medicine
The study is a solid step toward developing gene therapies against neurodevelopmental disorders.
It’s not just fun: DNA origami has the potential to revolutionize engineering at the nanoscopic scale.
There is currently no easy way to treat high Lp(a). A single shot could change that.
The first human trial of base editing delivered strong results along with some safety concerns.
People with higher immune resilience live longer, resist diseases, and are more likely to survive diseases when they do develop.
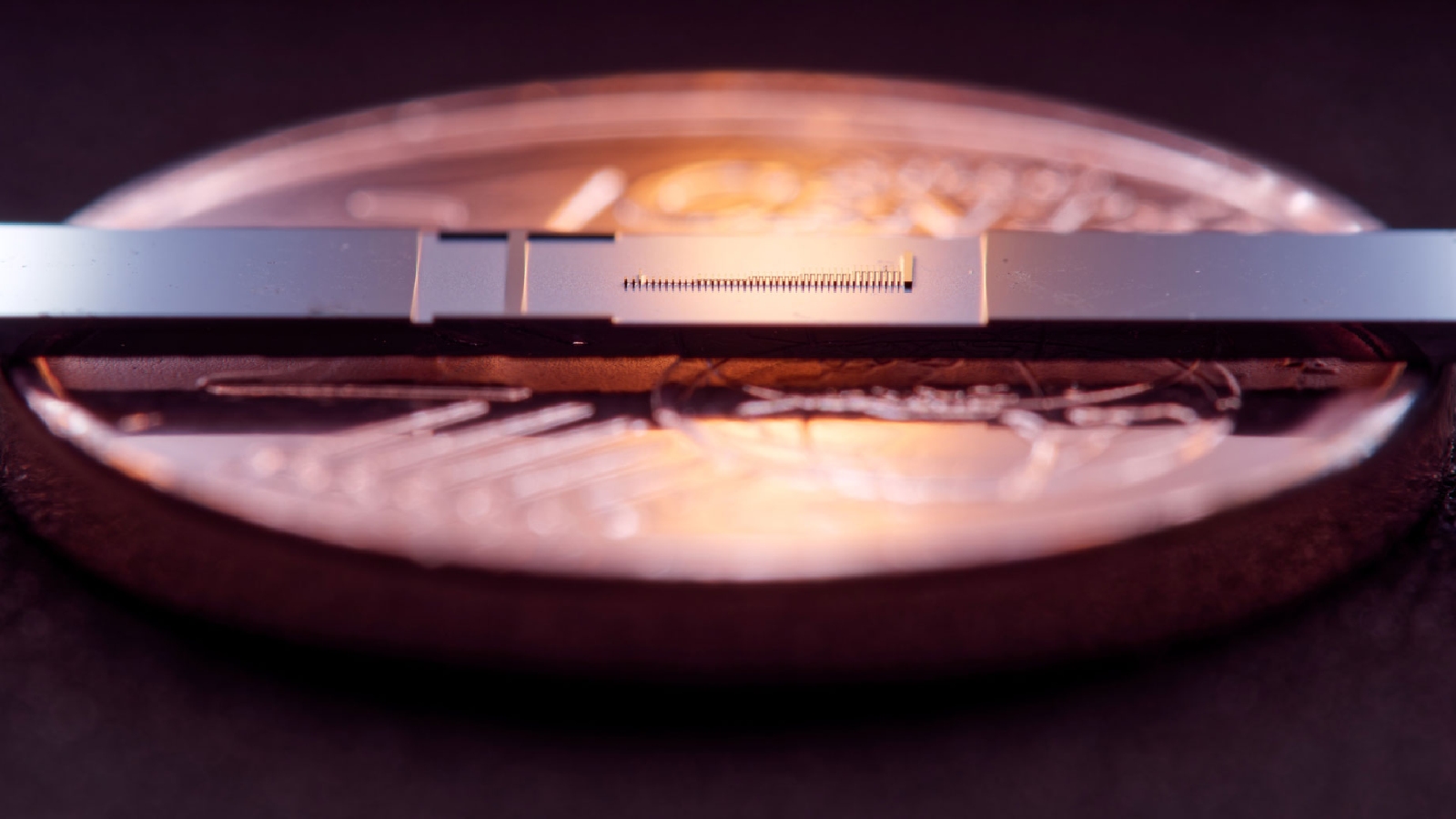
The miniaturization of particle accelerators could disrupt medical science.
