Did Fermilab’s new result blow a hole in the Standard Model?
- The Standard Model, our most successful theory of elementary particles of all-time, has some very deep and intricate relationships between the properties of the different particles baked into it.
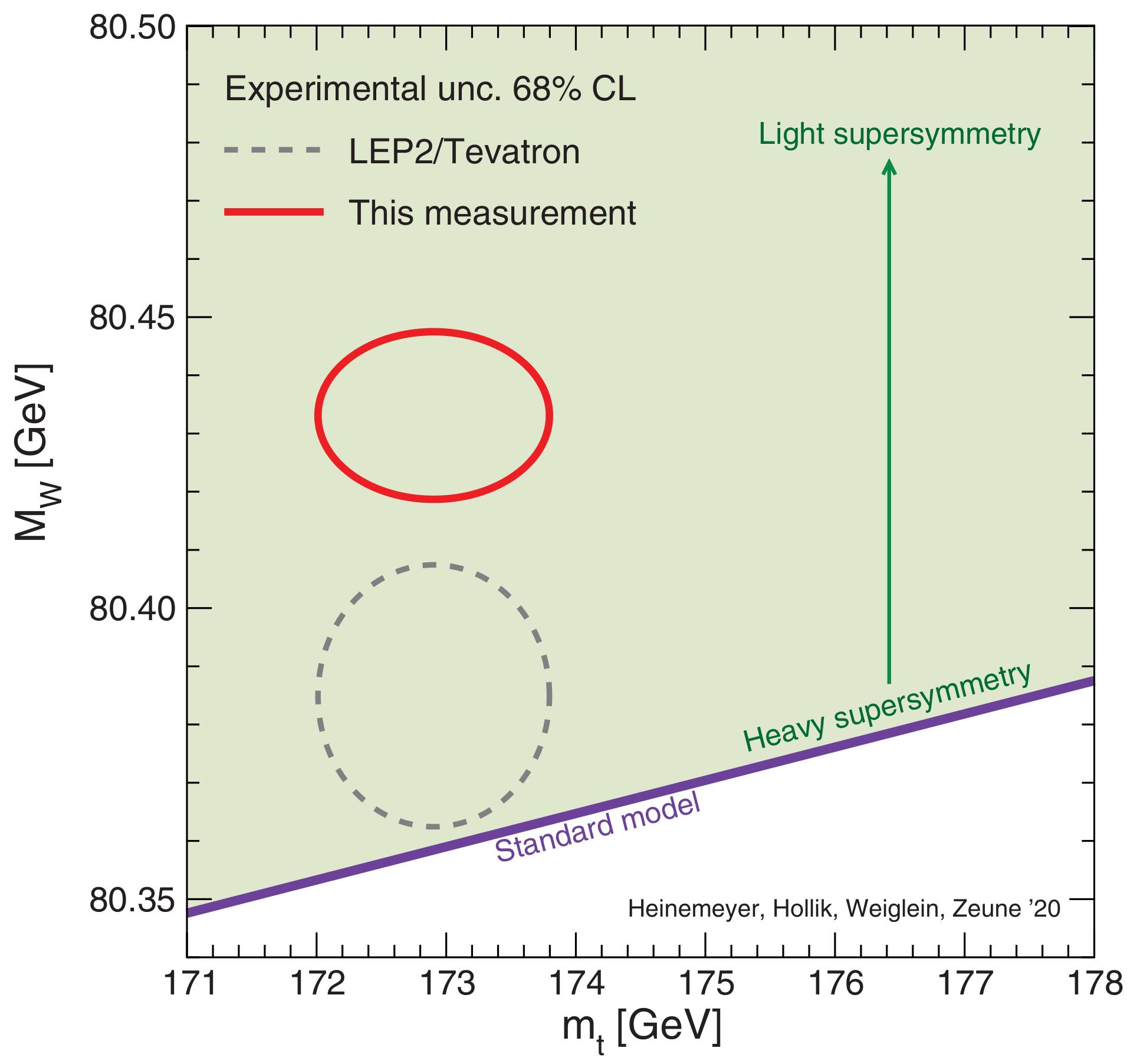
- Based on the measured properties of the other particles, the rest mass energy of the W-boson ought to be 80.35 GeV, but the latest results from the CDF collaboration reveal a value of 80.43 GeV, at a remarkable 7-sigma significance.
