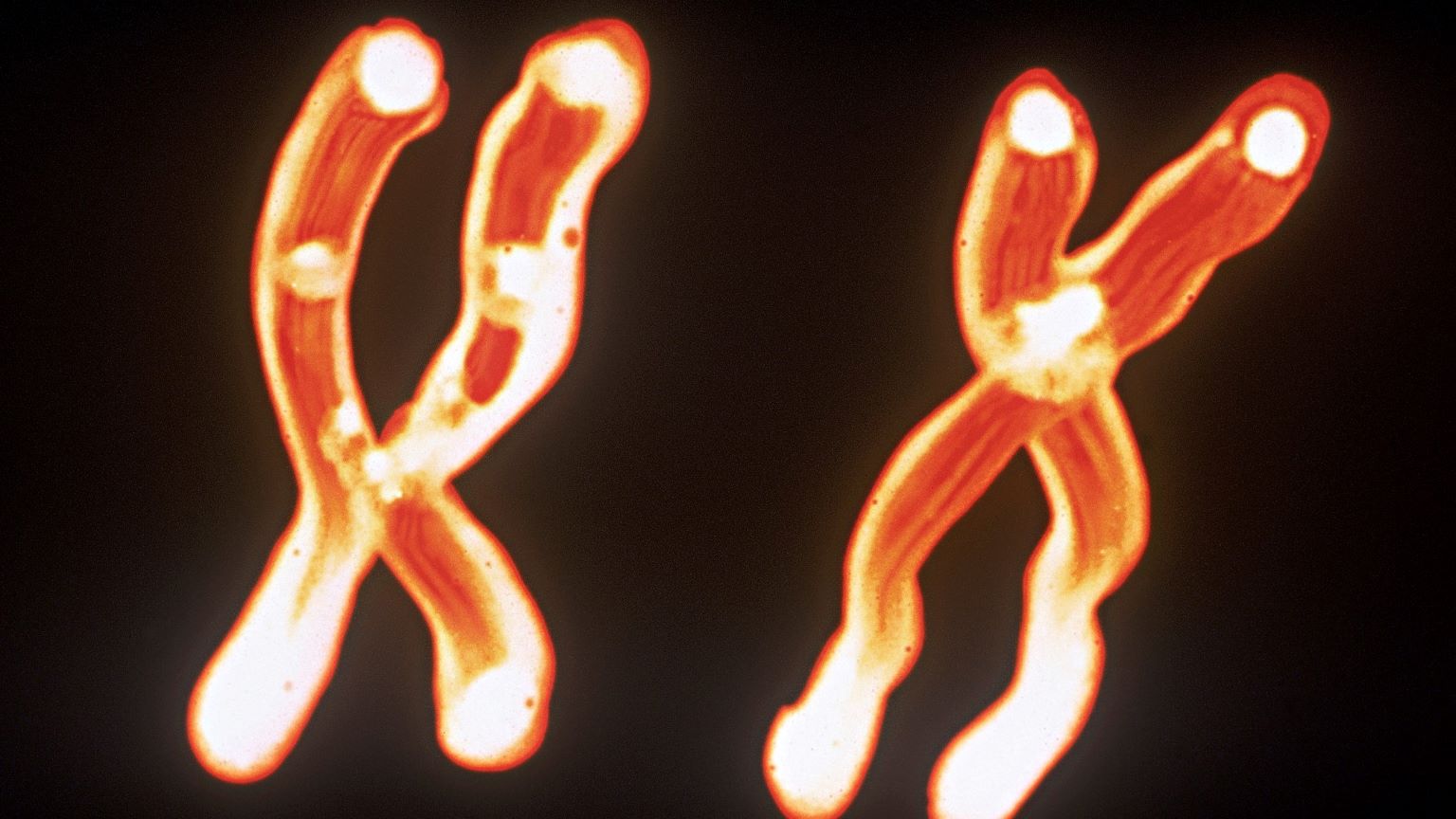medicine
Most patients with cancer die from metastasis. Stopping it would be a major advance in cancer therapy.
The world has improved in mind-blowing ways.
Many animals engage in “zoopharmacognosy” or self-medication.