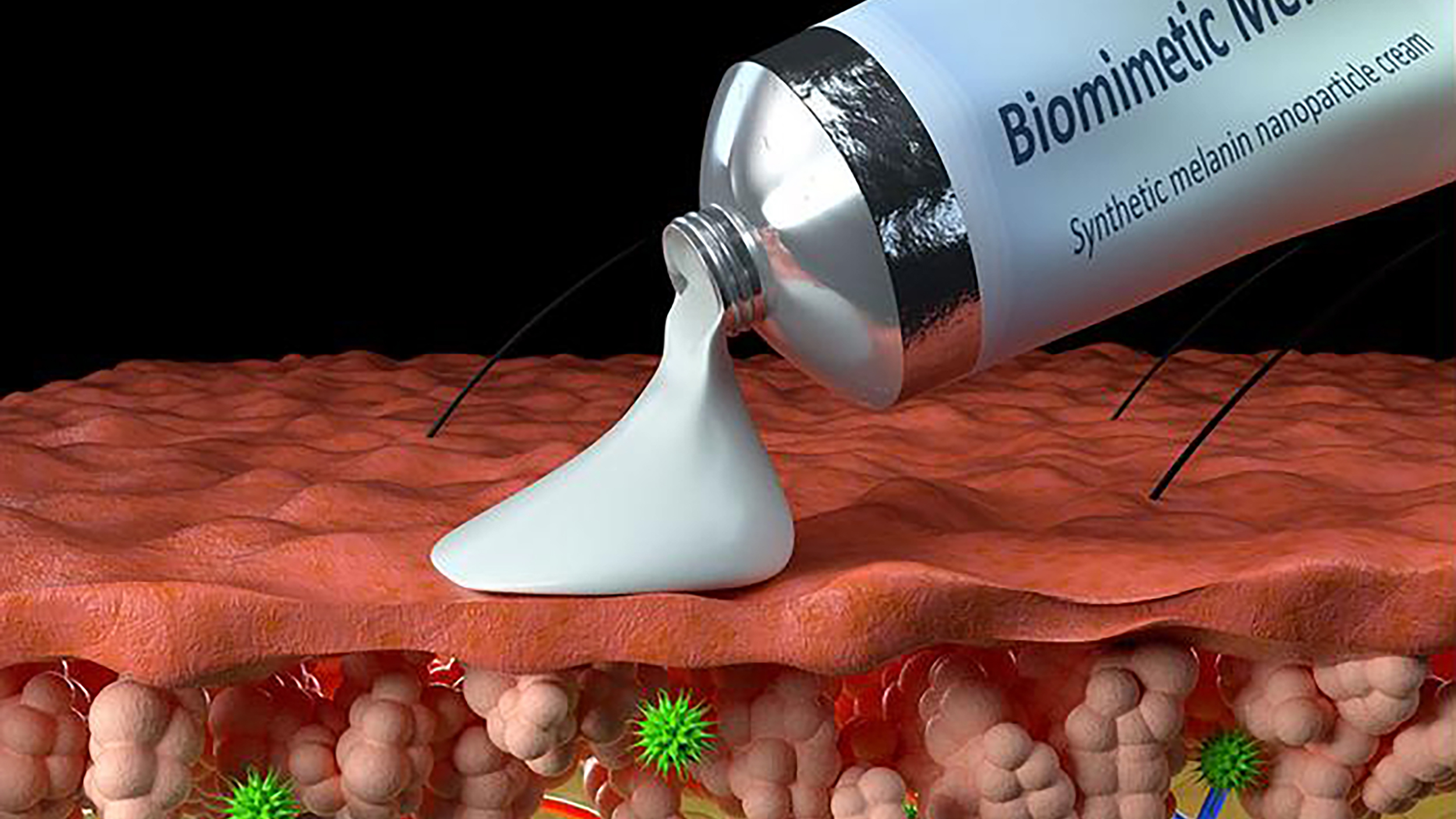
It could prevent sun damage and help chemical burns heal faster.
In hospice care and hospitals, we prioritize those with more life to live over those who are terminally ill. What is that, if not prejudice?