- This marks the first experimental particle physics result that disagrees with the Standard Model at such high significance. If there’s no mistake, it could be our first clue to what lies beyond the known frontiers of physics.
In the entire history of science, no theory has been more successful, in terms of predictions matching the results of experiments and observations, than the Standard Model of particle physics. Describing all of the known elementary particles as well as three of the fundamental forces relating them — electromagnetism, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force — we’ve never once conducted an experiment whose results contradicted this theory’s predictions. Particle accelerators from Brookhaven to SLAC to LEP to HERA to Fermilab to the Large Hadron Collider have tried again and again, but have never once found a robust anomaly that’s held up to further scrutiny.
And yet, in a new paper published in the April 8, 2022 issue of Science, the Collider Detector at Fermilab (CDF) experimental collaboration just released their latest results, which offer the most precise measurements of the mass of one of those fundamental particles, the W-boson, ever. Although the Standard Model predicts its rest mass energy, exquisitely, to be 80.36 giga-electron-volts (GeV), the CDF collaboration instead found 80.43 GeV, with an uncertainty of just 0.0094 GeV attached to it. This represents a 7-sigma discrepancy from the Standard Model’s predictions: the most robust experimental anomaly ever seen. Here’s the science behind this incredible result, and what it means for the Universe.
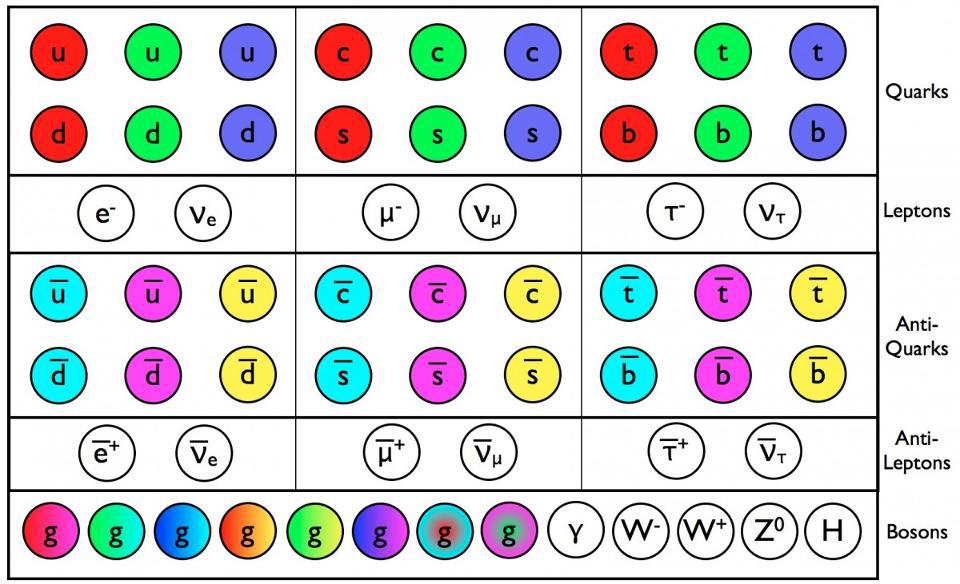
