Stephen Johnson
Managing Editor, Big Think
Stephen Johnson is the Managing Editor of Big Think. Formerly a long-time contributor to Big Think, he is a St. Louis-based writer and editor whose work has been featured in U.S. News & World Report, PBS Digital Studios, Eleven Magazine, and The Missourian.

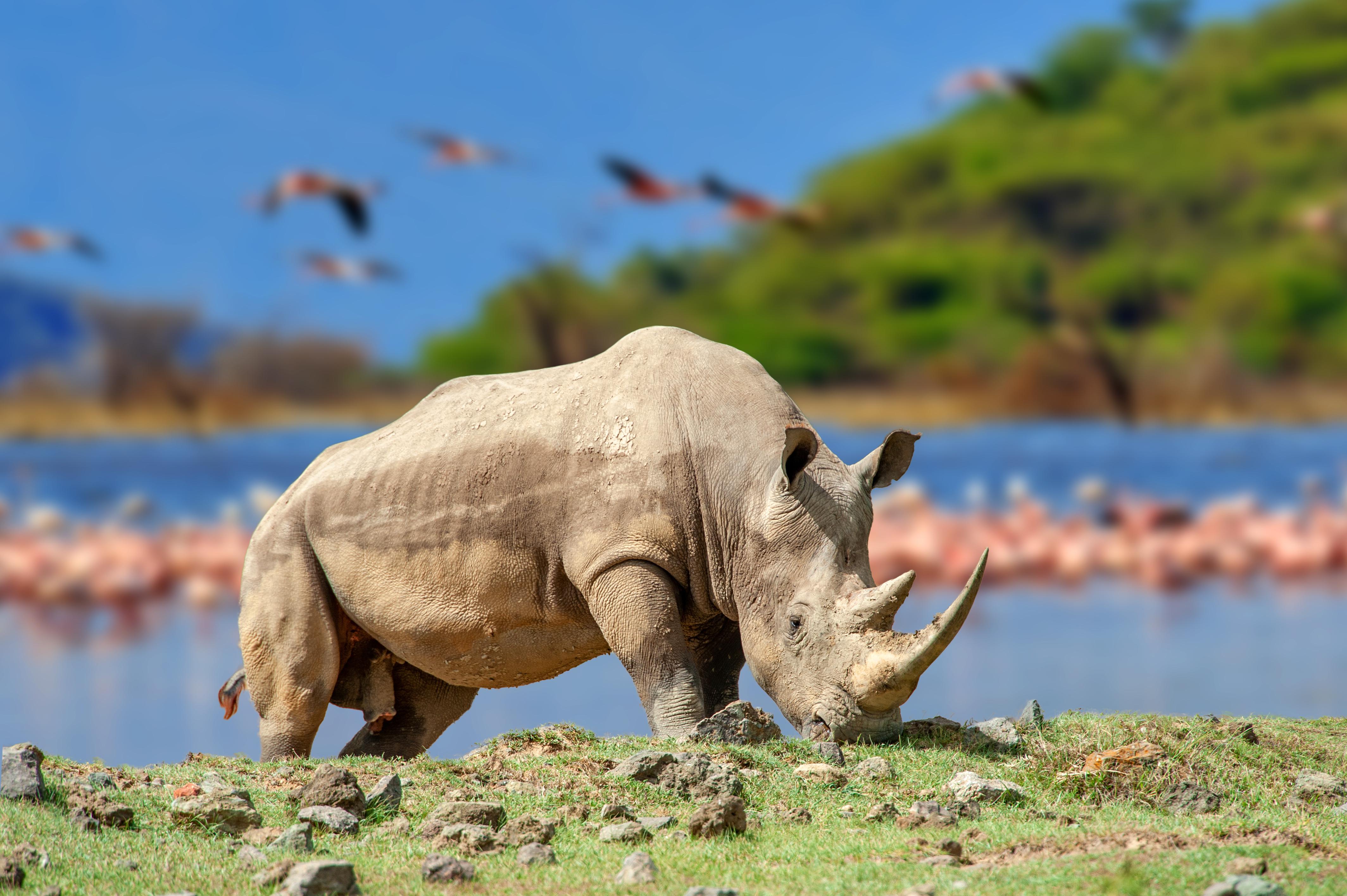
A recent study sheds light on the evolutionary history of rhinoceroses and their remarkably low levels of genetic diversity.
Our brains did not evolve to shop on Amazon.
A new study found that people who scored high in certain psychopathic traits are more likely to limit head movements.