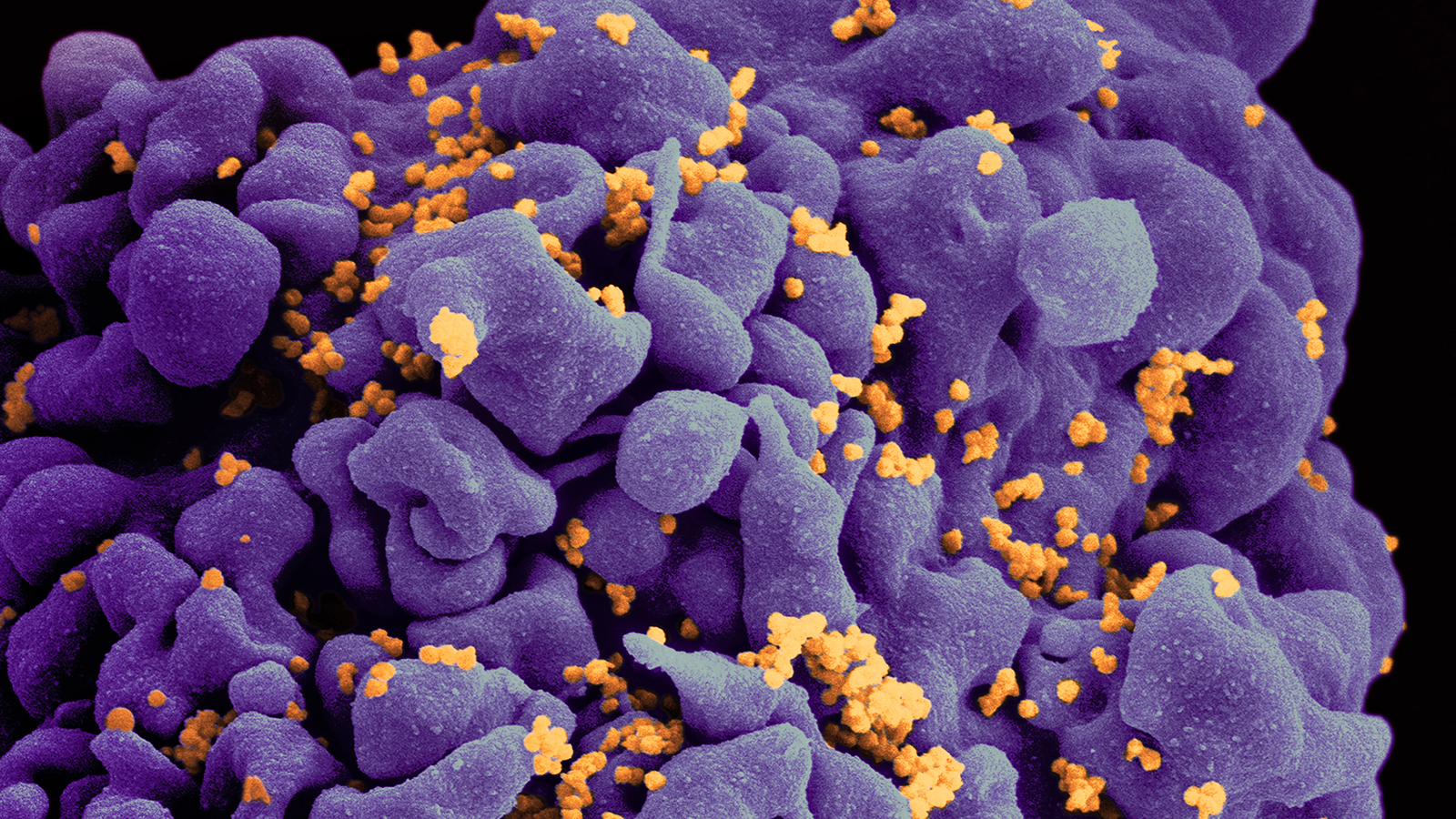
A cure may be on the horizon.
EBT-101 is not the only candidate for an HIV cure. Stem cell transplants, medications, and other CRISPR therapies are being researched.
AI was key to making Moderna’s COVID mRNA vaccine. Its role in mRNA therapeutics will rapidly grow in the coming years.
Capsaicin is already used to treat nerve pain. Early research hints it could do more.
