drugs
Psychedelic medicines are surging in popularity. Here’s how they work.
▸
6 min
—
with
Dr. Carl Hart breaks taboos surrounding drug use in America.
▸
4 min
—
with
Before it fueled Woodstock and the Summer of Love, LSD was brought to America to make spying easier.
Some of these trends may be due, in part, to the lockdown.
Psychedelics have been shown to help reduce depression. This study may show us why.
Can the main psychoactive ingredient of magic mushrooms help treat the world’s sixth most debilitating illness?
Cannabidiol (CBD) seems to reduce the unpleasantness of pain, a finding that surprised the researchers behind a new, first-of-its-kind study.
Growing marijuana in large, climate controlled warehouses is good for production but has a massive carbon footprint.
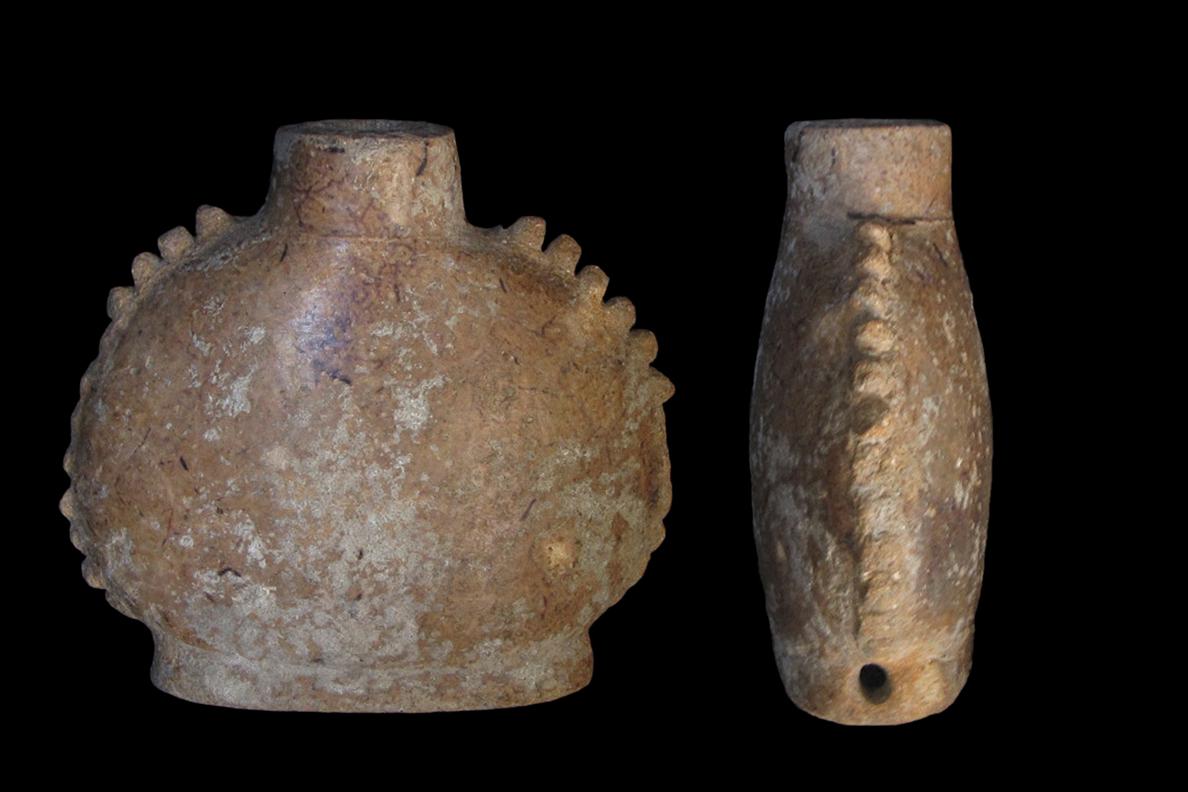
Scientists use new methods to discover what’s inside drug containers used by ancient Mayan people.
Traces of heroin and cocaine have been found in the tartar of 19th-century Dutch farmers.
A new study on mice showed that ginger may counter certain autoimmune disorders such as lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome.
A new study explores the therapeutic potential of the psychedelic drug ibogaine, which has been used in Africa for centuries.
Psychedelic therapy will become legal in Oregon in 2023. That’s thanks largely to a renaissance of psychedelic research that’s changing attitudes on the substances’ medical potential.
A biologist-reporter investigates his fungal namesake.
The Chumash people poked bits of psychoactive plants into cave ceilings next to their paintings.
The heart of the religious ritual is mysticism, argues Brian Muraresku in “The Immortality Key.”
The compound found in “magic mushrooms” has significant and fast-acting impact on the brains of rats.
It’s “the biggest blow to the war on drugs to date,” said Kassandra Frederique, executive director of the Drug Policy Alliance.
