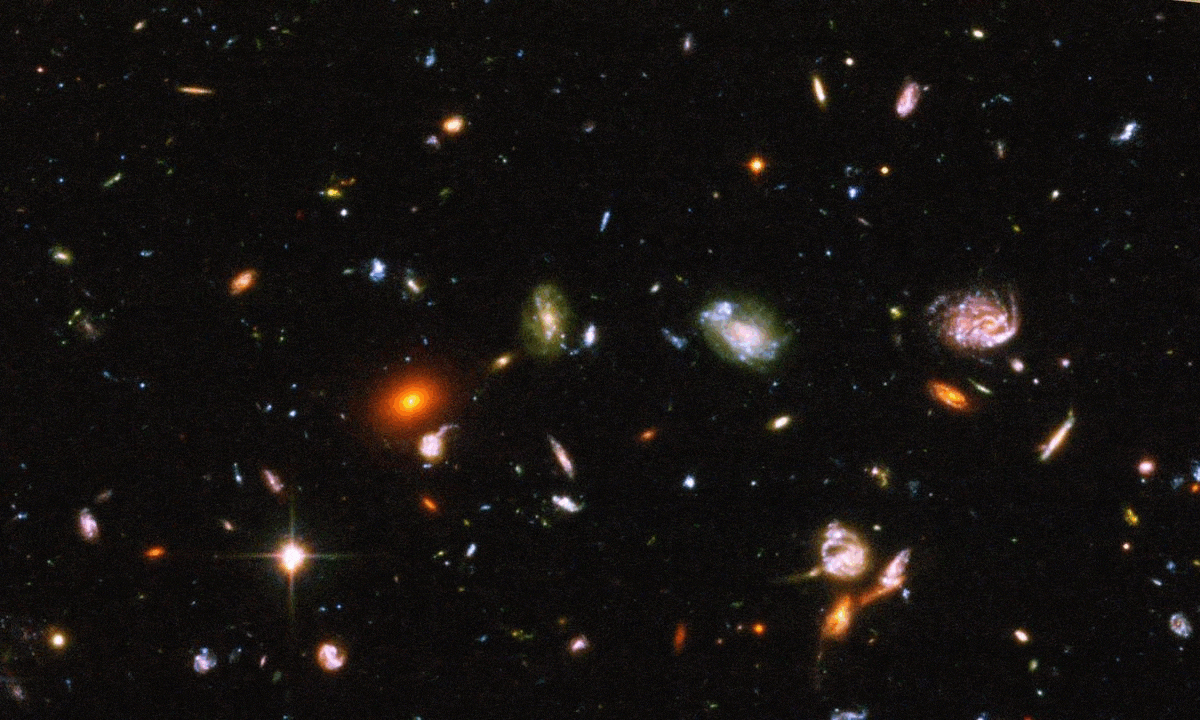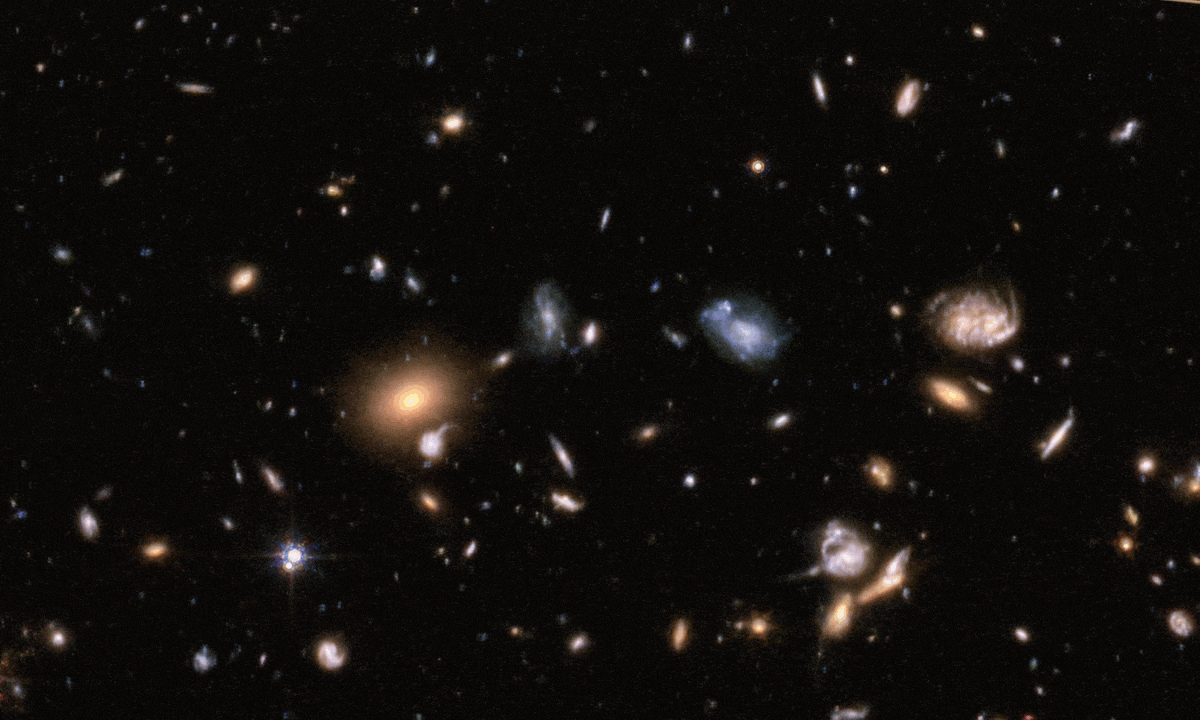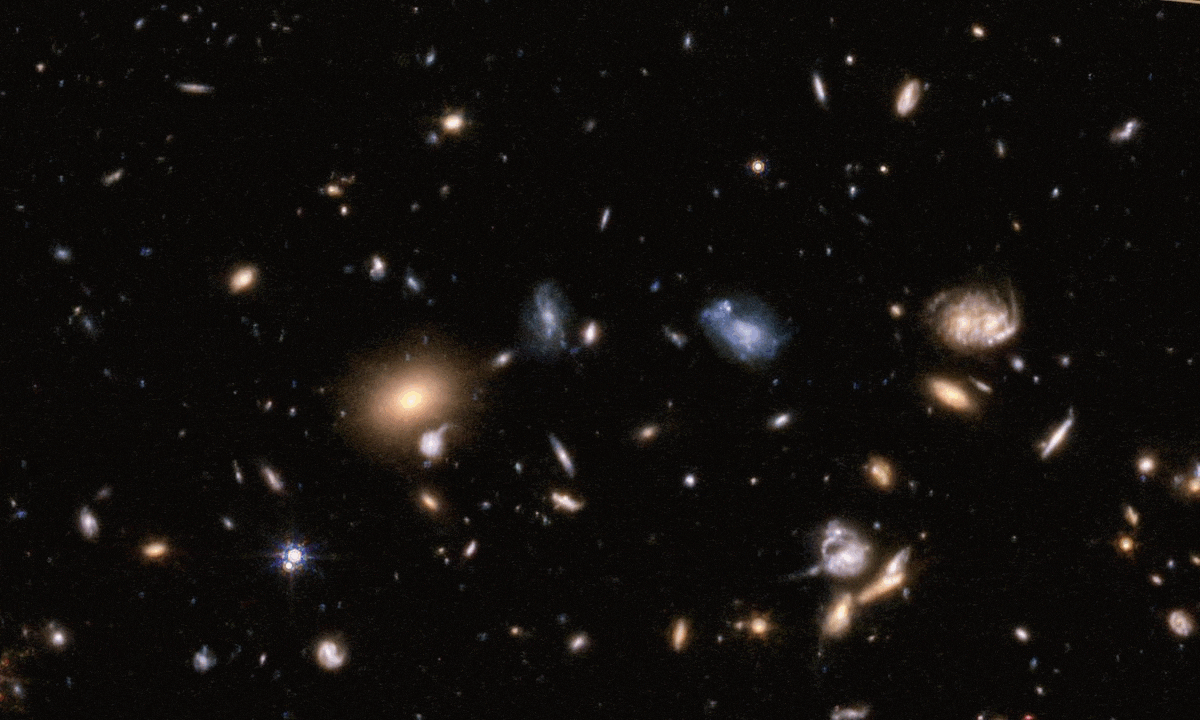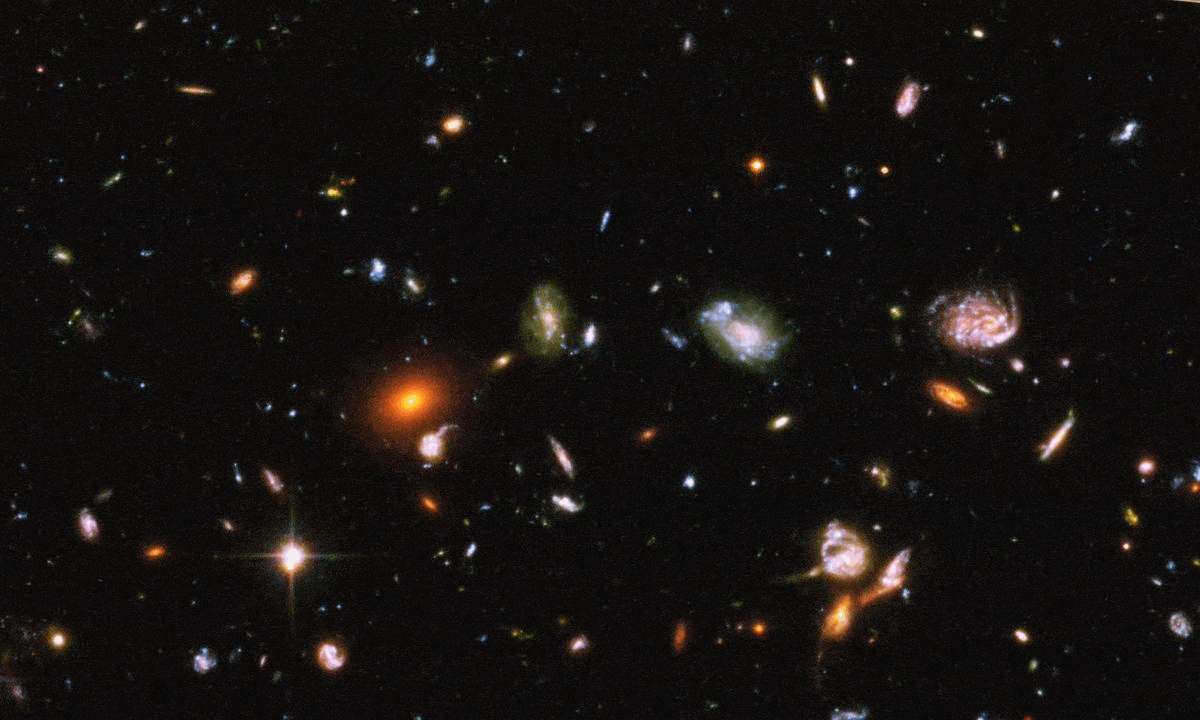The mass that gravitates and the mass that resists motion are, somehow, the same mass. But even Einstein didn’t know why this is so.