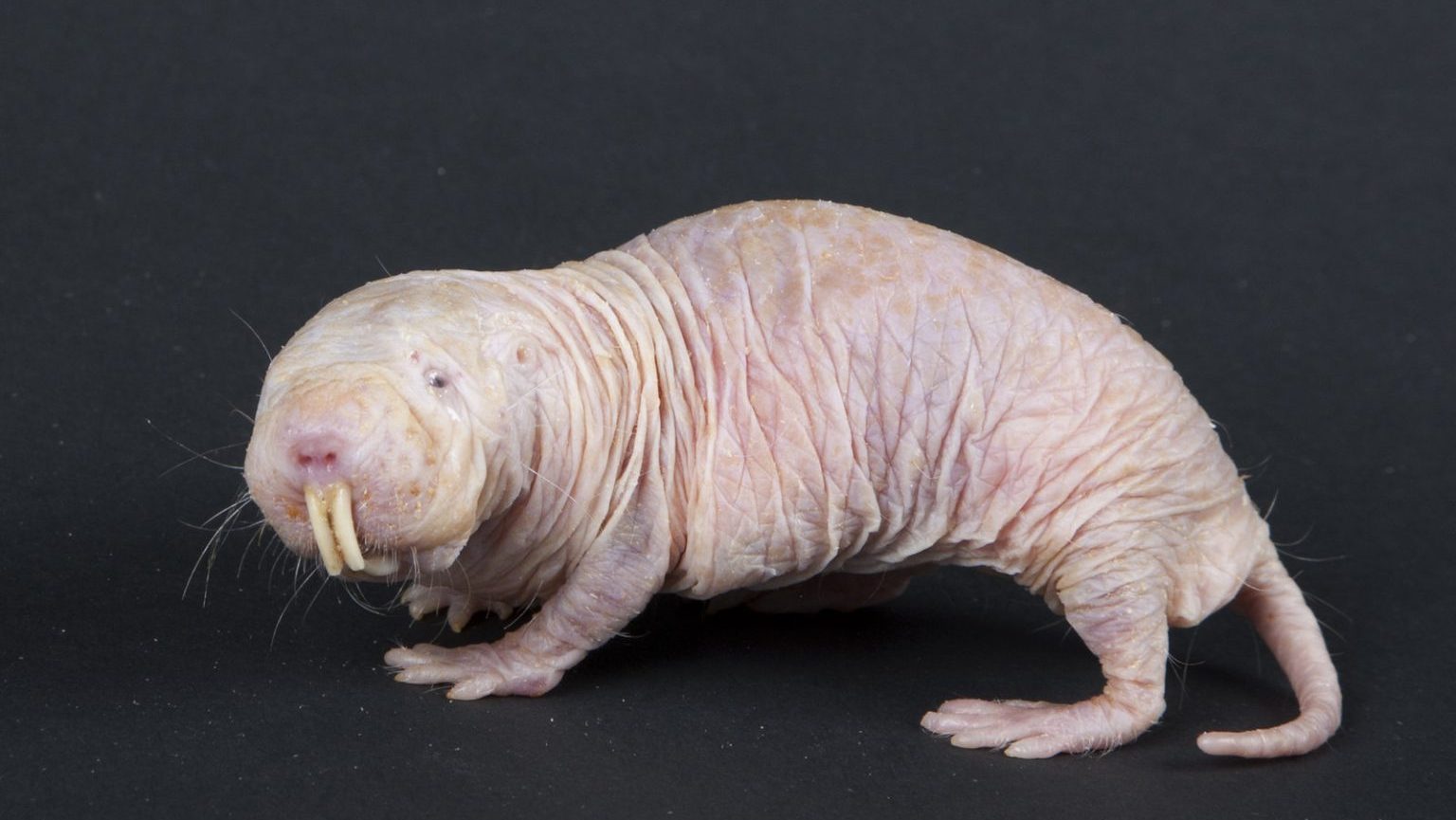
A new study provides the first proof-of-principle that genetic material transferred from one species to another can increase both longevity and healthspan in the recipient animal.
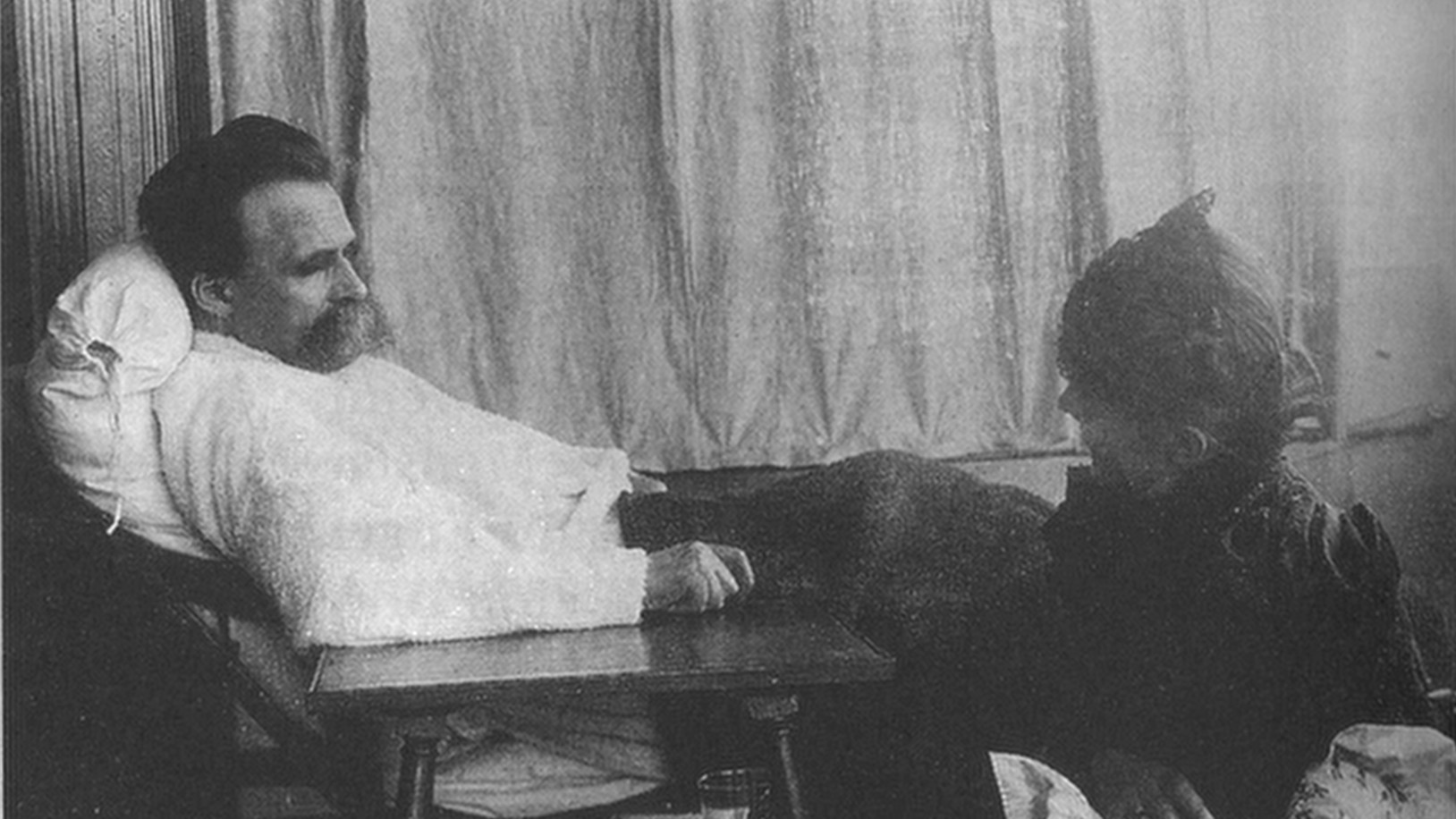
The great philosopher spent the final portion of his painful life in a