One award was for a medical procedure that incapacitated thousands of people.
Fluphenazine, once used to treat schizophrenia, is capable of blocking a compound connected to chronic pain.
The new agency wants to push the boundaries of science and technology.
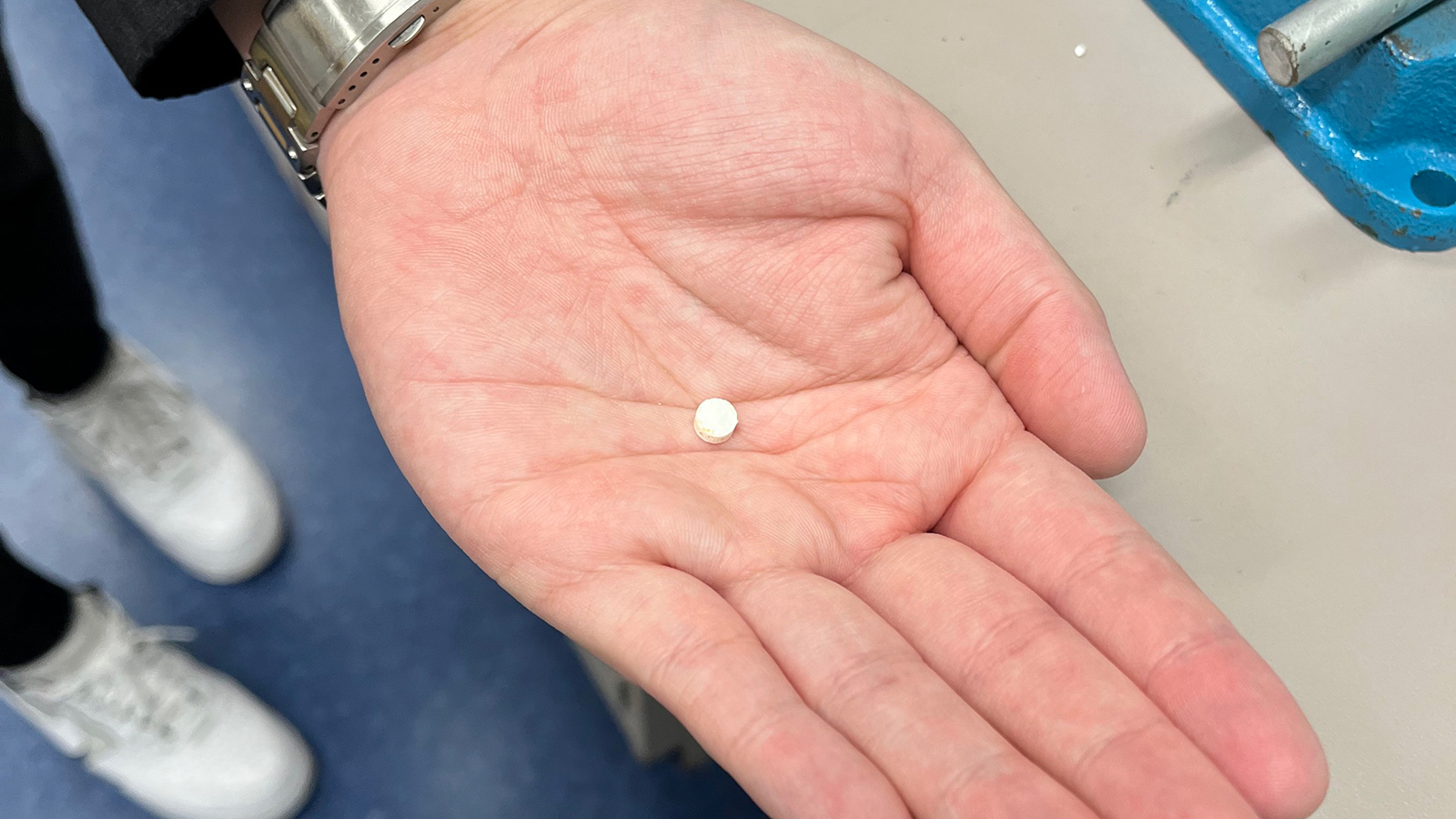
These dissolvable pills aren’t meant to be swallowed, though.
