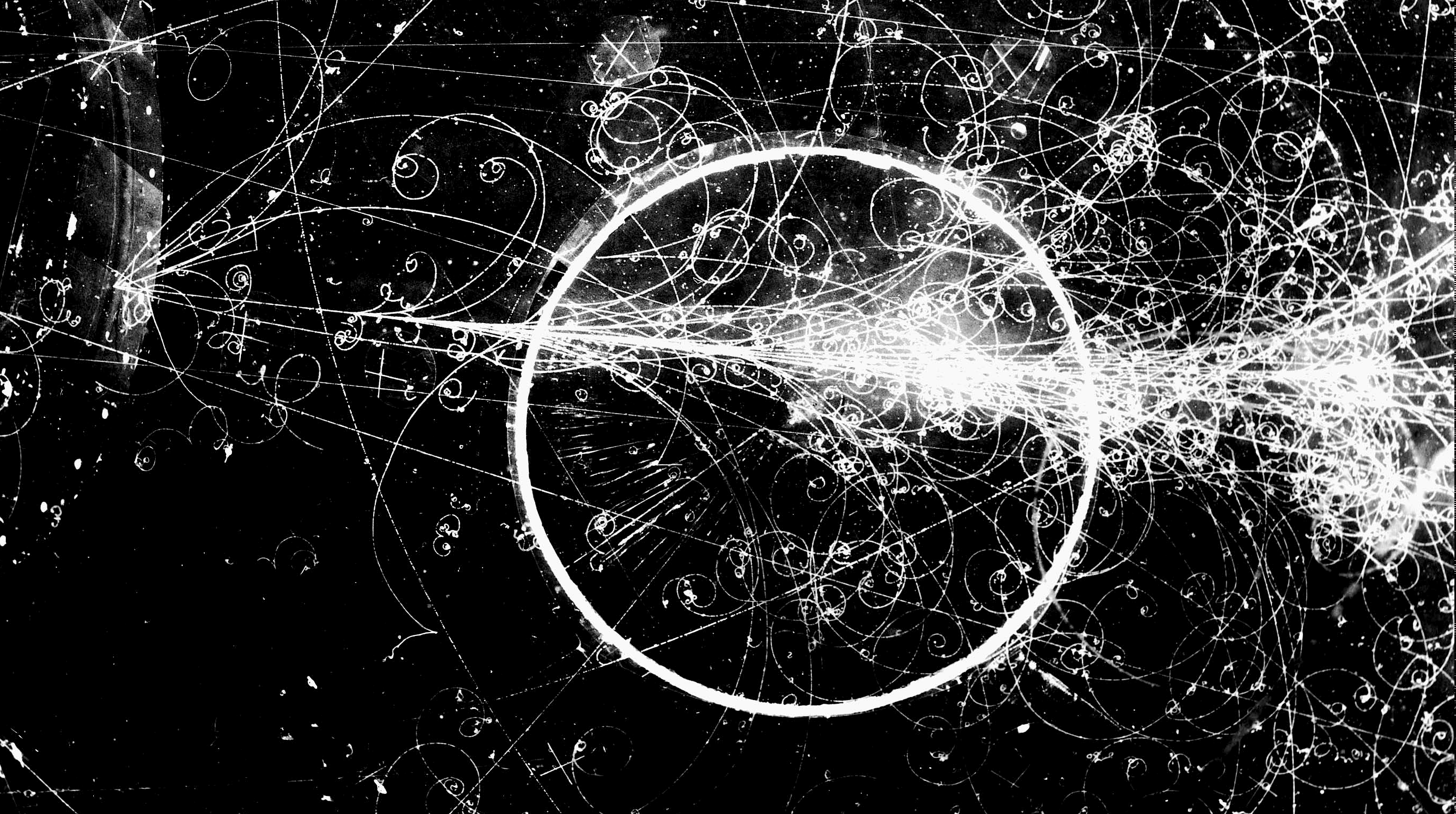
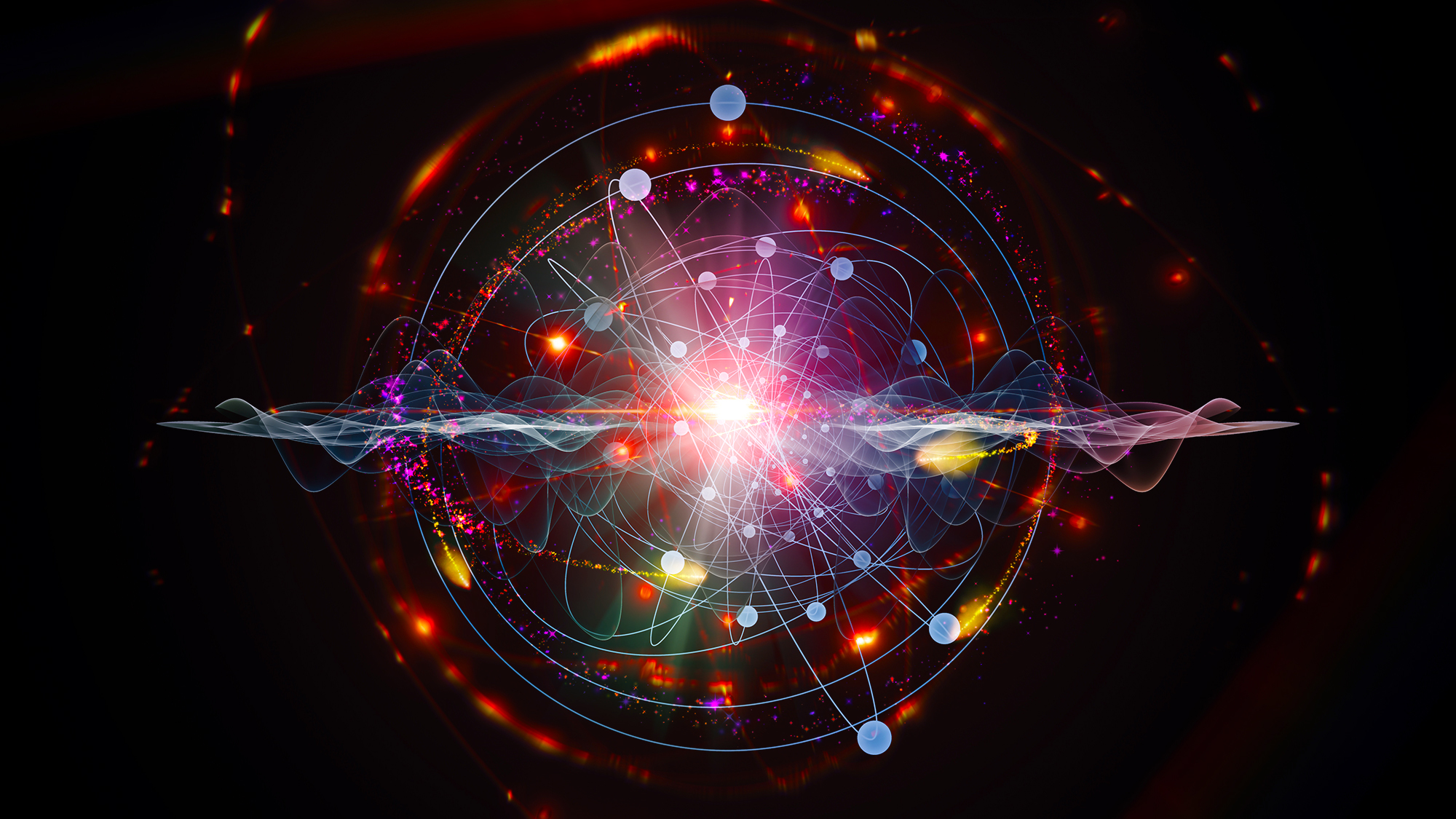
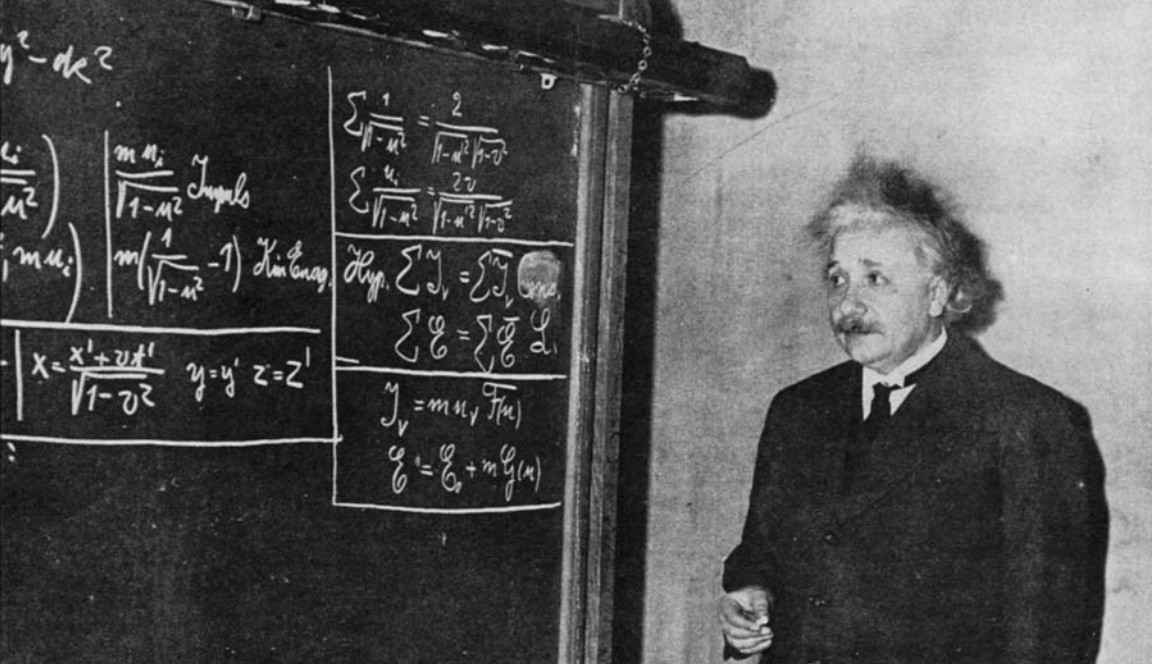In the early stages of the hot Big Bang, matter and antimatter were (almost) balanced. After a brief while, matter won out. Here’s how.
Search Results
You searched for: E P
Einstein’s most famous equation is E = mc², which describes the rest mass energy inherent to particles. But motion matters for energy, too.
If nature were perfectly deterministic, atoms would almost instantly all collapse. Here’s how Heisenberg uncertainty saves the atom.
The AI is helping Twitter users plot movies, design meal plans, and more.
For the first time in nearly 1500 years, fewer than half the people in England and Wales consider themselves Christian.