vegetative state. Did illness get him there, or was it his own philosophy?
Since the 1980s, engineered monoclonal antibodies have been knocking out invading germs. Sperm may be next.
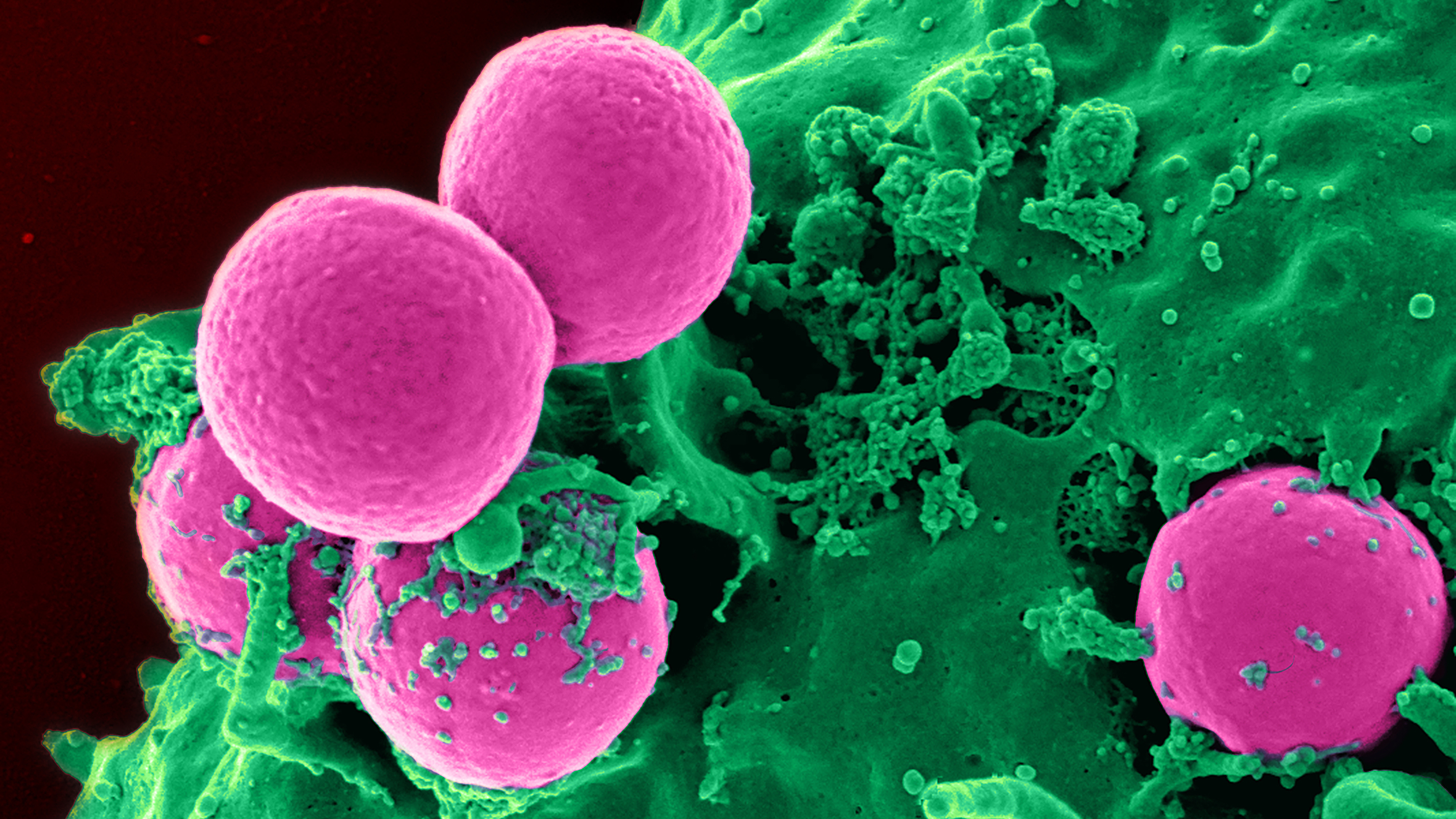
It temporarily puts the immune system on high alert to prevent MRSA, pneumonia, and other infections in the hospital.