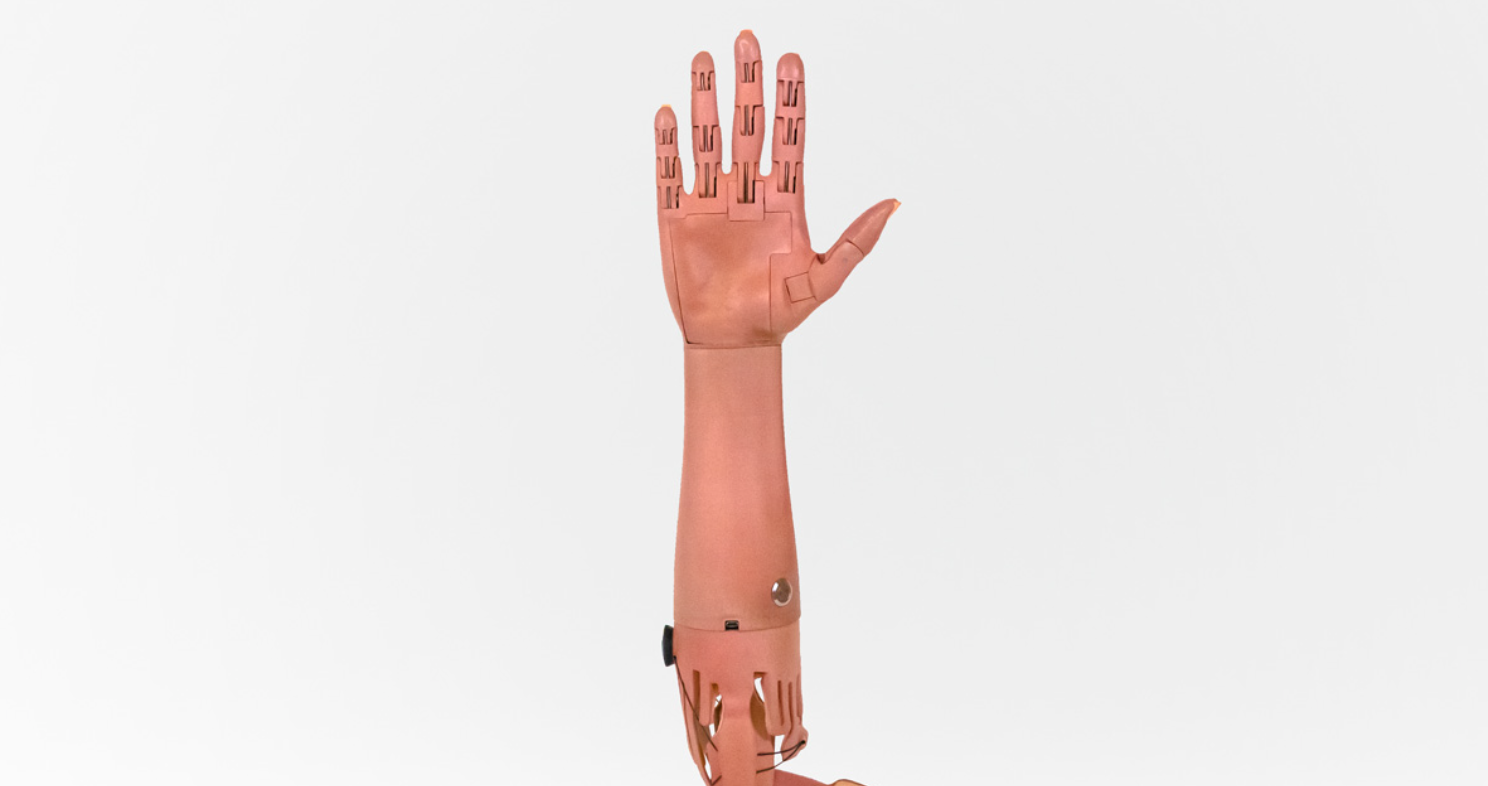
Prosthetic arms can cost amputees $80,000. A startup called Unlimited Tomorrow is aiming to change that by making customized 3D-printed bionic arms for just $8,000.
Money can buy happiness — if you spend it on others, research suggests.
For nearly two centuries, courts have relied on the subjective “reasonable person standard” to solve legal disputes. Now, science can help.
Cancer cells seem to have a harder time growing among pair-bonded mice, according to a new study that explored the “widowhood effect.”
Our brains believe $10 today is more tangible than $100 next year.
Fintech companies are using elements of video games to make personal finance more fun. But does it work, and what are the risks?
A new brain imaging study explored how different levels of the brain’s excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters are linked to math abilities.
The non-contact technique could someday be used to lift much heavier objects — maybe even humans.