If it weren’t for the intricate rules of quantum physics, we wouldn’t have formed neutral atoms “only” ~380,000 years after the Big Bang.
The combination of charge conjugation, parity, and time-reversal symmetry is known as CPT. And it must never be broken. Ever.
Salk scientists studied complex decision-making capabilities in a worm with just 302 neurons and a mouth full of teeth. It’s smarter than you would think.
Whether you run the clock forward or backward, most of us expect the laws of physics to be the same. A 2012 experiment showed otherwise.
Could a theory from the science of perception help crack the mysteries of psychosis?
More than any other of Einstein’s equations, E = mc² is the most recognizable to people. But what does it all mean?
Resilience training can be instrumental in helping employees recover from difficulties and embrace change in the workplace.
Photons come in every wavelength you can imagine. But one particular quantum transition makes light at precisely 21 cm, and it’s magical.
The Poisson distribution has everyday applications in science, finance, and insurance. To compare the results of some biomedical studies, more people ought to be familiar with it.
In the early stages of the hot Big Bang, there were only free protons and neutrons: no atomic nuclei. How did the first elements form from them?
The conservation of energy is one of the most fundamental laws governing our reality. But in the expanding Universe, that’s just not true.
Seneca thought the use of ice was a “true fever of the most malignant kind.”