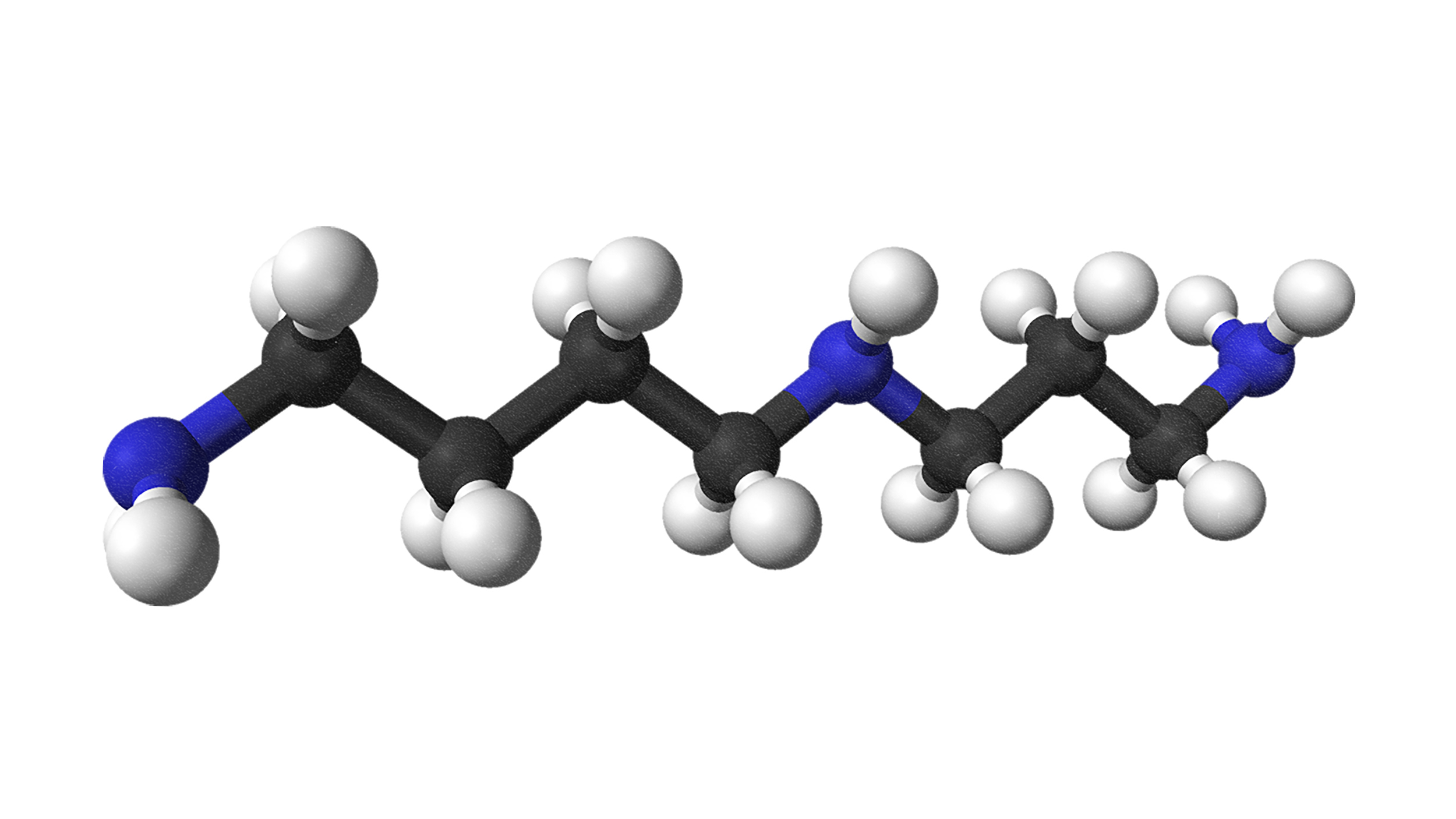
Long thought a pipe dream, scientists have discovered a drug that mimics the effects of exercise.