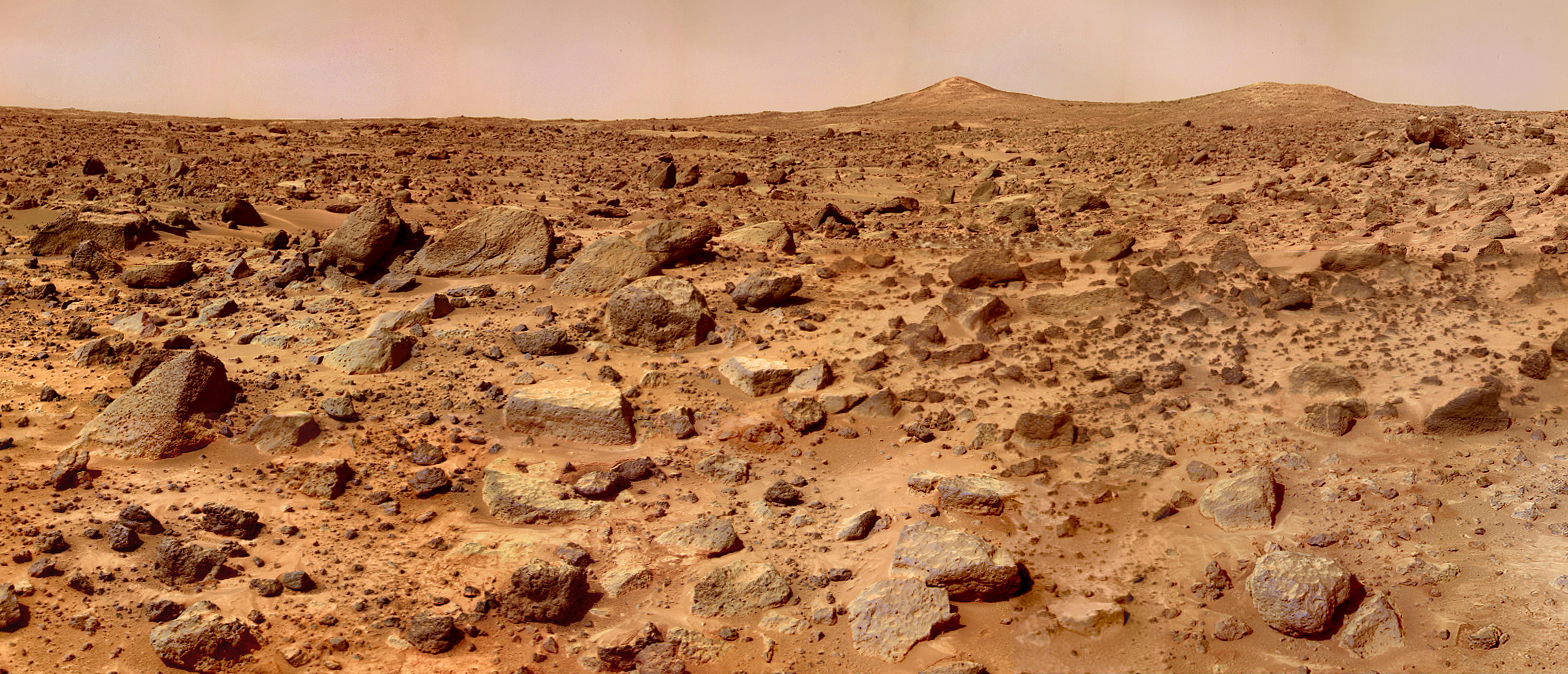
We are likely to see the first humans walk on Mars this decade.
A new episode of “Your Brain on Money” illuminates the strange world of consumer behavior and explores how brands can wreak havoc on our ability to make rational decisions.
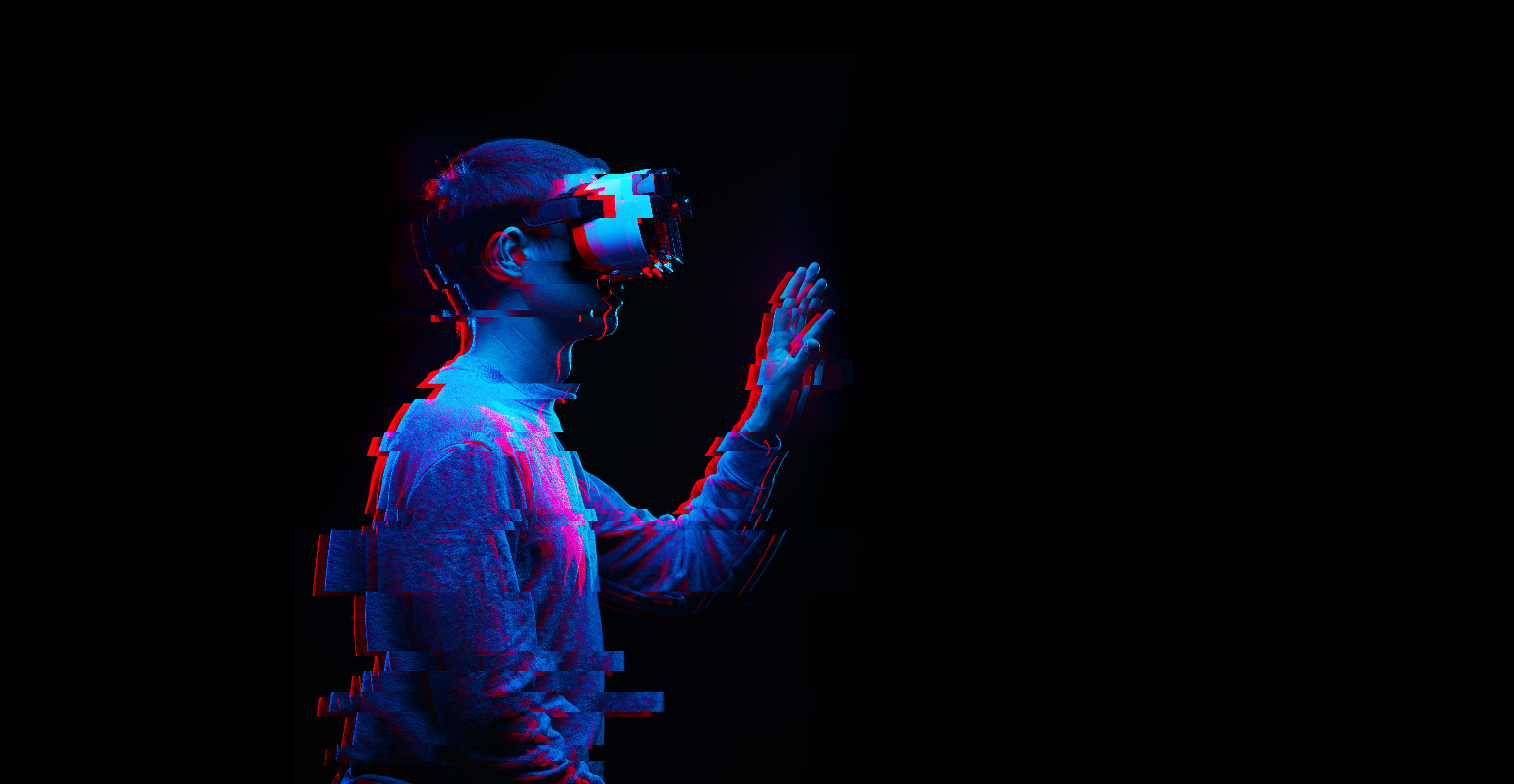
Virtual reality continues to blur the line between the physical and the digital, and it will change our lives forever.