Scientific surprises, driven by experiment, are often how science advances. But more often than not, they’re just bad science.
The “little red dots” were touted as being too massive, too early, for cosmology to explain. With new knowledge, everything adds up.
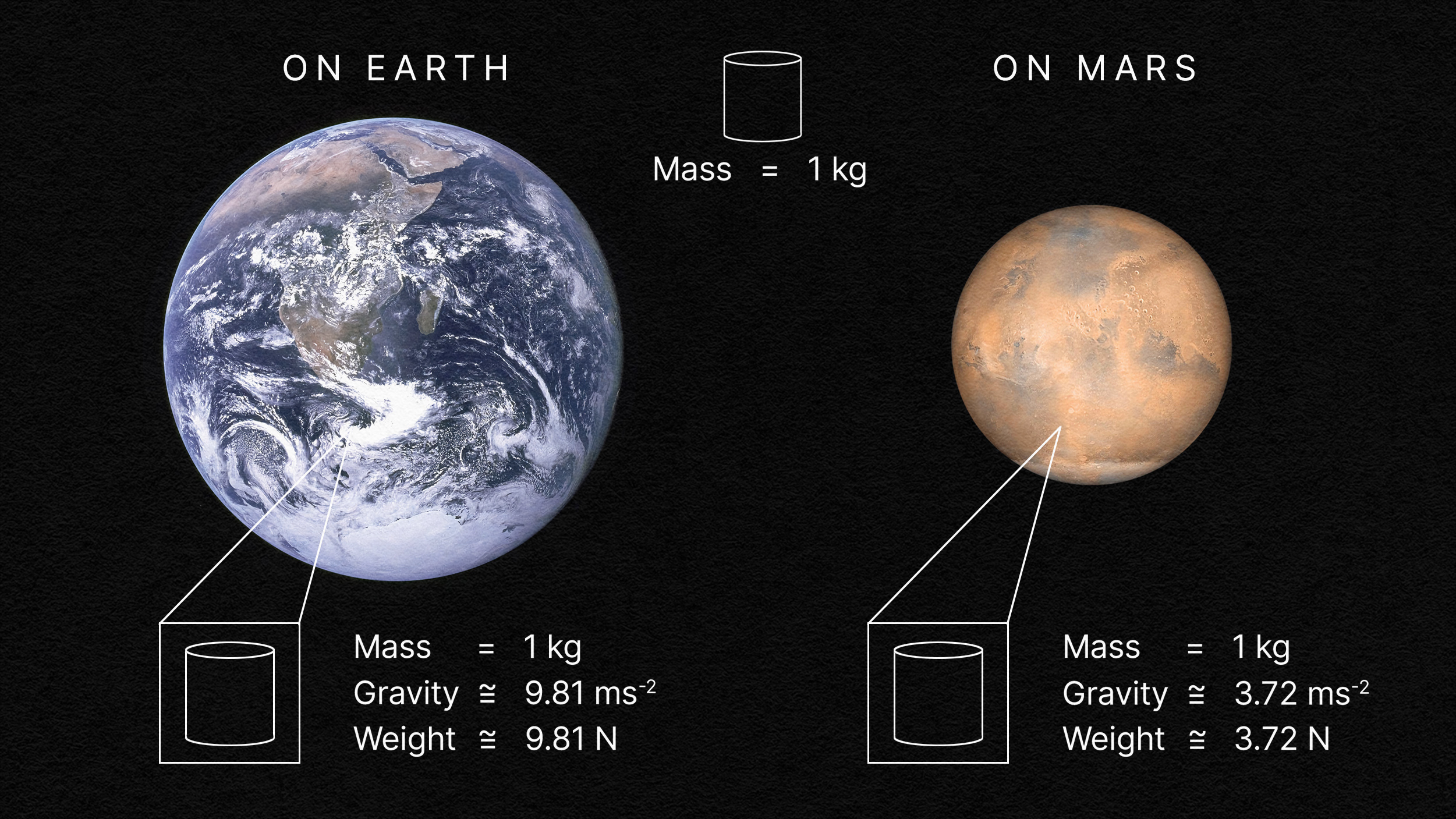
Here on Earth, we commonly use terms like weight (in pounds) and mass (in kilograms) as though they’re interchangeable. They’re not.
So far, Earth is the only planet that we’re certain possesses active life processes. Here’s what we shouldn’t assume about life elsewhere.