Inside the “out there” quest for a drug that would help doctors save lives before it’s too late.
Undeterred by years of failure, Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman proved that mRNA is the future of vaccines.
“I think it has a real chance to reverse motor symptoms, essentially replacing a missing part.”
Cancer cells hoard iron in unusually high quantities. Scientists have discovered how to leverage this to create safer cancer drugs.
CRISPR, stem cells, and even cancer drugs are helping shape an AIDS-free future.
Subtle clues emerge ahead of the attack via changes in scent.
Interventions can make the most difference when Alzheimer’s is detected early.
Today’s popular weight-loss drugs could soon be joined by brain stimulation and gene therapies.
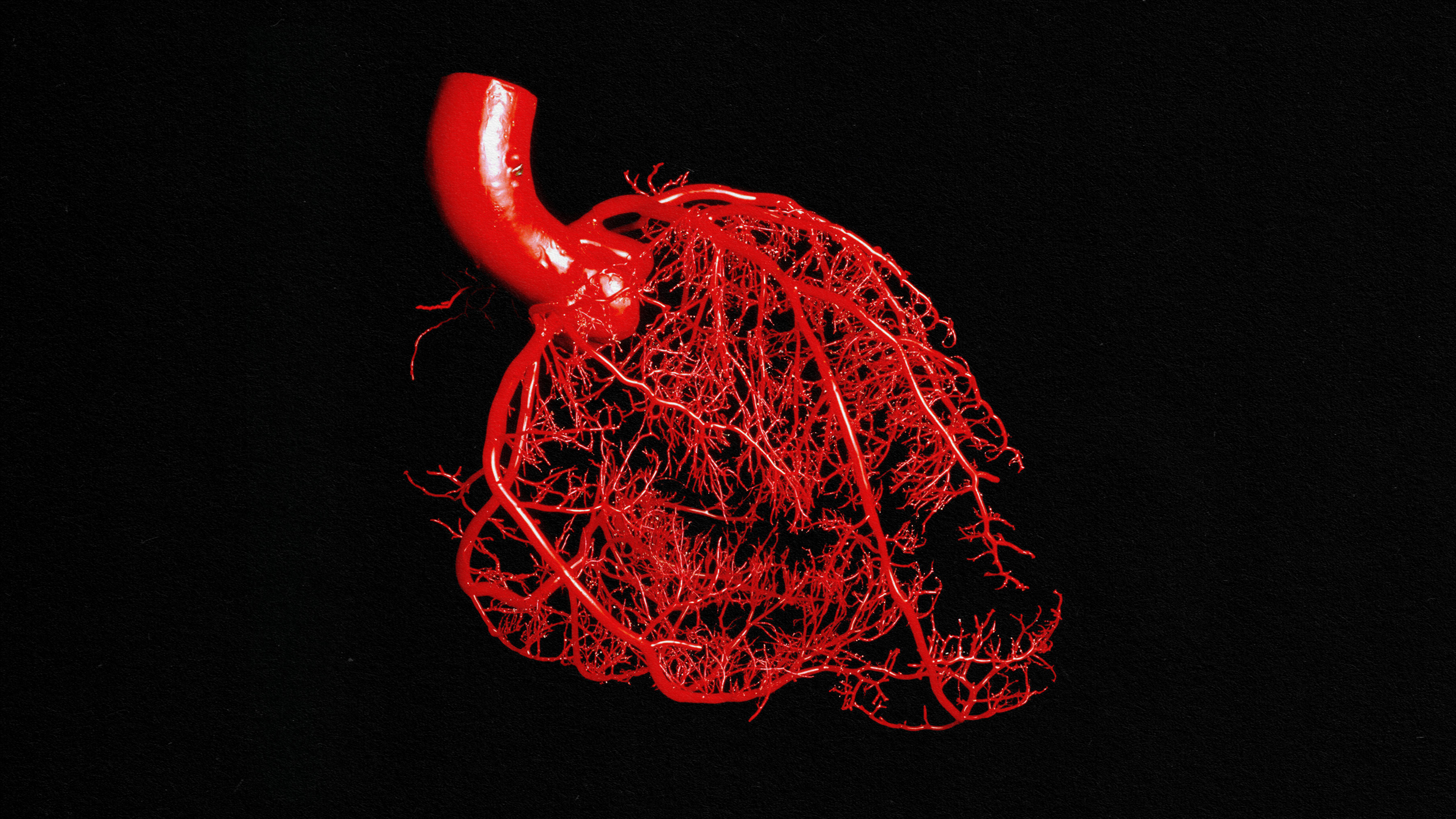
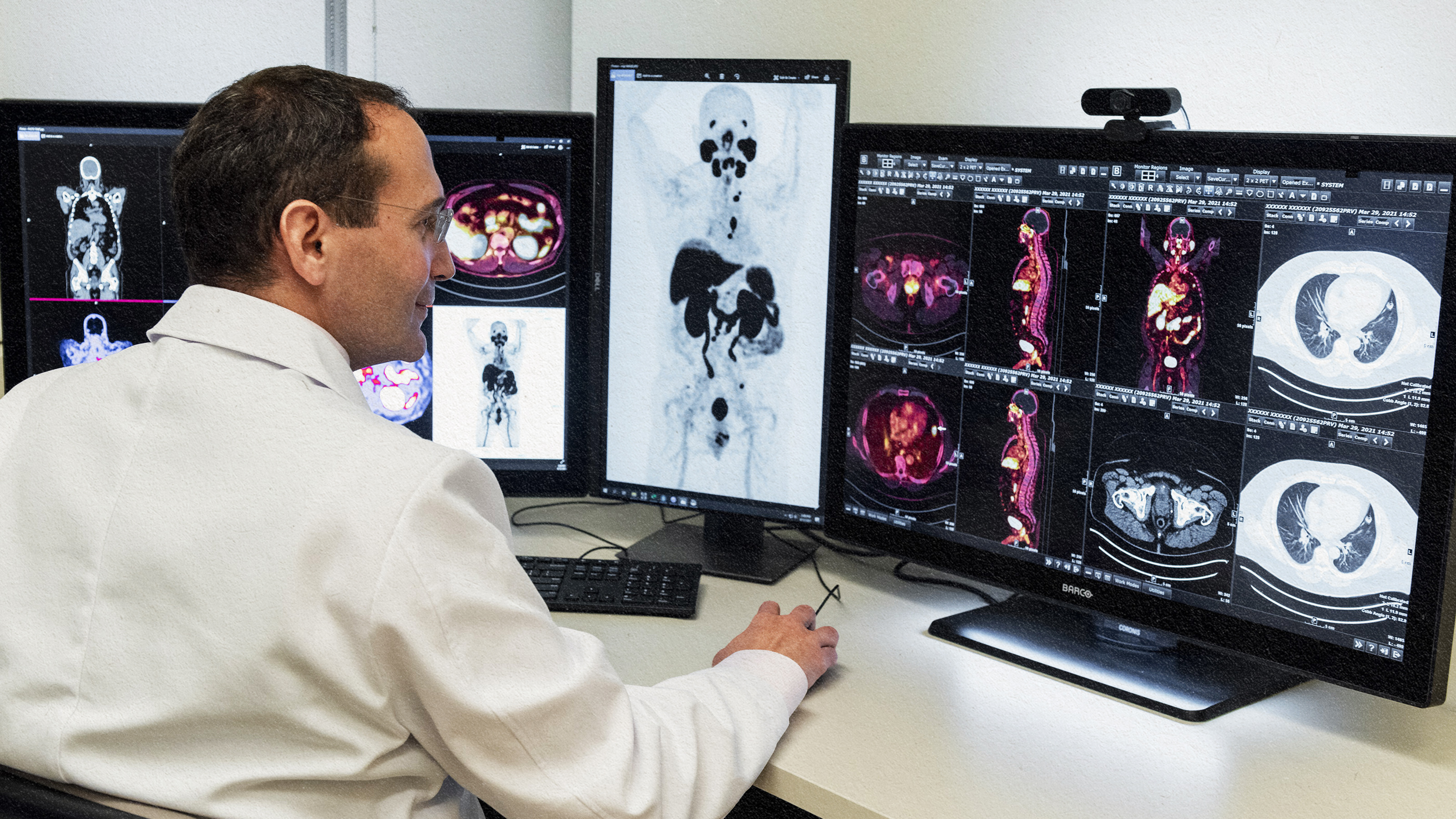
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans use positrons — the antimatter equivalent of an electron — to locate cancer in the body.
“They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.”
Ethicist and doctor Simon Whitney argues that society’s overly cautious approach to medical research is blocking breakthroughs.
Someday, scientists could use stem cells to guide the development of synthetic organs for patients awaiting transplants.