The same parts of the brain that help us navigate complex social interactions can also drive us to make wildly bad investments.
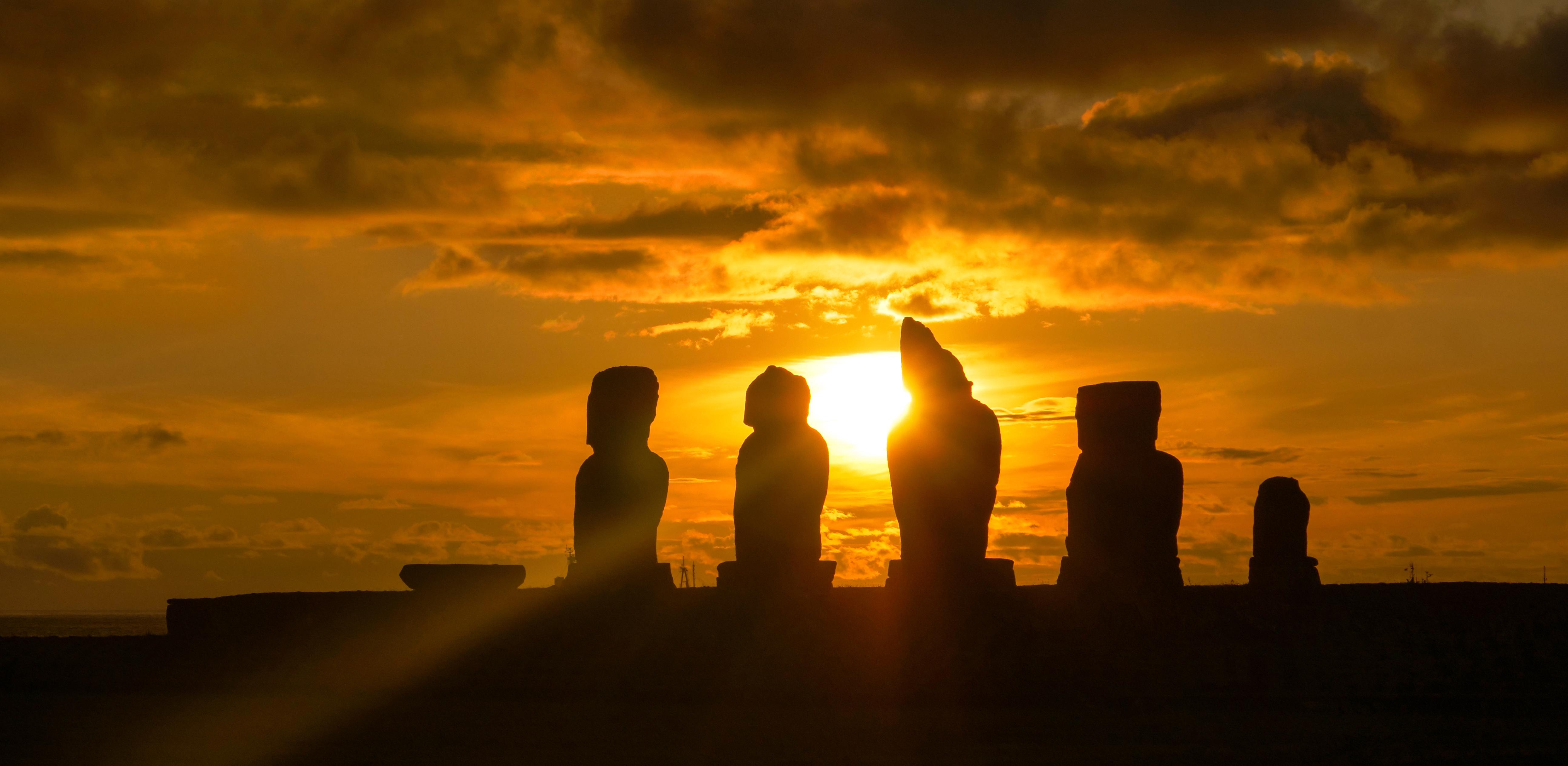
For decades, researchers have proposed that climate change and human-caused environmental destruction led to demographic collapse on Easter Island. That’s probably false, according to new research.