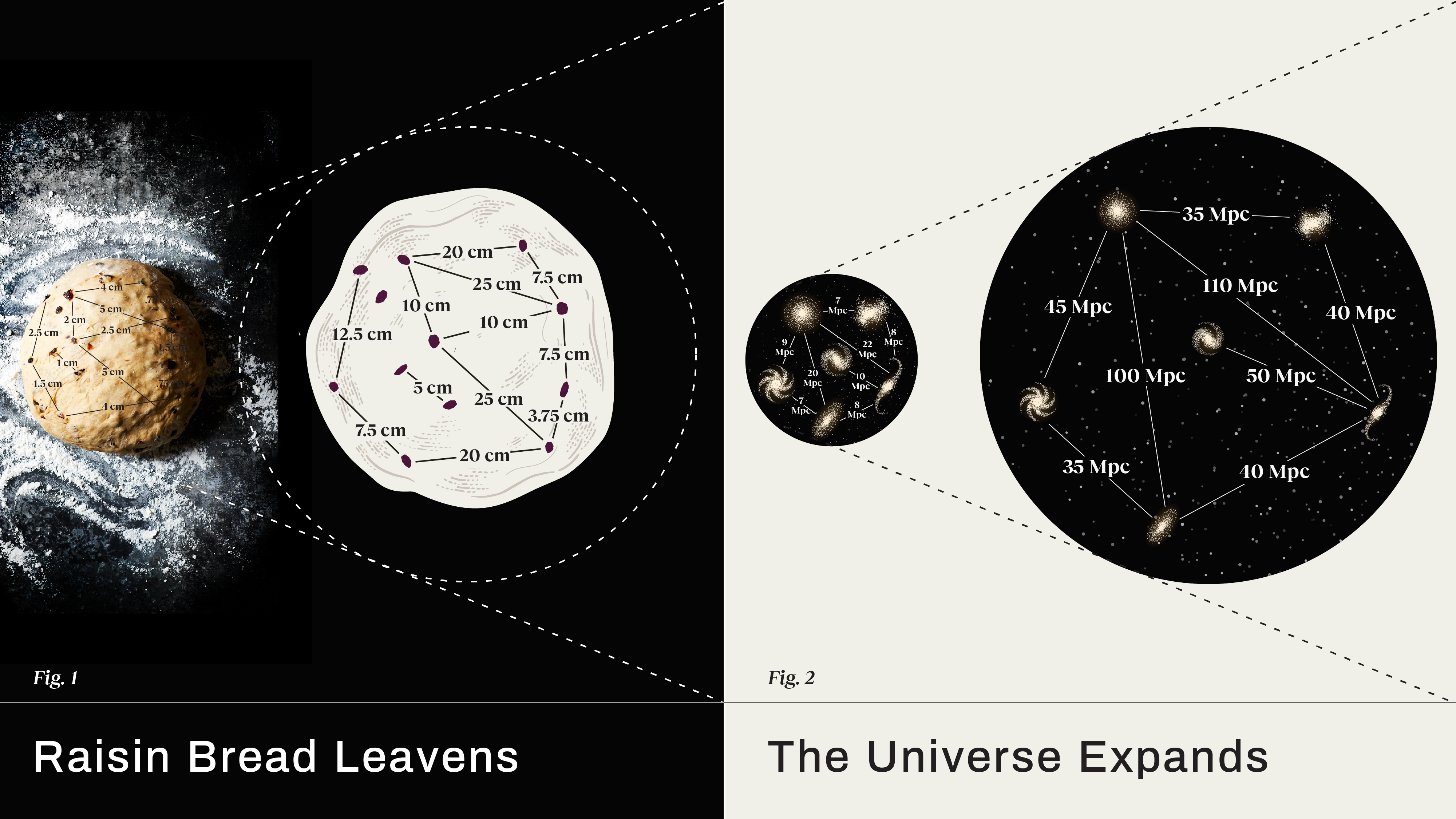
The Universe isn’t just expansion, but the expansion itself is accelerating. So why can’t we feel it in any measurable way?
No matter how good our measurement devices get, certain quantum properties always possess an inherent uncertainty. Can we figure out why?
Life arose on Earth early on, eventually giving rise to us: intelligent and technologically advanced. “First contact” still remains elusive.
If you think of the Big Bang as an explosion, we can trace it back to a single point-of-origin. But what if it happened everywhere at once?
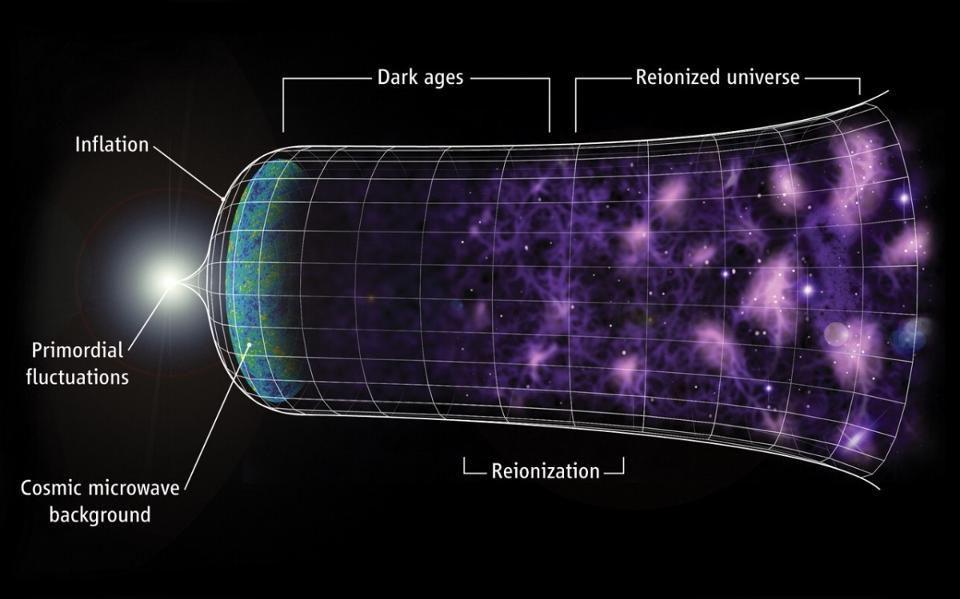
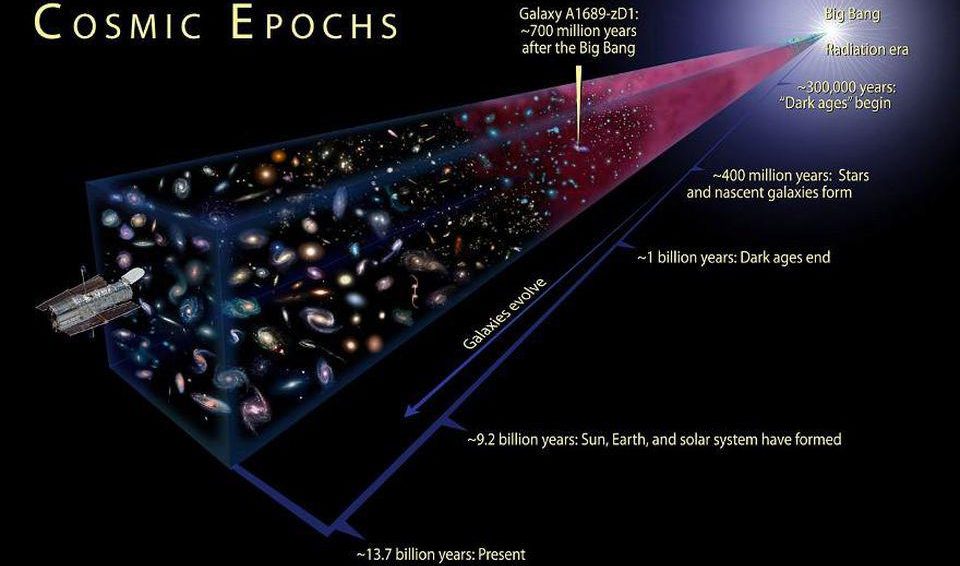
The Universe is 13.8 billion years old, going back to the hot Big Bang. But was that truly the beginning, and is that truly its age?