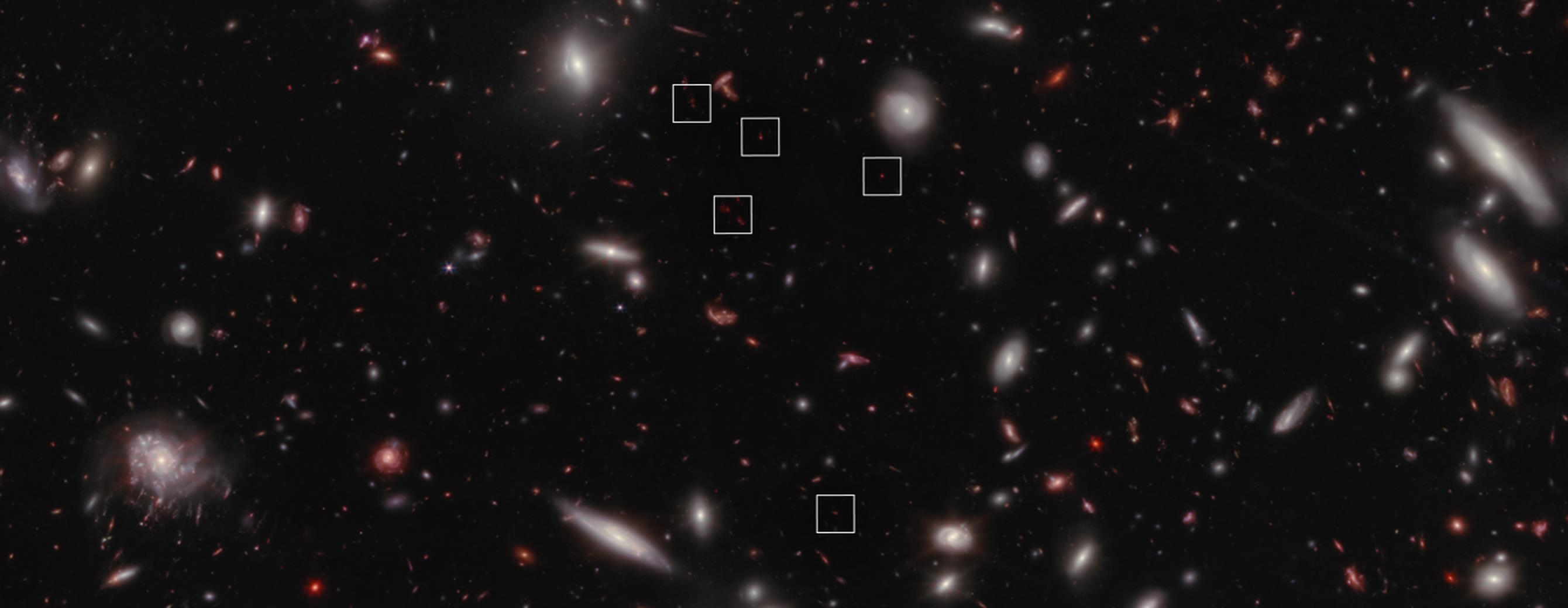
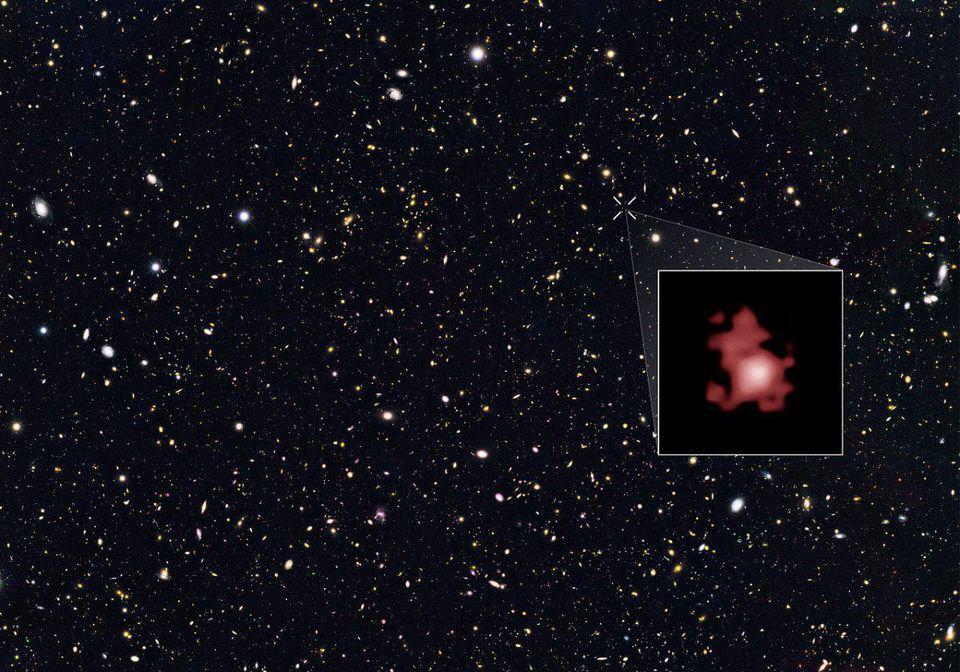
Finding out how the Universe grew up was the biggest science goal of JWST. This ultra-early proto-galaxy cluster is one amazing discovery.