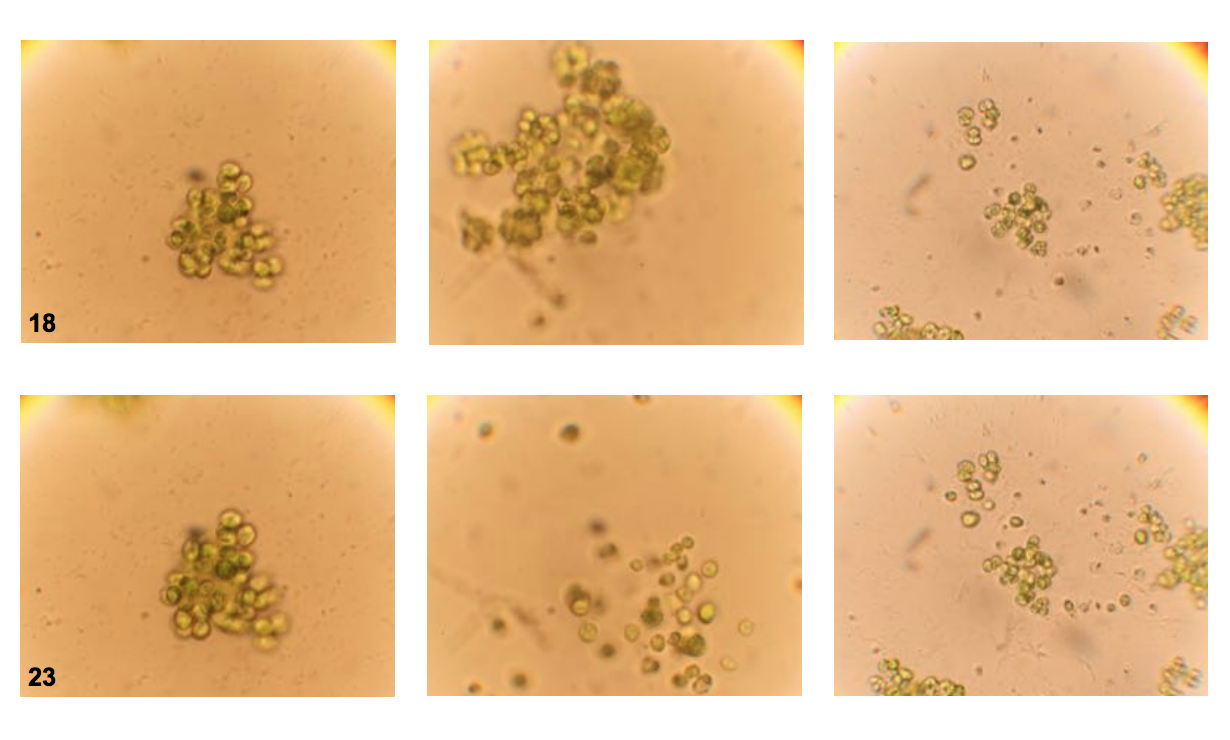
When facing a predator, single cells sometimes unite to defend themselves, paving the way for more complex multicellular life forms to evolve.
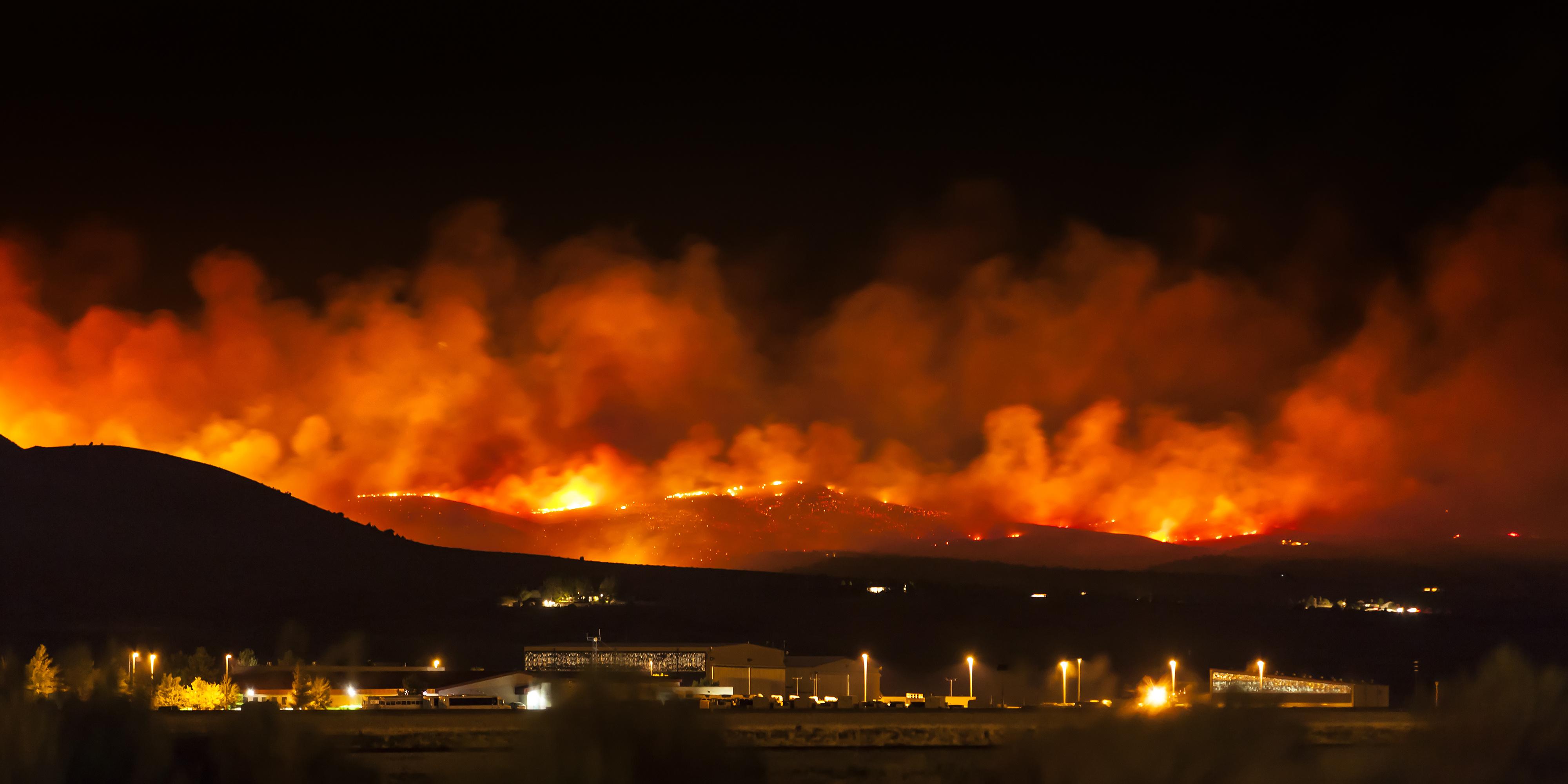