Many contrarians dispute that cosmic inflation occurred. The evidence says otherwise.
In all the Universe, only a few particles are eternally stable. The photon, the quantum of light, has an infinite lifetime. Or does it?
The big question isn’t whether the Universe is expanding at 67 or 73 km/s/Mpc. It’s why different methods yield such different answers.
The original principle of relativity, proposed by Galileo way back in the early 1600s, remains true in its unchanged form even today.
Most stars in the Universe are located in big, massive, Milky Way-like galaxies. But most galaxies aren’t like ours at all.
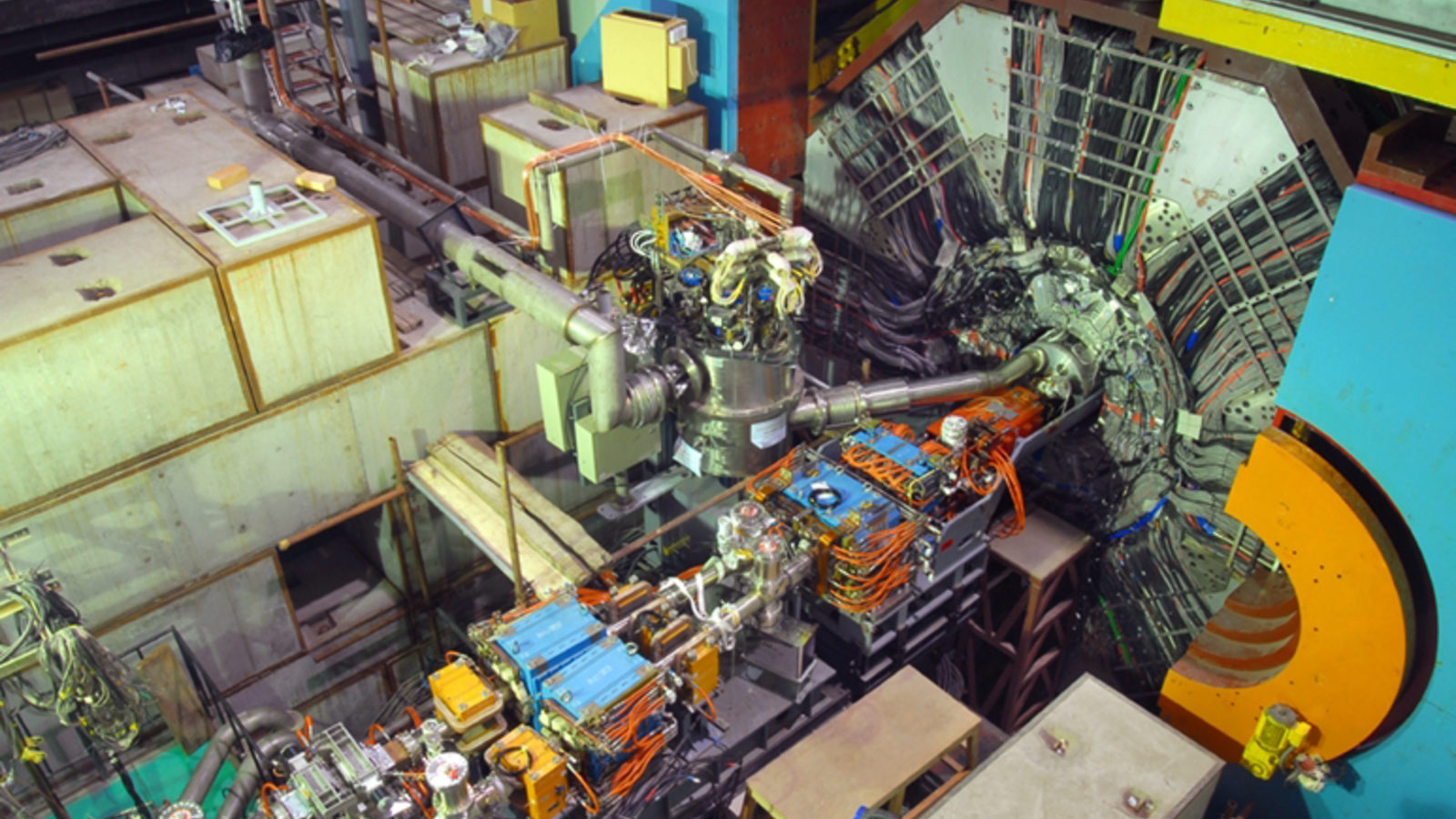
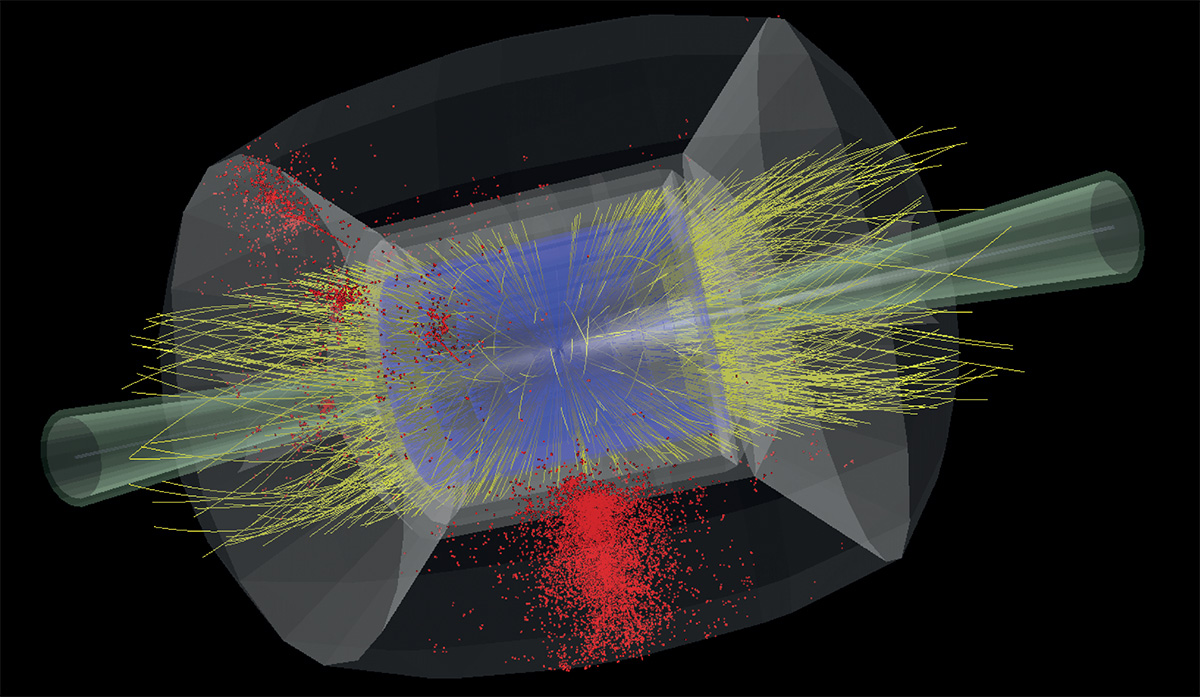
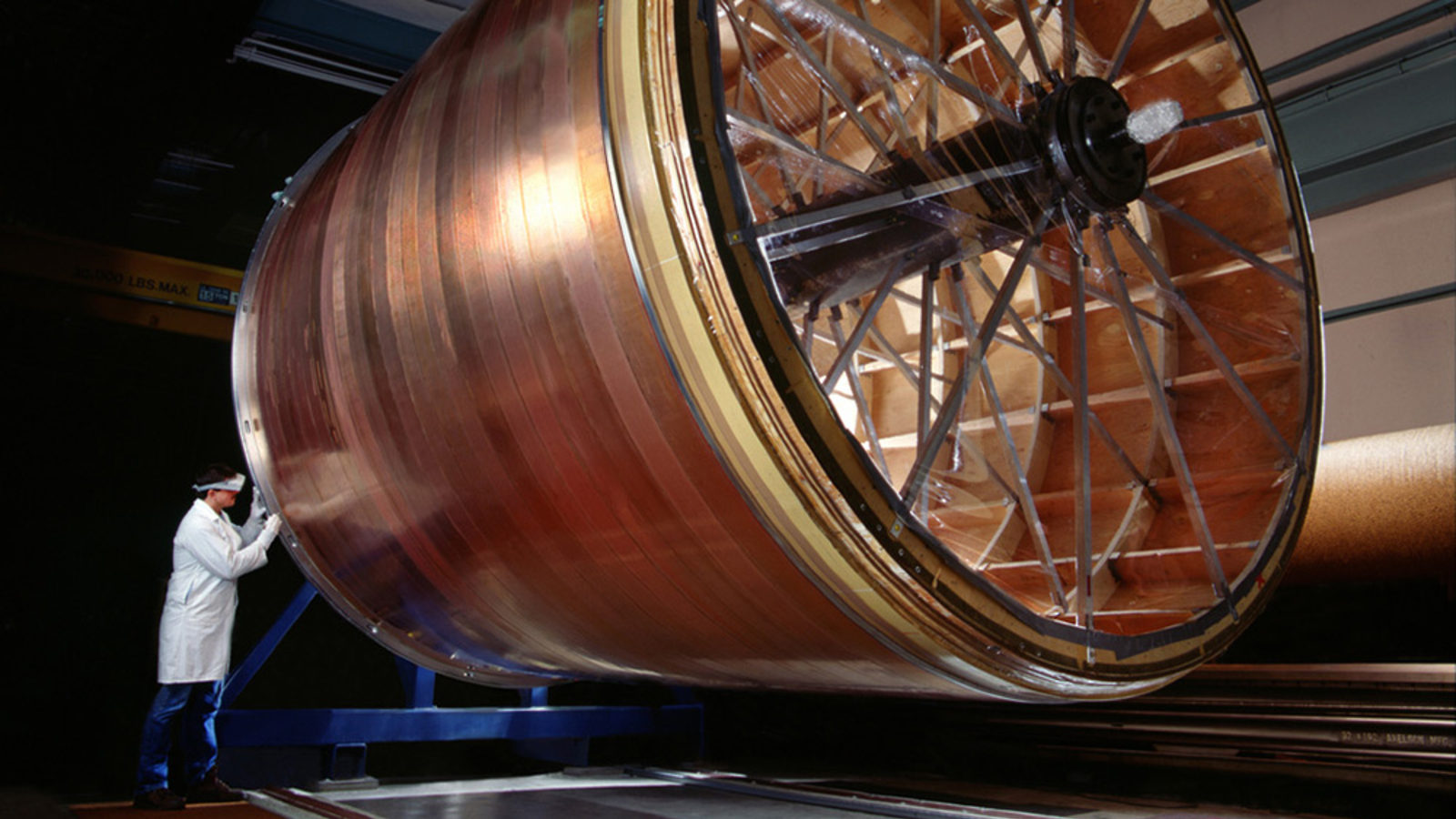
