Surprising Science
All Stories
Looking into a sliver of sky known as the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, astronomers have found light from galaxies born just after the big bang, telling scientists more about the early universe.
This month, proceeds from the purchase of any of three branded items displayed within the popular social game FarmVille 2 will go to the nonprofit organization Water.org.
Physicist Lawrence Krauss finds creation stories depressing – not because they’re implausible, but because they extinguish curiosity and limit human agency.
As neuroscience, cognitive science, computer programming, and artificial intelligence progress, we’re understanding better and better how we learn.
While guns don’t kill people, they certainly do make killing easier.
Oliver Sacks, professor of neuroscience at NYU, challenges fellow neuroscientists who have capitalized on near-death and out-of-body experiences to justify their belief in God and heaven.
Researchers at Northwestern University are testing a new chemical formula that relieves the symptoms of depression within hours. The drug works similarly to Ketamine, the animal sedative.
Children begin to show empathy and charity before they understand what those words mean, says pediatrician Perri Klass. And, she says, parents can help cultivate these prosocial attitudes.
In the developed world, the fight against infectious disease has largely been won. Anti-aging advocates say medical research should now concentrate on slowing the process of aging.
The field of tissue engineering is close to some big advances after helping to create human tissues that can be stored like data on computer chips and tested to create novel drugs.
An increasingly coveted cancer treatment has Mary Mulcahy, MD, Northwestern University, asking when the harms of tough medicines outweigh the benefits they can realistically deliver.
The most comprehensive report ever on global health concludes that, for the first time, our access to food as a species is more unhealthy than the shortages that have plagued us.
The ability of exercise to improve how our body clocks run may be especially effective in the afternoon, say researchers at UCLA’s Brain Research Institute who studied how exercise affects mice.
The condom has remained essentially unchanged since the 1920s but now researchers at the University of Michigan are proposing a high-tech polymer as the next-generation contraceptive.
Now that more kids have cellphones at younger ages, teachers and administrators are looking for ways in which they can be used to benefit everyone
Scientists have succeeded in shaping a solar cell into a fiber that’s flexible enough to be woven into a fabric that can be used to power an electronic device.
Like X-rays, terahertz frequencies see through items, but most machines that use them are large and costly. Two engineers have found a way to shrink the technology onto a chip.
The iTube is a device that attaches to a smartphone and uses its camera and an accompanying app to perform a lab-quality food allergen test.
NASA’s Cassini has taken the first-ever high-resolution shot of a river and its tributaries on a planetary body that’s not Earth.
Forget about Mars: British scientists have begun drilling through a two-mile-thick sheet of ice to reach a lake that hasn’t seen sunlight in at least 100,000 years.
The project, sponsored by 28 nations, has collected more valuable oceanographic data in the last 13 years than any other projects in the history of the science.
The team is one of the first selected to perform research during the first official cycle of the world’s largest airborne observatory.
Johns Hopkins Medicine has implanted the first pacemaker for the brain in the US. The device generates tiny electrical impulses that fire into the brain’s memory region 130 times a second.
The same set of skills, called caregiving responsiveness, that make someone a good partner can be carried over into parent-child relationships, says a new study out of England.
A European health body approved the West’s first gene therapy treatment last month. The move signals a long-awaited acceptance after accidents during the 1990s derailed the therapies’ progress.
A chemical compound found in the skin of grapes has been shown to have substantial health benefits, but how the chemical affects humans, and how much of it is helpful, is under investigation.
Recent research confirms that getting a good night’s rest is essential to doing good work during the day. Depriving yourself of sleep may even increase your risk of contracting serious illnesses.
Once thought to be useless muck, scientists now believe that the majority of our genetic information plays an important role in making proteins and helping to differentiate species.
A study of over 1,000 senior citizens found that higher levels of resilience and lower levels of depression were most associated with those who considered themselves to have “successfully aged.”
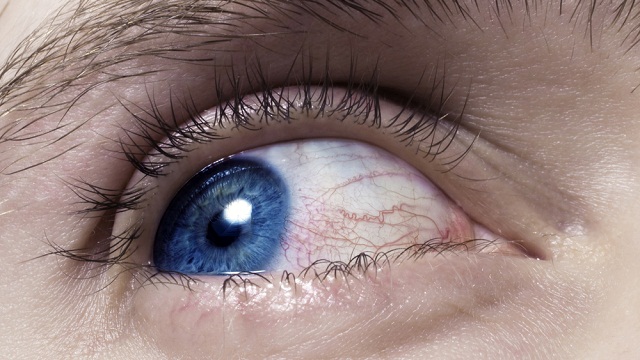
Just like fingerprints, the pattern of veins in the eyes is unique to each individual. New software takes pictures of those patterns and uses them for authentication.