What is more important, that a treatment helps keep people healthy or that it meshes with our morals?
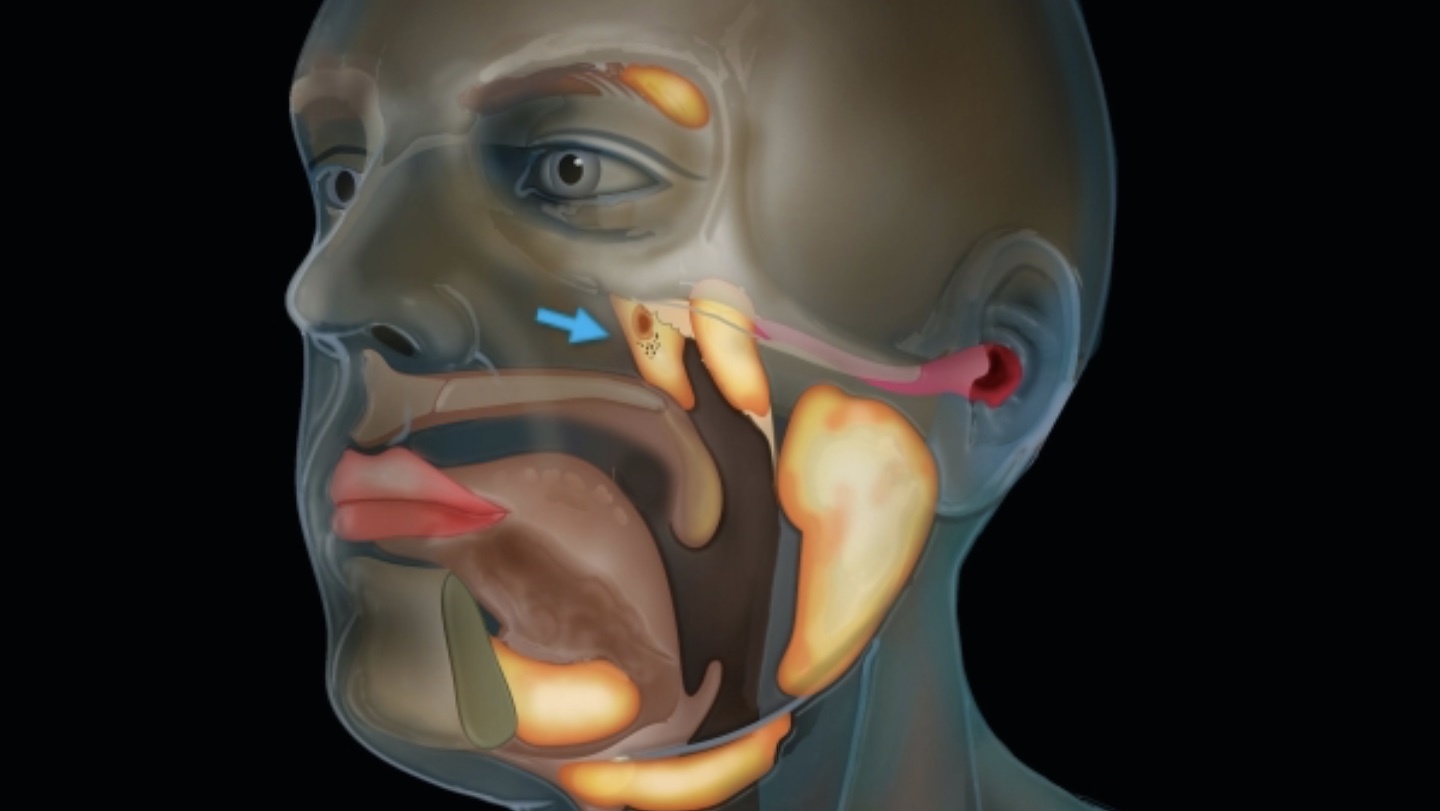
New cancer-scanning technology reveals a previously unknown detail of human anatomy.
We owe a lot to vaccines and the scientists that develop them. But we’ve only just touched the surface of what vaccines can do.
▸
17 min
—
with
The U.S., China, and Russia are in a “vaccine race” that treats a global challenge like a winner-take-all game.
New research conducted on mice suggests repeated heavy drinking causes synaptic dysfunctions that lead to anxiety.
UNC School of Medicine researchers identified the amino acid responsible for the trip.
Research from Ohio State finds that acetaminophen affects our emotions.
By projecting lifetime risk, an alarming new medical study centers the human lives that will be lost due to gun violence and drug addiction in the United States.
Is CRISPR the solution?
A study looks at the performance benefits delivered by asthma drugs when they’re taken by athletes who don’t have asthma.
Addiction is not a moral failure. It is a learning disorder, and viewing it otherwise stops communities and policy makers from the ultimate goal: harm reduction.
▸
19 min
—
with