Cotton mask fibers prove 33 percent more effective at blocking viruses in trials.
From up close, the cracking sound of a thunderclap dominates. From far away, it’s more like a drawn-out rumble. Can science explain why?
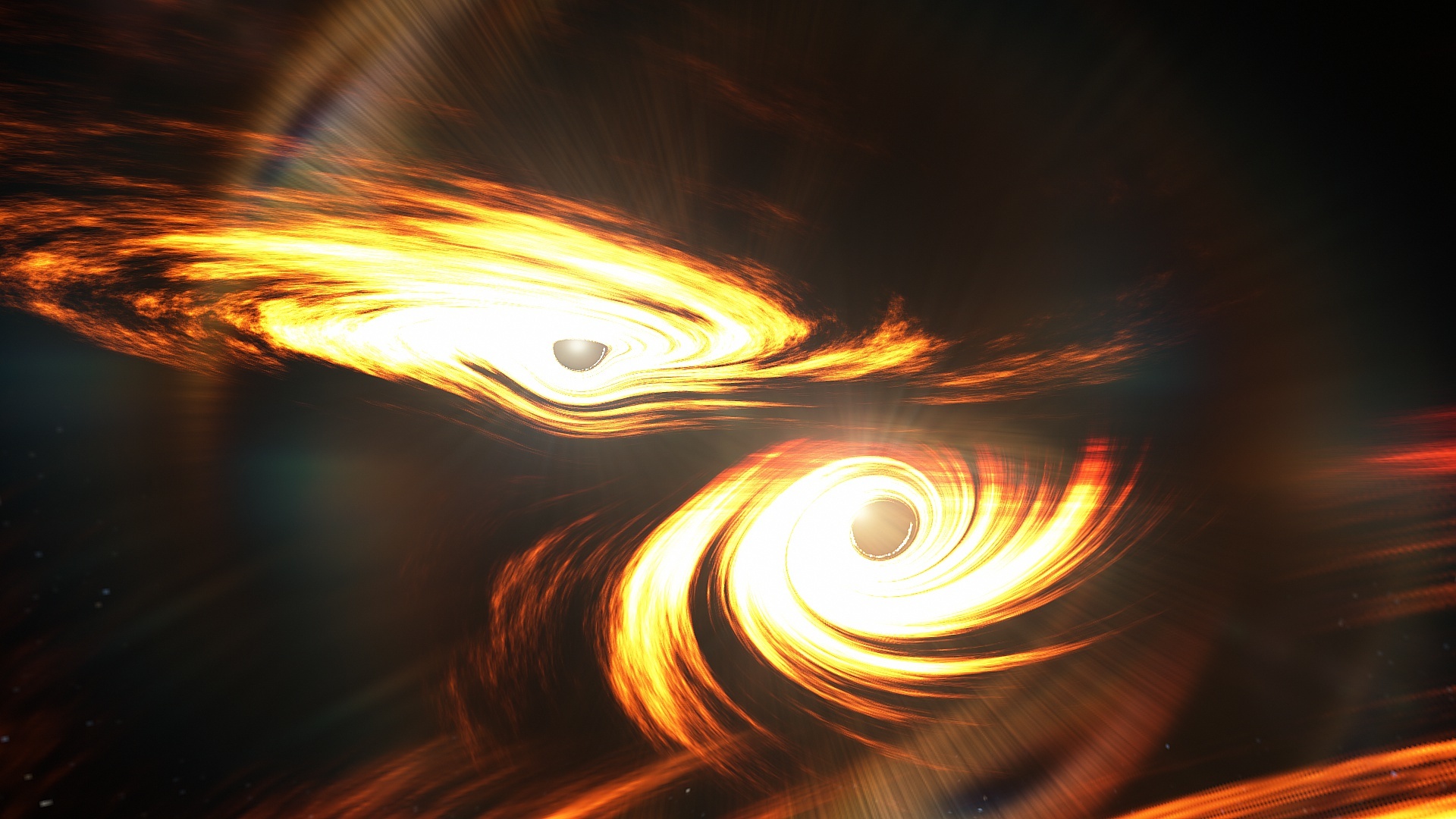
All matter particles can act as waves, and massless light waves show particle-like behavior. Can gravitational waves also be particle-like?
