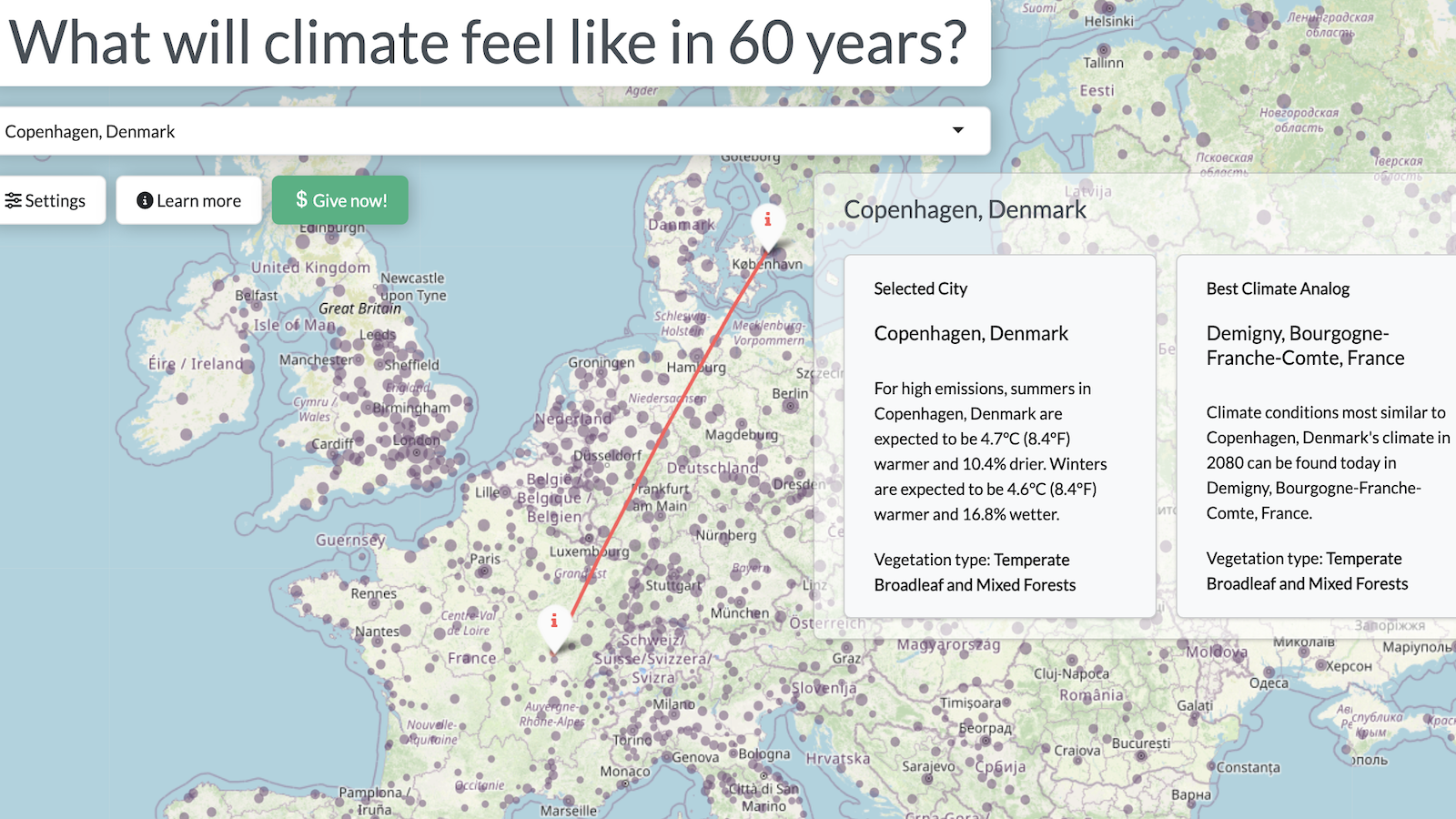
Scientists Calculate When Earth Will No Longer Be Able to Support Life
What’s the Latest Development?
According to new scientific calculations, planet Earth will be able to sustain life for another 1.75 billion years, after which point the surface will become too hot to support liquid water. Scientists define a star’s ability to support the existence of liquid water on orbiting planets as its habitable zone. “The inner edge of the Sun’s habitable zone is moving outwards at a rate of about 1 metre per year. The latest model predicts a total habitable zone lifetime for Earth of 6.3 billion–7.8 billion years, suggesting that life on the planet is already about 70% of the way through its run.”
What’s the Big Idea?
The calculations suggest that Earth began well-within the Sun’s habitable zone, and for this reason, our planet may be a relatively mean host to life. Planets that begin on the outer edges of a star’s habitable zone may be able to host life for 42 billion years or longer. As usual, astronomers’ eyes turn toward Mars. Just as the sun brightens and the Earth becomes too hot for life, Mars will be entering the habitable zone. Study co-author Mark Claire, an astronomer at the University of St Andrews, UK, said: “If humans are going to be around in a billion years, I would certainly imagine that they would be living on Mars.”
Photo credit: Shutterstock.com