The separation of conjoined twins is fraught with stomach-churning biomedical and ethical challenges.
These salamanders are helping unlock the mysteries of brain evolution and regeneration.
The spray uses snippets of DNA to gum up virus replication.
HIV mutates rapidly, which has made the development of a vaccine an enormous challenge for decades. Finally, we might have one.
Athletes often use creatine to boost performance and aid muscle recovery. Accumulating evidence suggests it could also help with depression.
The AI test can be done every night at home while the person is asleep, without even touching their body.
We also don’t know how Tylenol works. But it does work.
By creating a type O kidney, they hope to make more organs available for transplant.
Before anesthetics, some patients would die of the pain on the operating table.
Is it deliberate fraud or just bad research?
The synthetic cartilage was made from cellulose fibers — the stuff found in wood — mixed with a goo called polyvinyl alcohol.
The antibodies elicited by the “S2 vaccine” not only neutralize COVID’s multiple strains but also coronaviruses that cause the common cold.
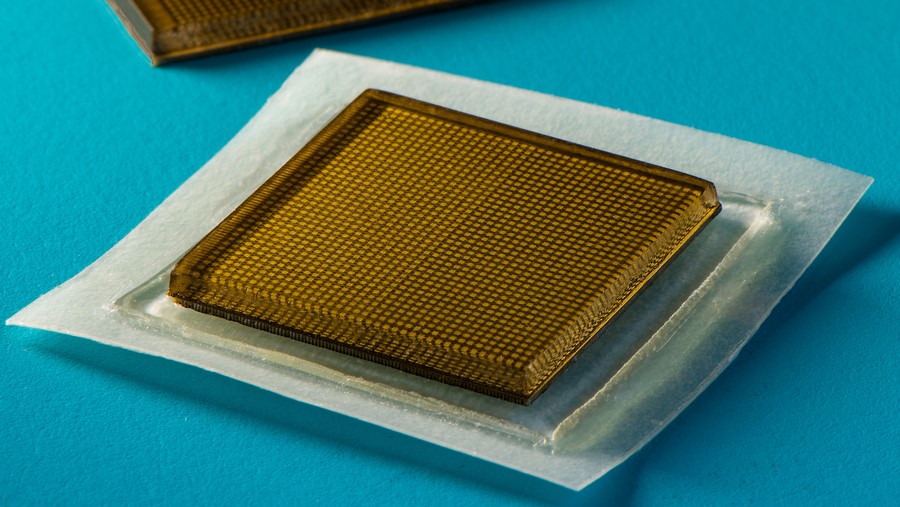
New stamp-sized ultrasound adhesives produce clear images of heart, lungs, and other internal organs.
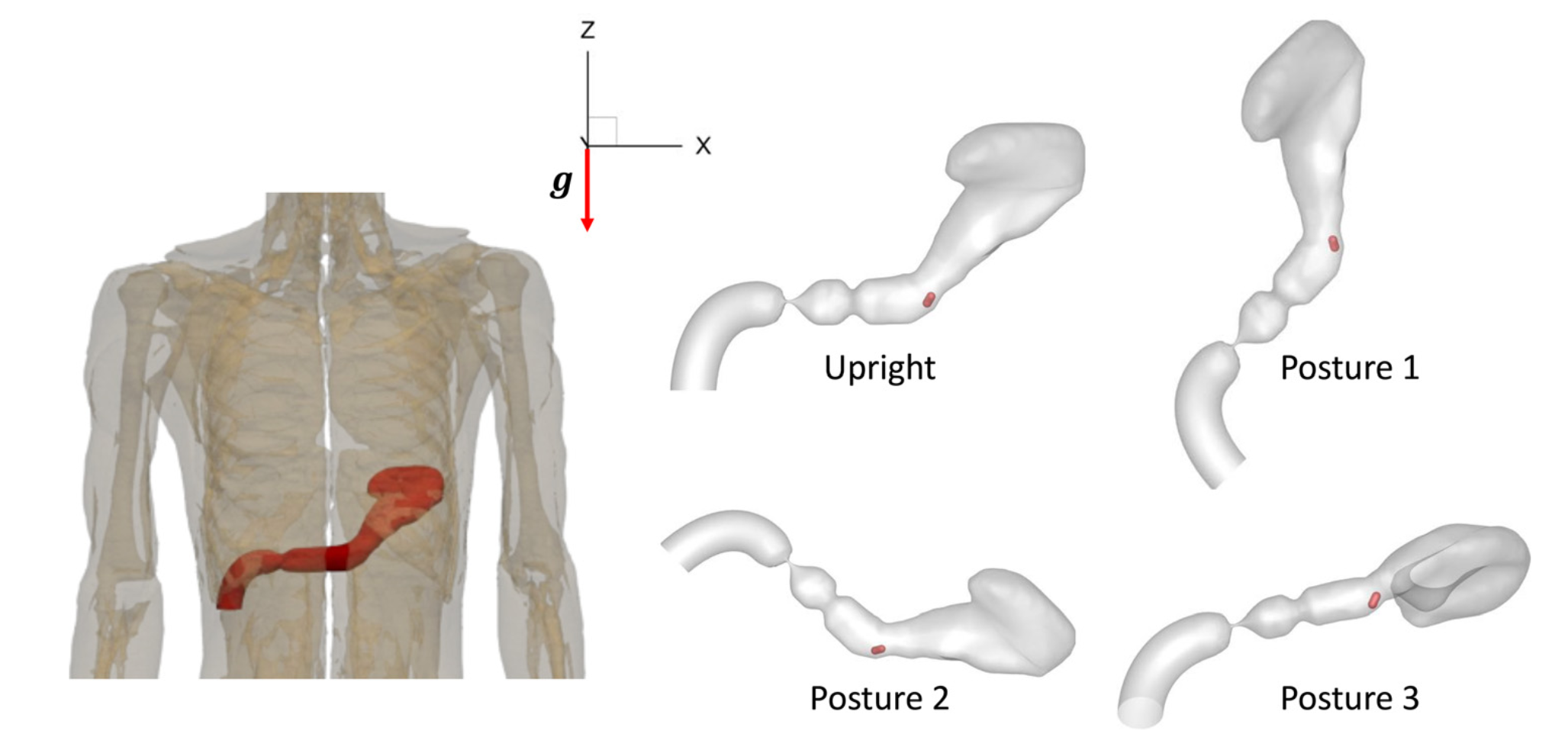
If you want a medication to kick in faster, lean right.
While one may be helpful, the other may be harmful.
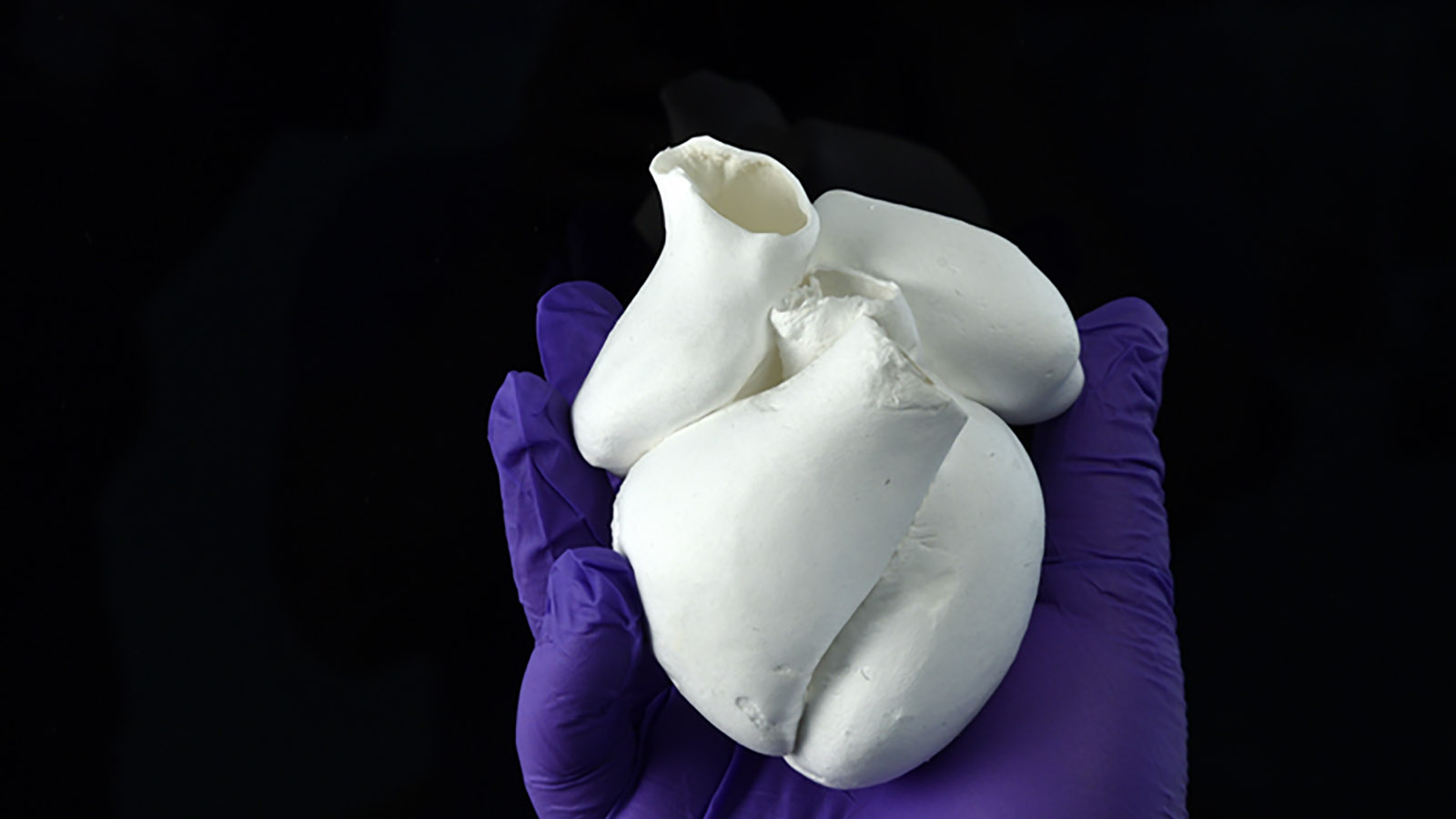
Heart muscle is shaped like a spiral, a mystery that has eluded scientists since 1669. New research has recreated the structure.
It’s simple to make, easy to use, and should work against any variant.