The largest particle accelerator and collider ever built is the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. Why not go much, much bigger?
More than any other equation in physics, E = mc² is recognizable and profound. But what do we actually learn about reality from it?
The Michelson-Morley experiment of 1887, despite expectations, revealed a null result: no effect. The implications were revolutionary.
For centuries, Newton’s inverse square law of gravity worked beautifully, but no one knew why. Here’s how Einstein finally explained it.
From size to mass to density and more, each world in our Solar System is unique. When we compare them, the results are truly shocking.
Today, the Large Hadron Collider is the most powerful particle physics experiment in history. What would a new, successor collider teach us?
Dark matter’s hallmark is that it gravitates, but shows no sign of interacting under any other force. Does that mean we’ll never detect it?
Peaking on the night of August 11/12, up to 100 bright meteors per hour will be visible. Here’s how to make the most of it.
Earth, the only rocky planet with a large, massive satellite, is greatly affected by the Moon. Destroying it would cause 7 major changes.
Straddling the bounds of science and religion, Newton wondered who set the planets in motion. Astrophysics reveals the answer.
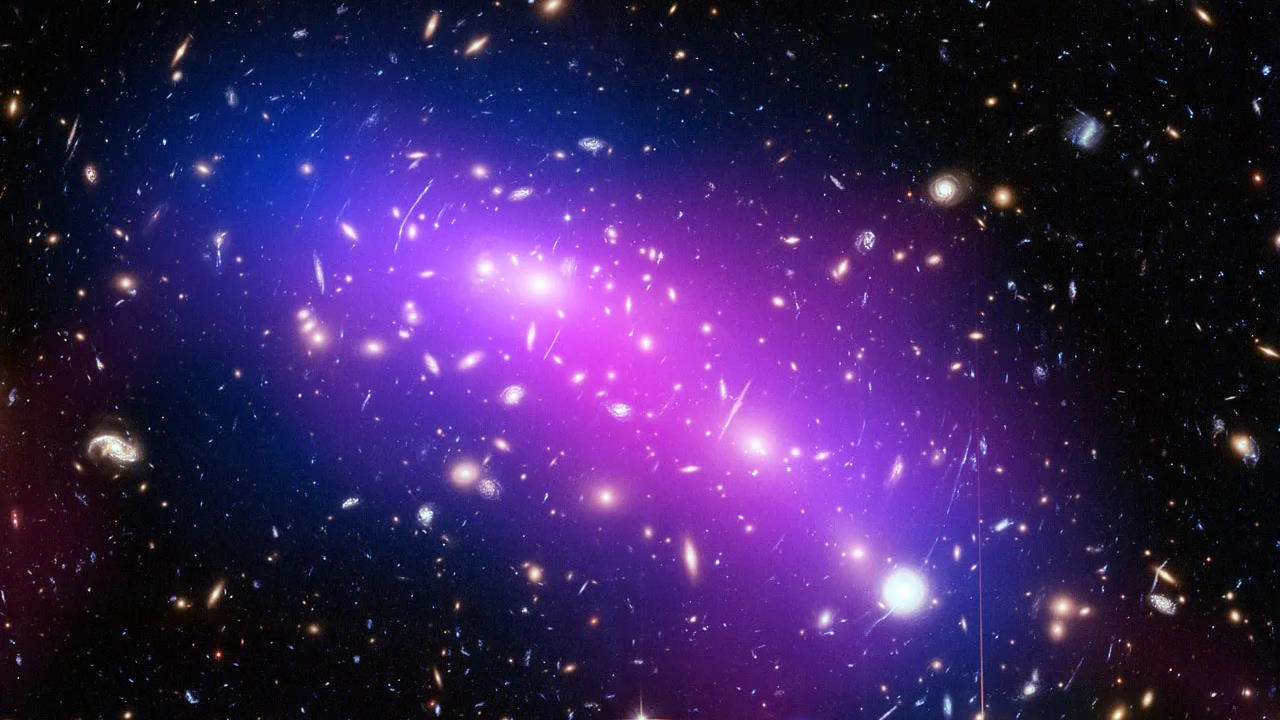
How do normal matter and dark matter separate by so much when galaxy clusters collide? Astronomers find the surprising, unexpected answer.