The facts of the Standard Model
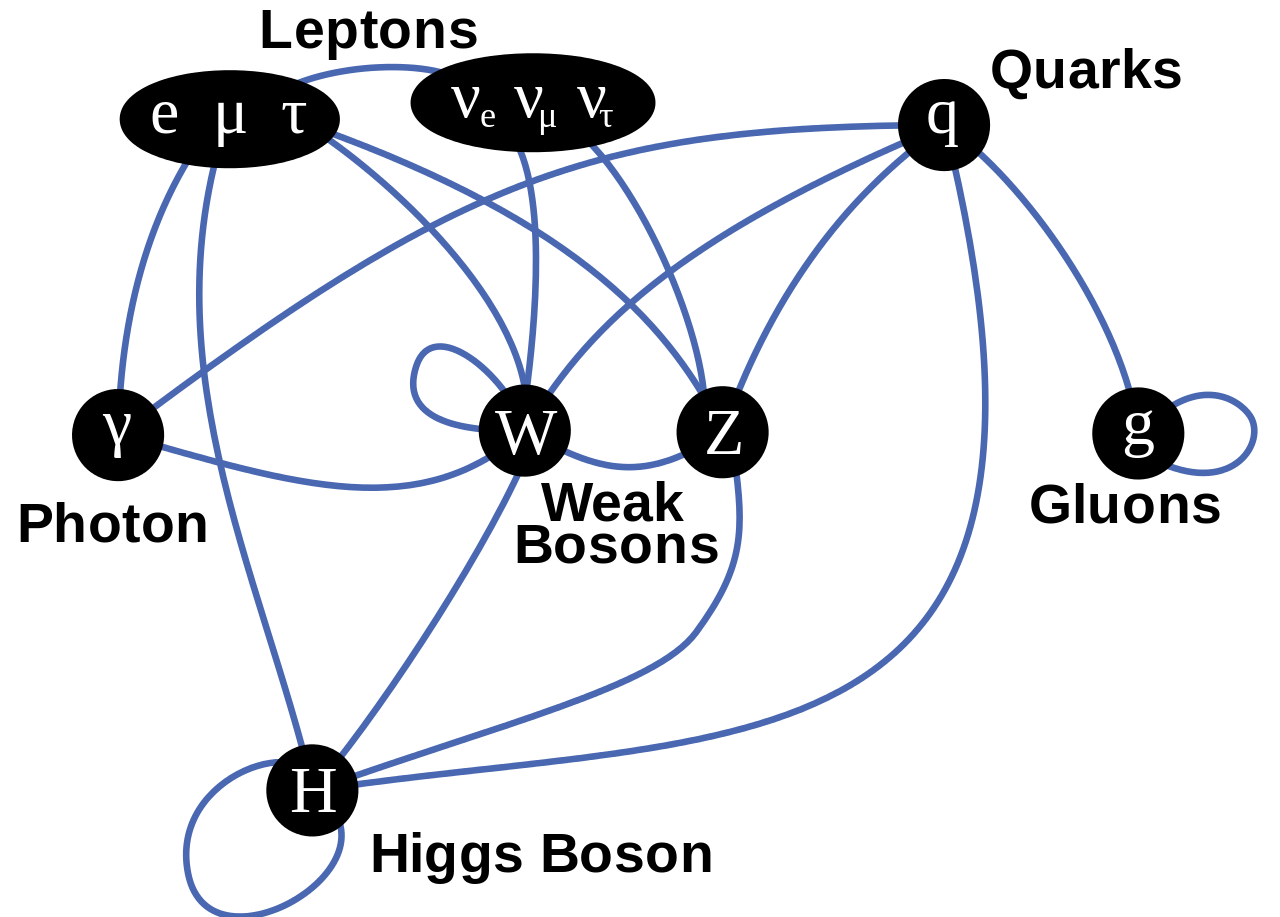
The Standard Model is, in a nutshell, our modern theory of particle physics. It includes:
- six flavors of quark with three colors each, along with their anti-quark counterparts,
- three types of charged leptons and three types of neutral, left-handed leptons (the neutrinos), along with their anti-lepton counterparts,
- the photon, which is the massless boson that mediates the electromagnetic force,
- the eight gluons, which are the eight massless bosons that mediate the strong nuclear force,
- the three weak bosons — the W+, the W-, and the Z — which have large masses and mediate the weak nuclear force,
- and the Higgs boson, which is a scalar particles that couples to, and gives mass to, all particles that have a non-zero mass.
The Standard Model itself details the relationships between these various particles, such as what couples to and interacts with which other particles. However, there are some properties that can only be determined from measuring them, such as the masses of the individual fundamental particles.
One very important property that the Standard Model doesn’t give you wiggle-room for, however, is how the particles affect one another. If the top quark was much more massive than it is, for example, it would increase the mass of the proton, because the particles inside the proton couple to particles which also couple to the top quark. As a result, if you can measure the masses of all-but-one of the Standard Model particles, the rest of the Standard Model will tell you what that last particle’s mass ought to be.