Scientific journals, which are supposed to be the sacred scriptures of academia, are often full of shoddy research and misinformation.
For decades people have arranged to freeze their bodies after death, dreaming of resurrection by advanced future medicine. Many met a fate far grislier than death.
It could permanently lower cholesterol — and permanently reduce your risk of having a heart attack.
While Y chromosome loss was first observed in 1963, it was not until 2014 that researchers found the link to a shorter life span.
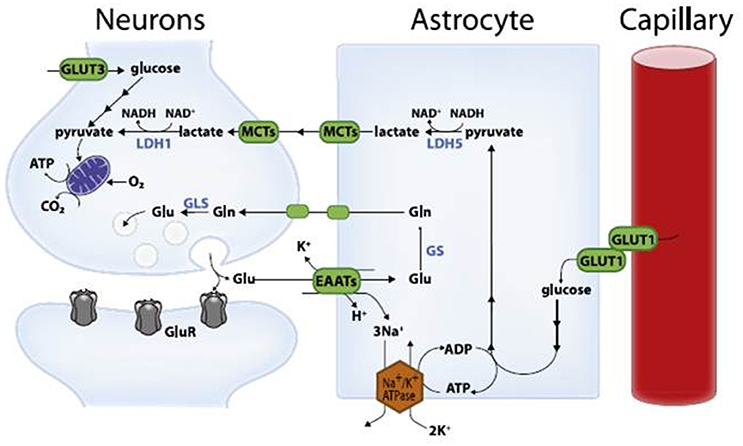
For over three decades, toxic proteins were believed to cause Alzheimer’s disease. However, recent studies suggest it might be metabolic reprogramming.
Music and sounds only seem to reduce pain in mice when played at a specific volume.