A new study mapped areas of the U.S. that are most likely to suffer natural disasters.
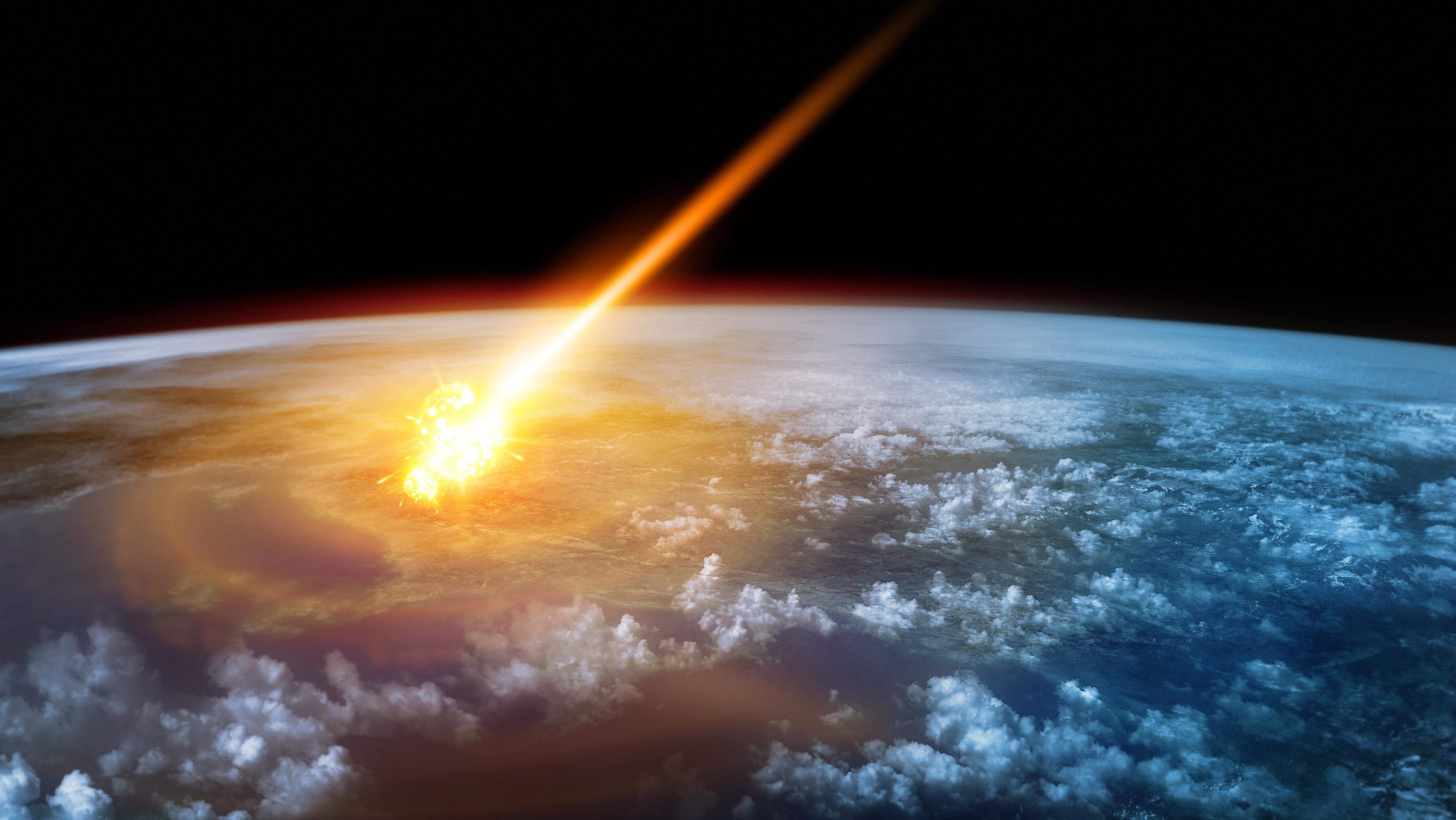
The Younger Dryas impact hypothesis argues that a comet strike caused major changes to climate and human cultures on Earth about 13,000 years ago.