How to measure the mass of the W-boson
The way we measure particle masses, experimentally, is relatively straightforward. We collide particles together at very high energies, and those collisions — so long as all the appropriate conservation laws are obeyed — enable the creation of new particles and antiparticles from that energy itself, via Einstein’s most famous equation: E = mc2.
When you produce new particles, if they contain any particles other than the lightest quarks and leptons, they’ll be unstable, which means they’ll decay into lighter particles.
And this is where colliders shine. We bunch particles together, and circulate them in opposite directions within giant, magnetically confined rings. Then, at the location where we’ve built our detectors, we magnetically “pinch” them to maximize the probability of a collision, and monitor what comes out. Although there are limitations, we can usually reconstruct the energy and momentum of every particle that results from this collision, except for any neutrinos, whose energy and momentum are inferred from conservation laws. Just like by knowing how much energy was in a grenade explosion where you can find all the pieces of shrapnel except one, you can reconstruct where that final piece must be, we can reconstruct what happened back at the collision point, including knowing what was created and what its properties, like mass, were.

What the CDF collaboration found
Up until the Large Hadron Collider began operations a little over a decade ago, Fermilab’s TeVatron was the world’s greatest particle accelerator. By circulating protons and antiprotons at a total energy of 2 tera-electron-volts (TeV), and colliding them for years in the centers of the CDF and D0 detectors, physicists were able to record millions upon millions of events where something “interesting” may have been created.
Analyzing their data more precisely than ever before, the CDF collaboration found more than four million events where a W-boson was created, and attempted to use that data to reconstruct the W-boson’s mass. All told, they found:
- 1,811,700 events where a W-boson decayed into an electron and a neutrino,
- 2,424,486 events where a W-boson decayed into a muon and a neutrino,
and used the energy and momentum of the detected particles to infer the “missing” energy and momentum carried away by the neutrino. The W-boson has an incredibly short lifetime of about 3 × 10−25 s, which translates into the rest mass energy of any individual W-boson having an inherent uncertainty of about 2.5% of the actual value: about ±2.1 GeV. Therefore, in order to meaningfully constrain the average mass of the W-boson, an enormous number of statistics were needed.
Prior to the latest CDF result, the expectation, from the Standard Model and the measured masses of all the other particles, was that the W-boson’s rest mass energy would be right around 80.35 to 80.36 GeV.
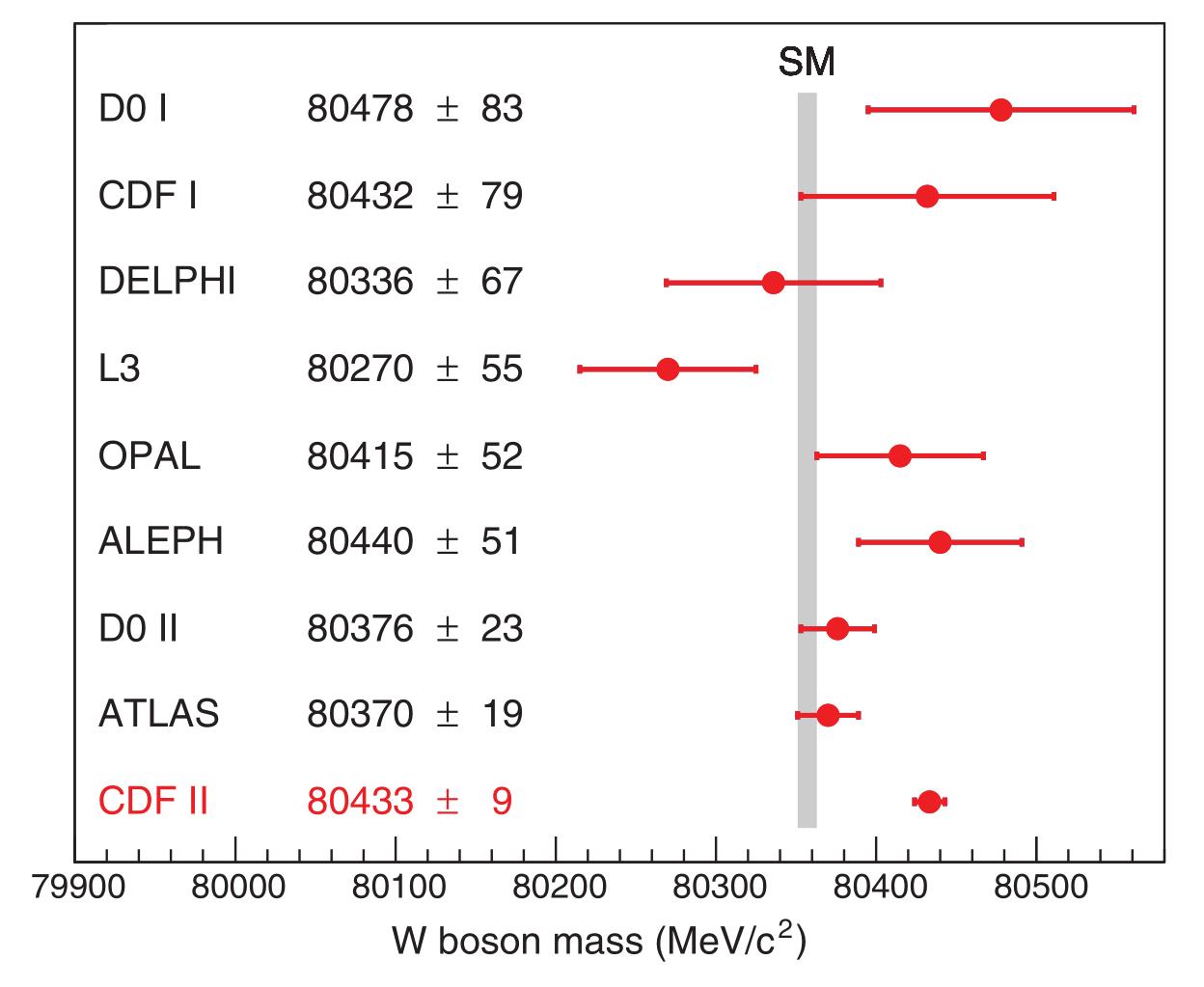