Even in the very early Universe, there were heavy, supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies. How did they get so big so fast?
Often viewed as a purely theoretical, calculational tool only, direct observation of the Lamb Shift proved their very real existence.
In July of 2022, the first science images from JWST were unveiled. Two years later, it’s changed our view of the Universe.
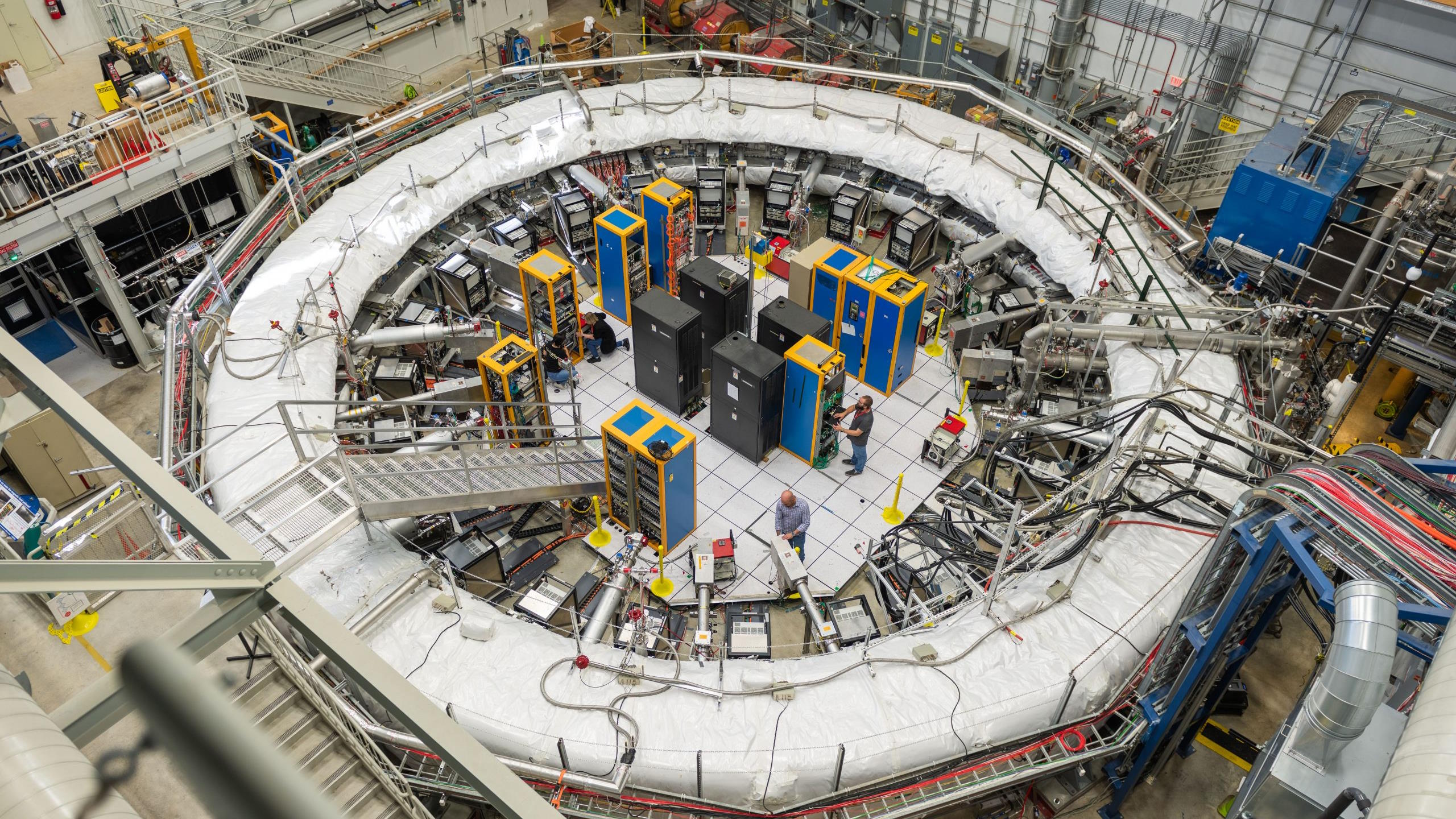
A longstanding mismatch between theory and experiment motivated an exquisite muon measurement. At last, a theoretical solution has arrived.