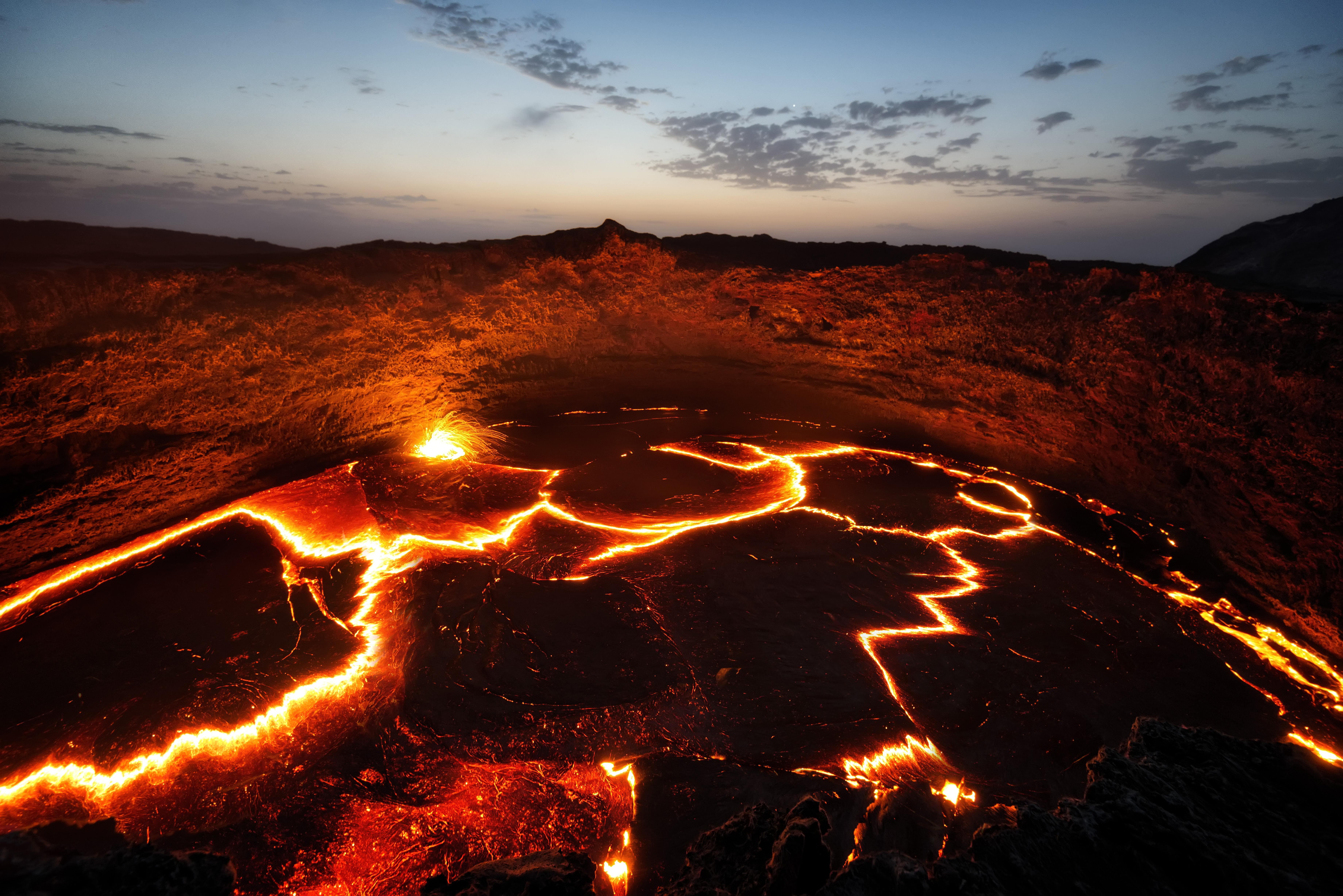
The Taupo volcano was responsible for one of the most violent eruptions on record.
A new device cured the hiccups 92 percent of the time in a recent study involving more than 200 participants.