A recently identified stage of sleep common to narcoleptics is a fertile source of creativity.
The laws of physics state that you can’t create or destroy matter without also creating or destroying an equal amount of antimatter. So how are we here?
Yet another ocean monster has been discovered.
Here are the signs that you inherited “money anxiety” from your parents.
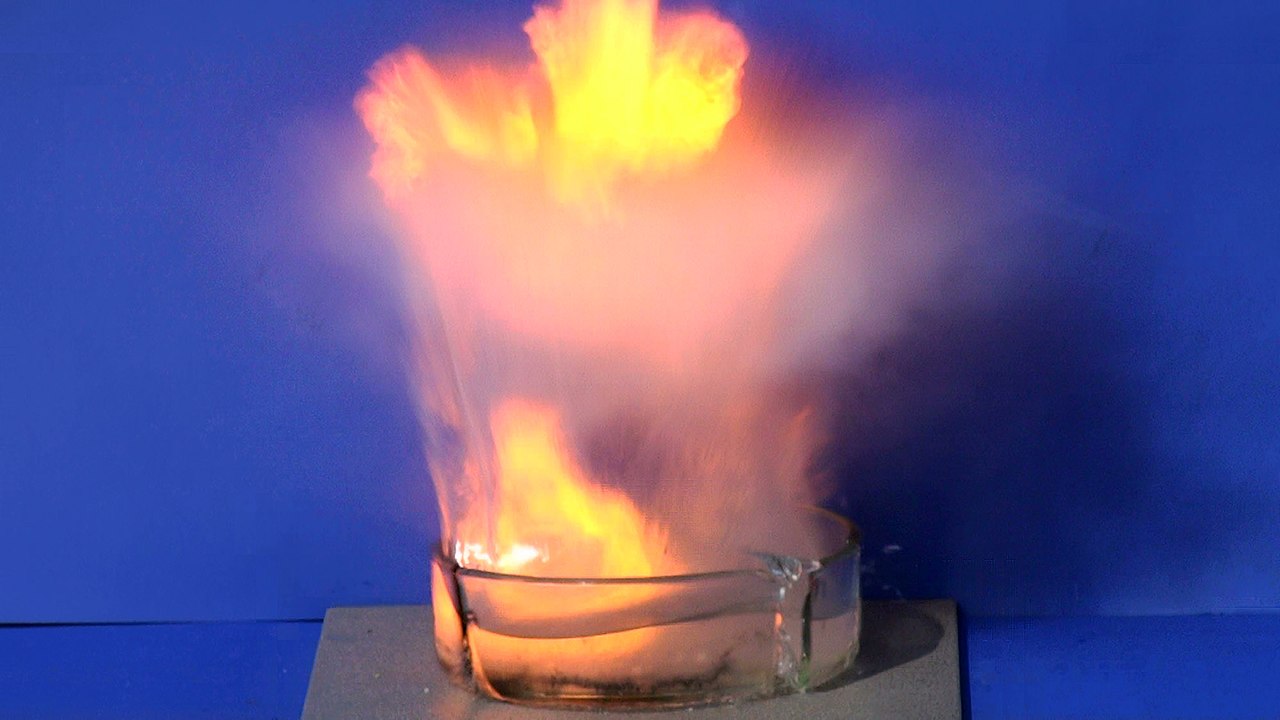
Drop sodium in water, and a violent, even explosive reaction will occur. But quantum physics is needed to explain why.