Prior to the latest CDF result, the world average, from all other experiments, including D0, LEP, and the ATLAS experiment at the LHC, was that the W-boson’s rest mass energy was 80.379 GeV, with an uncertainty of ±0.012 GeV.
But now, with smaller uncertainties and better statistics than ever before, the CDF collaboration finds a value that’s inconsistent with other groups measurements and with the Standard Model’s prediction by seven standard deviations, finding a rest mass energy of 80.433 GeV, with an uncertainty of ±0.0094 GeV, or just 0.012%.
Why does “old TeVatron data” give better results than “new Large Hadron Collider data”?
This seems a little weird, doesn’t it? The Large Hadron Collider has had many more particle collisions, cumulatively, than the TeVatron at Fermilab ever experienced. The LHC’s collisions occur at about seven times the energy of the TeVatron, yielding a much higher potential for revealing effects that only appear at high energies.
So why, then, does the TeVatron give a better result for the mass of the W-boson than the LHC does?
There are two main reasons. The first is that, at the lower energies experienced by the TeVatron, almost all of the energy of the accelerated protons and antiprotons are split between the three valence quarks that make those particles up: two up and one down quark for the proton, and two anti-up and one anti-down quark for the antiproton. What physicists call the parton distribution function of these particles, which is how the energy and momentum of the proton (or antiproton) is distributed among its constituent components, is well-understood at low energies, but gets messy at higher energies, where gluons (and the associated “sea quarks”) play a greater role. In the TeVatron, almost all the W-bosons we make are produced through quark-antiquark collisions, while in the LHC, they’re produced when a quark collides with a gluon (through a sea quark), where the parton distribution function is much less well-understood.
The second reason is that the LHC has what we call a much greater luminosity, or density of particles in the beam, than the TeVatron ever did. This is an incredibly complicating factor, since at the TeVatron, there were typically three proton-antiproton pairs that collided in every bunch of particles, meaning there were three collisions that the debris needed to be sorted out from in each event. At the LHC, however, there are about 10 times as many particles (around ~30) that collide in every event. That means that reconstructing exactly what occurred in one specific collision is much, much more difficult, which is likely why only the ATLAS collaboration, and not the CMS collaboration, has even produced a result for the inferred mass of W-boson so far. In the future, the LHC will upgrade to even higher luminosities, producing more like ~200 collisions in every event. Although this makes discovering something novel more likely, it makes precision work like this that much more of a complex task.