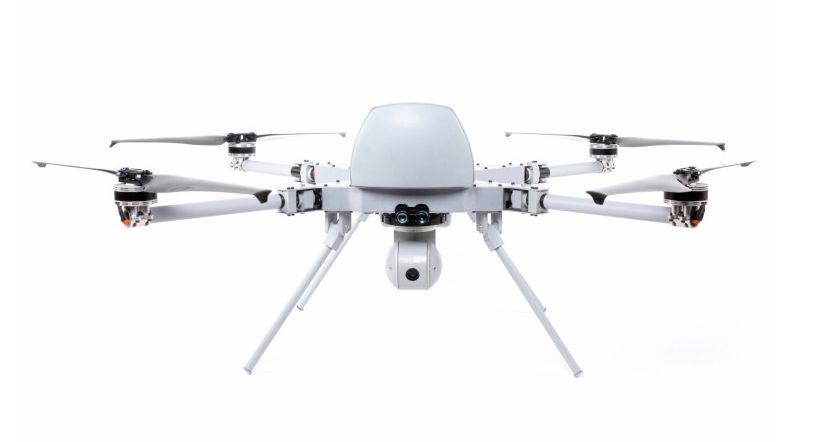
A brief passage from a recent UN report describes what could be the first-known case of an autonomous weapon, powered by artificial intelligence, killing in the battlefield.
Buildings don’t have to be permanent — modular construction can make them modifiable and relocatable.
Too few babies — not overpopulation — is likely to be a major problem this century.
As droughts threaten water supplies across the planet, some municipalities aim to utilize an untapped resource: sewage water.
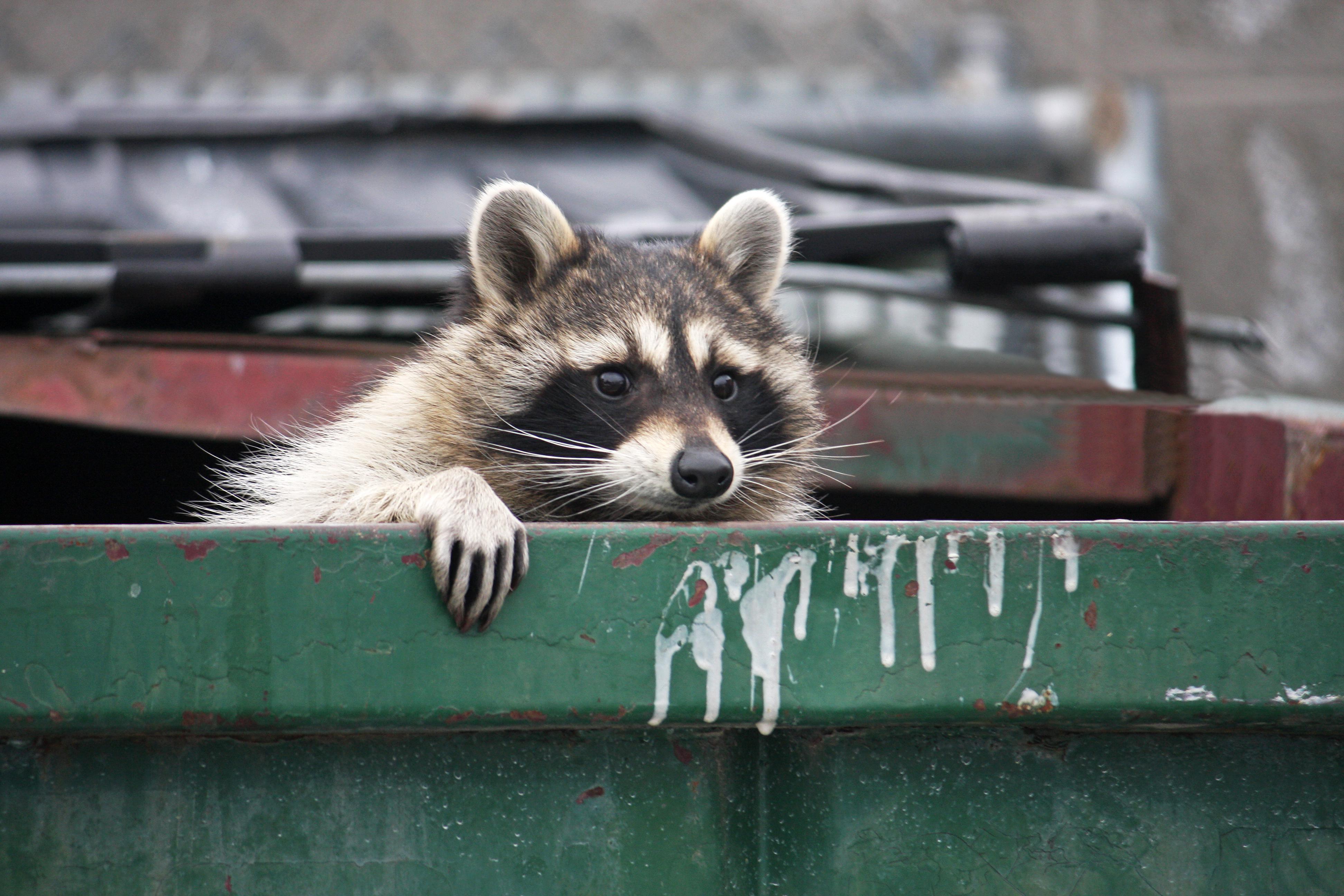
Some wild animals thrive near humans, but only up to a point.
Science journals may be lowering their standards to publish studies with eye-grabbing — but probably incorrect — results.
Can the main psychoactive ingredient of magic mushrooms help treat the world’s sixth most debilitating illness?
Political partisanship might be a treatable condition.
Since 1957, the world’s space agencies have been polluting the space above us with countless pieces of junk, threatening our technological infrastructure and ability to venture deeper into space.