When someone attempts to make you afraid of something that hasn’t happened instead of a true, present danger, suspect this nefarious ploy.
The universe is filled with unlikely events, but is also full of ways to fool ourselves.
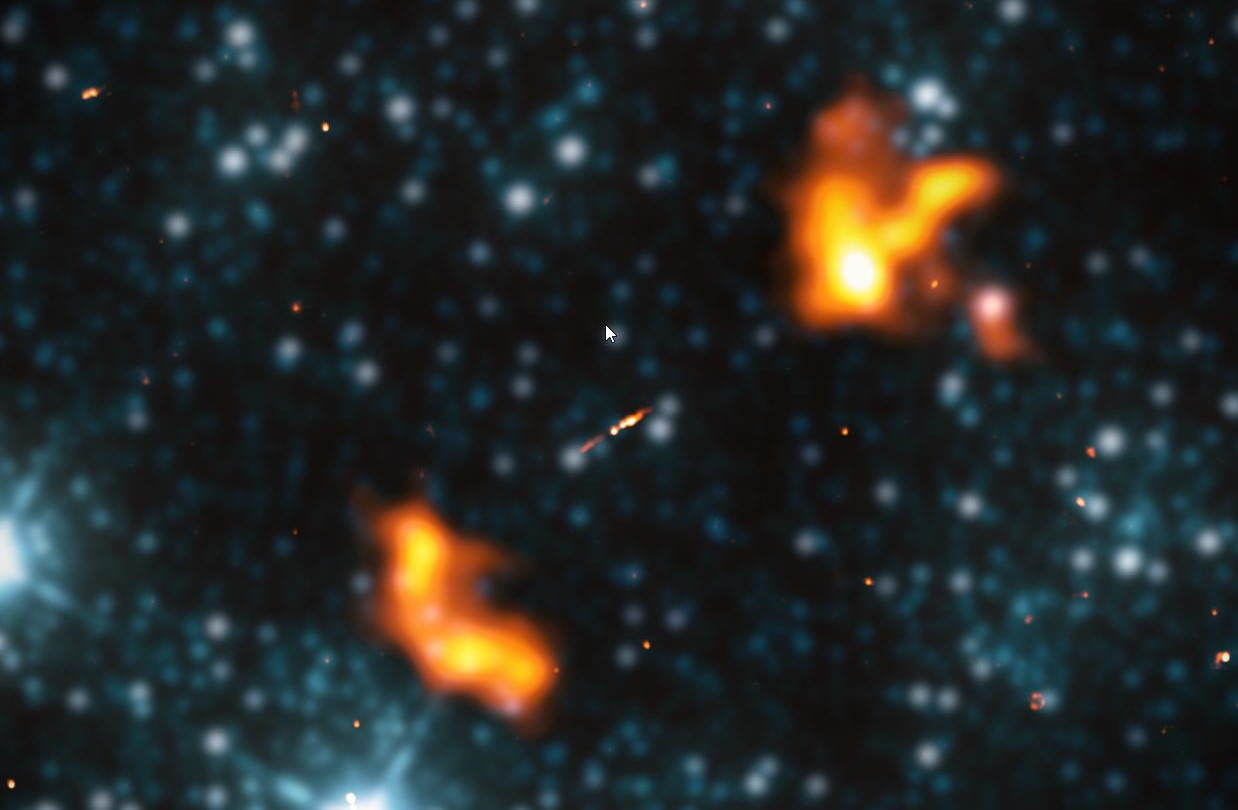
Move over, IC 1101. You may be impressively large, but you never stood a chance against the largest known galaxy: Alcyoneus.
“It doesn’t erase what happened to you. It just changes the impact it has on your life.”