How confident are we that this result is correct?
There are sources of error here that are not negligible.
- For one, it’s possible that some of the theoretical inputs — the parameters that go into the calculations for drawing conclusions about the mass of the W-boson — have one or more unidentified errors in them. (This has happened before in recent history, as the theoretical calculations behind the fine-structure constant had a mistake in them in the mid-2000s.)
- For another, we know that all detectors slightly mis-measure the energy of the particles that they see, and if this is a systematic error that isn’t sufficiently accounted for, it can bias the results.
- And for yet another possibility, we know we’re only detecting the “shrapnel” particles that aren’t emitted too closely to the original direction of the circulating beams; the detectors cannot accurately measure the particles that come off at too narrow of an angle.
The CDF collaboration has spent approximately a decade working to reduce their errors, and they think they’ve done incredibly well at this. Indeed, the uncertainties, both statistical and systematic combined, are less than half the size of any other experiment, including D0, LEP, and ATLAS. This is a very, very difficult measurement to make, and it may well be the case that the CDF collaboration has done what no other collaboration to date has successfully done. But there is a legitimate risk of a yet-unidentified error being at play, and we ignore that possibility at our own peril.
How does this compare with other “cracks” in the Standard Model?
Over the past few decades, there have been a number of alleged experimental results that disagreed with the Standard Model’s predictions. A short list of claims include:
- the discovery of particles with composite lepton-and-quark properties: leptoquarks,
- the discovery of faster-than-light neutrinos, where the initial significance was reported to be ~6-sigma,
- the discovery of a “bump” in both the diphoton and the diboson decay channels at the LHC,
- a violation of lepton universality, which is now suggested by a number of different decays particularly seen at the LHCb experiment,
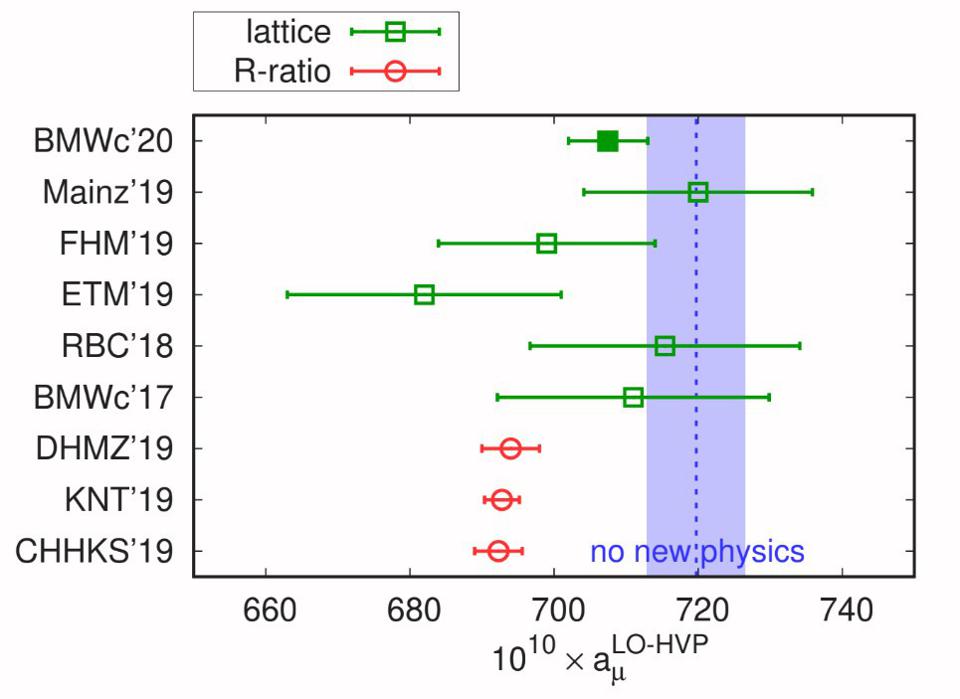
- and the recent discrepancy between theory and experiment from the muon g-2 experiment.
The first three were flukes, and they were not reproducible. The second two are still on the table, but neither one has hit the 5-sigma threshold: the “gold standard” for discoveries in particle physics. The muon g-2 experiment, in particular, might point towards a theoretical misunderstanding more than anything, as the two ways to calculate what the expected theoretical value ought to be — from quantum field theory calculations and from lattice QCD techniques — disagree with one another by approximately the same margin as the experiment disagrees with the field theory calculations.
In a very real sense, this new result is the biggest discrepancy we’ve ever found in the Standard Model via experimental particle physics.
What are the possible explanations for this discrepancy?
It’s possible that the theoretical inputs are wrong. It’s possible that the method that the CDF collaboration used for estimating certain parameters, which rely on the decays of the Z-boson as also measured by the CDF collaboration, are suffering from a bias. It’s possible that there are problems with the detector and how it measures energy; it’s possible that the undetected debris biases the results towards higher energies. In all experimental and observational sciences, the “unknown unknowns” are always a potential pitfall.
But if everything is correct, and it may well be, then this is the strongest hint we’ve ever found in a particle collider that new physics, beyond the Standard Model, may be at play. Although the two scenarios that the authors primarily consider (including in a related perspective piece) are well-worn ground, supersymmetry and scenarios where the Higgs is actually a composite particle, any new particle that couples to the Standard Model particles is a candidate that cannot be ignored. If there’s a new particle out there, a slight upward shift in the expected mass of one of the heavy particles we already know about is, arguably, the most likely first signal we’ll find.

What are the next steps?
There are three things we have to do if we want to truly convince ourselves that the newest CDF results are pointing towards new physics, and not some sort of fluke or error.
- We have to re-examine all of the theoretical inputs that went into this result. Just as experimentalists are often called upon to replicate their results, theorists have to ensure that there were absolutely no mistakes or omissions that occurred in the calculations that delivered the expected mass.
- We have to reproduce this new, high-valued mass results at other detectors. The D0 collaboration didn’t get the same value as the CDF collaboration; they found that the rest mass energy of the W-boson is 80.376 GeV, with an uncertainty of ±0.023 GeV. The ATLAS collaboration didn’t get the same result; they found 80.370 ± 0.019 GeV. And the CMS collaboration has no results at all. At least one, and preferably all three of these collaborations, should find something more consistent with CDF’s measured 80.433 ± 0.009 GeV.
- And finally, if this result is correct, there should be the potential to find both direct and indirect signatures that show up at the LHC’s upcoming high-luminosity run. If this occurs, we truly will have demonstrated we’ve gone beyond the Standard Model.
Ideally, all three of these criteria will be met in short order, but until the data is in, the jury is out.
One thing that’s worth remembering is this: in the history of experimental physics, it’s often been the case that one team comes along and measures a quantity, and gets a precise result. After that, the other experiments that come along measure that quantity again, and get results that agree, within the error bars, with whatever that precise result was. Then, at some point, another team, usually a well-funded and prestigious one with better equipment, gets a very precise result that disagrees with all prior measurements. And then, surprise surprise, subsequent measurements agree with the new result, as opposed to the old one.
Although the CDF collaboration did scrupulously blind their analysis against this kind of bias, it’s worth remembering what pitfalls we’ve encountered before, because it’s quite possible that a similar mishap will arise here once again.
But more importantly, there are three overall lessons.
- Despite what theorists may claim, physics is an experimental science, and if we have the possibility to measure something in a superior fashion to how it’s ever been measured before, we should. We never know what lessons the Universe has to teach us if we fail to ask the right questions.
- It’s vital to push the frontiers of precision: working to decrease our systematic errors and to gather increased statistics. In science, every additional significant figure, every increase in the number of events, and every improvement we make to our apparatuses and our analysis brings us closer to the truth that the Universe is hiding.
- And there is no substitute for pushing the frontiers of what we can access. Whether that’s higher energies (for particle physics), larger apertures (for astrophysics), or one more significant digit closer to absolute zero (for low-temperature physics), those are the unprobed realms where new, improved experiments with better technologies are absolutely required.
The Standard Model, for the first time in some 50 years, has a bona fide experimental crack in its foundations. It’s the best motivation we could ask for to continue pushing the frontiers of the unknown.
The author thanks Ben Kilminster and Don Lincoln for useful discussions surrounding this result.